Soil strength test board for wheel
A test bench and wheel technology, applied in wheel testing, force/torque/work measuring instruments, measuring devices, etc., can solve problems such as changing the load force in the vertical direction, and achieve the effect of easy handling and increased diversity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
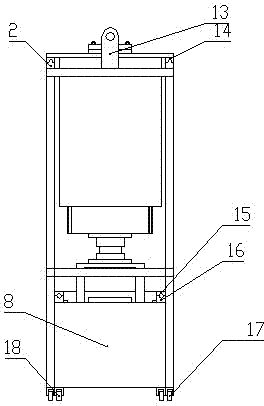
[0022] 1. see Figure 1 to Figure 7 , the wheel soil force test bench, including a test bench support A, a wheel 22 and a soil tank body 8 interacting with the wheel 22, is characterized in that: the soil tank body 8 is placed in the lower part of the test bench support A, The wheels 22 are rolled on the upper surface of the soil tank body 8; the wheels 22 are connected under a variable load mechanism C through a steering mechanism B, and the variable load mechanism C is connected to a vertical and horizontal movement mechanism D The wheel driven drive mechanism E is movably hoisted on the two upper beams 3 of the test bench support A; the rotating shaft of the wheel 22 is directly connected to a wheel active drive mechanism F.
Embodiment 2
[0024] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the special features are as follows:
[0025] The structure of the test bench support A: two left columns 11 and two right columns 7 are parallel to each other in the vertical direction, and are respectively fixedly installed on four test bench universal wheels 17, and the two upper beams 3 and the two lower beams The crossbeams 9 are parallel to each other along the horizontal direction, and the two ends are fixedly installed on the left column 11 and the right column 7 respectively, and the two middle columns 12 are parallel to the left column 11 and the right column 7, and the two ends are respectively installed on the upper beam 3 and the lower beam 9 Above, the two upper beams 3 are respectively equipped with a linear guide rail seat 2, and a linear guide rail 14 is installed on the linear guide rail seat 2.
[0026] The structure of the wheel active drive mechanism F and the steering mechanism B: the wheel...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Such as Figure 1 to Figure 7 As shown, the wheel soil force test bench includes an infrared sensor receiving end 1, a linear guide rail seat 2, an upper beam 3, a screw motor 4, a slide rail 5, a counterweight 6, a right column 7, a soil tank body 8, a lower Beam 9, soil tank beam 10, left column 11, center column 12, screw seat 13, linear guide rail 14, soil tank linear guide rail 15, soil tank linear guide rail seat 16, test bench universal wheel 17, soil tank body universal Wheel 18, soil scraping mechanism 19, infrared sensor transmitter 20, linear displacement sensor 21, wheel 22, vibration sensor 23, reducer 24, six-dimensional force sensor 25, steering motor 26, wheel bracket 27, torque sensor 28, hub motor 29. Angular velocity sensor 30, crank 31, connecting rod 32, magnet slider 33, magnet 34, pressure sensor 35, counterweight box 36, adjustment block 37, chute 38, reducer 39, crank motor 40, screw nut 41, Bolt 42, nut 43, horizontal moving bracket 44, vertic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com