Sub-aperture splicing measurement device and method for 45-degree plane mirror shape detection
A technology of splicing of sub-apertures and measuring devices, which is applied in the direction of measuring devices, optical devices, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting the accuracy of the surface shape, the deformation of the plane mirror, and the inconvenience of the experiment, and achieve high interference contrast, simple operation, and high splicing accuracy Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
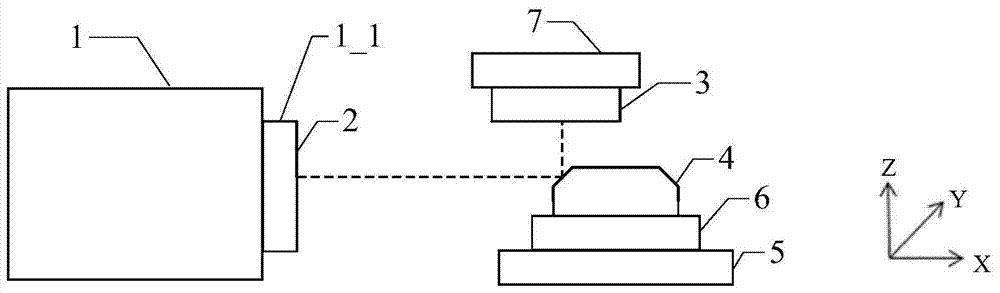
[0027] A sub-aperture splicing measurement device for 45-degree plane mirror shape detection, such as figure 1 As shown, the light emitted by the Fizeau interferometer 1 passes through the first standard mirror 2 with a nominal reflectivity of 1%, is reflected by a 45-degree flat mirror with a nominal reflectivity of 4%, and then reaches the first standard mirror with a nominal reflectivity of 99%. Two standard mirrors 3, after being reflected by the second standard mirror 3 with a nominal reflectivity of 99%, the light returns along the original path; the first standard mirror 2 is clamped on the reference mirror adjustment frame 1 of the Fizeau interferometer placed horizontally -1; the 45-degree flat mirror 4 is clamped on the two-dimensional adjustment frame 6 fixed on the splicing translation stage 5, and the light emitted by the Fizeau interferometer 1 is 45 degrees; the second standard mirror 3 is clamped on the tilted two-dimensional adjustment 7, and placed above the ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A sub-aperture splicing measurement device for 45-degree plane mirror shape detection, such as figure 1 As shown, the light emitted by the Fizeau interferometer 1 passes through the first standard mirror 2 with a nominal reflectivity of 4%, is reflected by a 45-degree flat mirror with a nominal reflectivity of 98%, and is reflected by a 45-degree flat mirror with a nominal reflectivity of 4%. After being reflected by the second standard mirror 3, the light returns along the original path. The first standard mirror 2 is clamped on the reference mirror adjustment frame 1-1 of the Fizeau interferometer placed horizontally; the 45-degree plane mirror 4 is clamped on the two-dimensional adjustment frame 6 fixed on the splicing displacement platform 5 to be connected with the Fizeau interferometer. The light emitted by the cable interferometer 1 is at 45 degrees; the second standard mirror 3 is clamped on the inclined two-dimensional adjustment frame 7, and placed above the 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com