Methods for treating waste waters using sulfidized red mud sorbents
A red mud and wastewater technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, solid adsorbent liquid separation, etc., can solve problems such as unsuccessful red mud
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
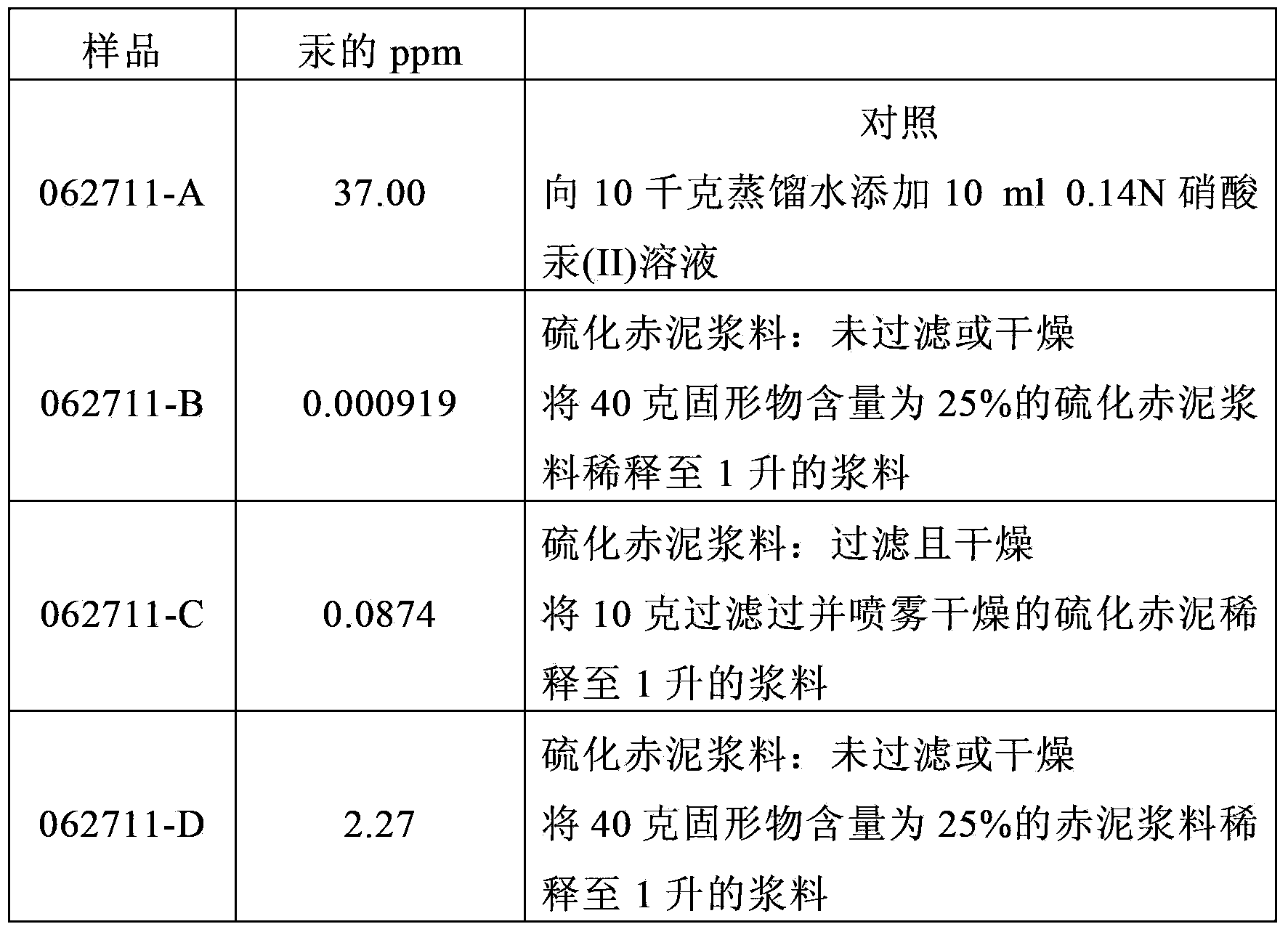
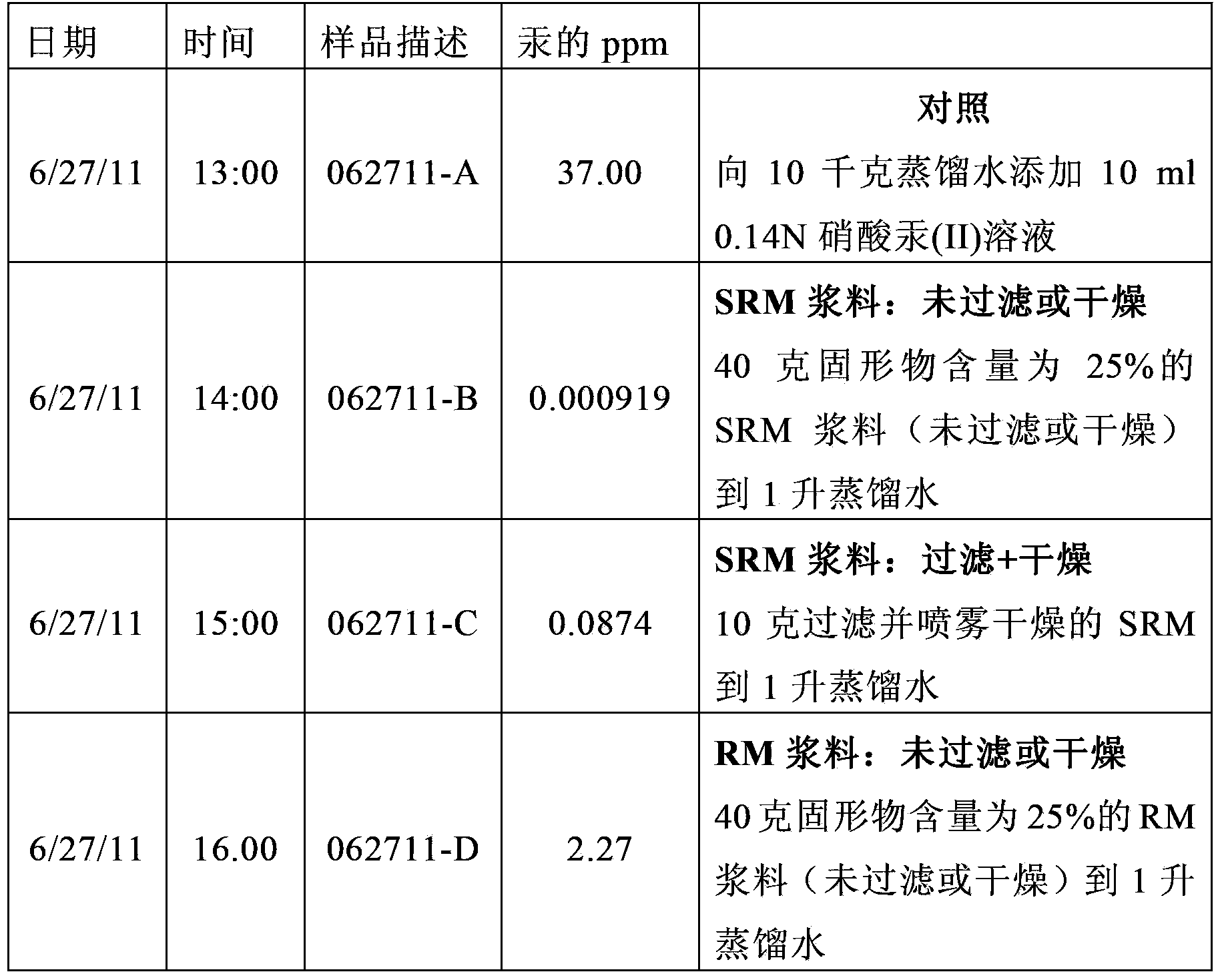
[0035] This example illustrates the preparation of red mud. A 1 kg sample of red mud received from the Sherwin Alumina Company of Corpus Christi, Texas was slurried at 15% solids in demineralized water and filtered on a Buchner funnel. The resulting filter cake was reslurried with demineralized water, refiltered, and used as starting material in Example 2. The red mud thus prepared was used in certain subsequent examples as described in detail herein.
Embodiment 2
[0037] This example illustrates the use of hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) Preparation of sulfide red mud. Washed red mud from Example 1 (100 g) was slurried in demineralized water at 15% solids and the stirred slurry was saturated with hydrogen sulfide for 30 minutes at room temperature. The samples were dried overnight at 100°C and the resulting cake was comminuted.
Embodiment 3
[0039] This example shows the use of H under pressure in a Parr cartridge 2 S to prepare sulfide red mud. The vulcanization procedure of Example 2 was repeated using a laboratory Parr shot. After the slurry was saturated with hydrogen sulfide gas, the bomb was sealed and heated at 100° C. for 4 hours while stirring. The bombs were then cooled, depressurized, and the contents filtered, dried and comminuted.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com