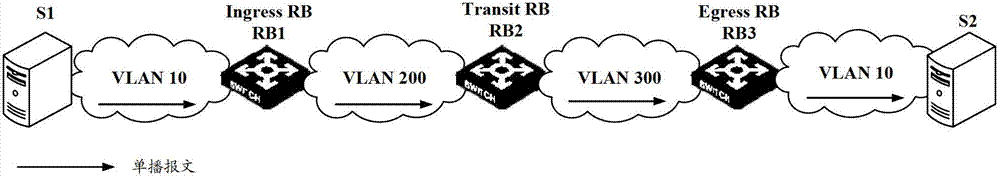
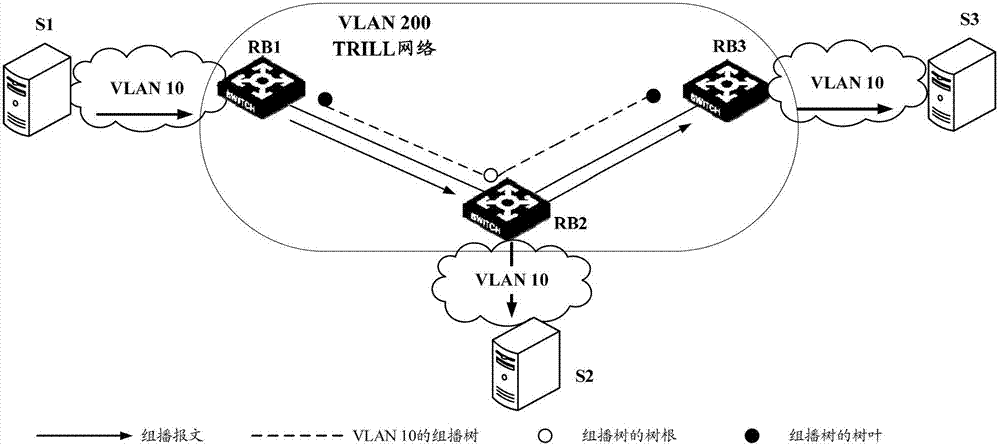
Processing method of multicast forwarding entry in trill network and routing bridge
A technology of multicast forwarding table and processing method, which is applied to the processing method of multicast forwarding table items and the field of routing bridges, and can solve the problems of wasting table item resources and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
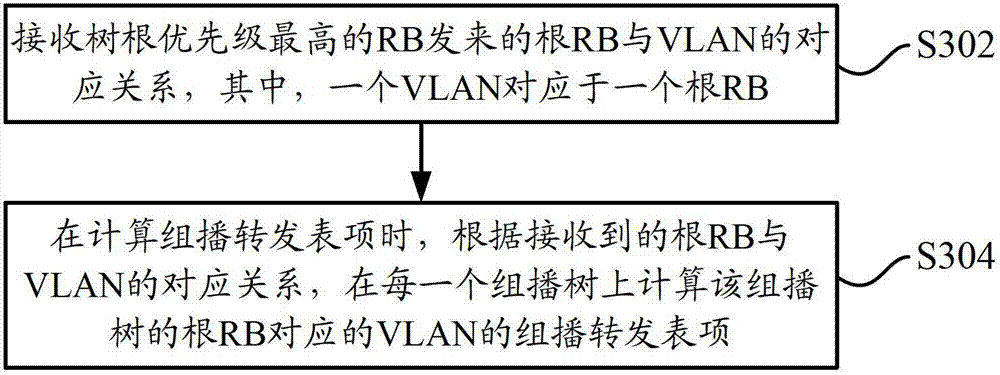
[0030] The method for processing the multicast forwarding entry in the TRILL network of this embodiment may be performed by an RB in the TRILL network, as image 3 As shown, the method includes the following steps:
[0031] Step S302, receiving the correspondence between the root RB and the VLAN sent by the RB with the highest priority of the tree root, wherein one VLAN corresponds to one root RB;
[0032]Each RB in the TRILL network uses NickName as the tree root priority, sorts the tree root priorities of all RBs, and the RB with the highest tree root priority broadcasts the NickName of the root RB of the multicast tree that all RBs need to calculate . In this embodiment, the RB with the highest tree root priority will also allocate a corresponding VLAN to the root RB of the multicast tree, wherein a VLAN corresponds to a root RB, and the correspondence between the root RB and the VLAN (that is, the root RB The corresponding relationship with the VLAN assigned to the root ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] In the method of this embodiment, when an RB is used as the RB with the highest root priority, the operations that the RB needs to perform also include the following steps:
[0048] Step S402, assigning a corresponding VLAN to the root RB of the multicast tree, wherein a VLAN corresponds to a root RB;
[0049] Step S404, broadcast the correspondence between the root RB and the VLAN, that is, the correspondence between the root RB and the VLAN assigned to the root RB.
[0050] In the prior art, the RB with the highest tree root priority broadcasts the NickName of the root RB of the multicast tree that all RBs need to calculate. In this embodiment, the RB with the highest tree root priority will not only broadcast the NickName of the root RB of the multicast tree that all RBs need to calculate, but also broadcast the correspondence between the root RB and the VLAN assigned to the root RB Broadcast out. In the specific implementation process, the RB with the highest tree...
Embodiment 3
[0060] For the methods in the first and second embodiments above, this embodiment provides an RB in a TRILL network, such as Image 6 As shown, the RB includes the following modules: a receiving module 10 and a computing module 20, wherein:
[0061] The receiving module 10 is configured to receive the correspondence between the root RB and the VLAN sent by the RB with the highest tree root priority, wherein one VLAN corresponds to one root RB;
[0062] Calculation module 20, for calculating the multicast forwarding entry, according to the corresponding relationship between the root RB and VLAN received by the receiving module 10, on each multicast tree, calculate the group of the VLAN corresponding to the root RB of the multicast tree broadcast forwarding entry.
[0063] In addition, when the RB is used as an Ingress RB, the RB may also include: an establishment module for establishing the root RB, VLAN, and multicast MAC of the multicast tree according to the corresponding rel...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com