Method for treating m-dinitrobenzene wastewater through catalytic reduction
A technology for m-dinitrobenzene and waste water, which is applied in the fields of reduced water/sewage treatment, chemical instruments and methods, water/sludge/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of simple preparation, strong operability, and simple and easy method.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1: sodium sulfide reduction m-dinitrobenzene
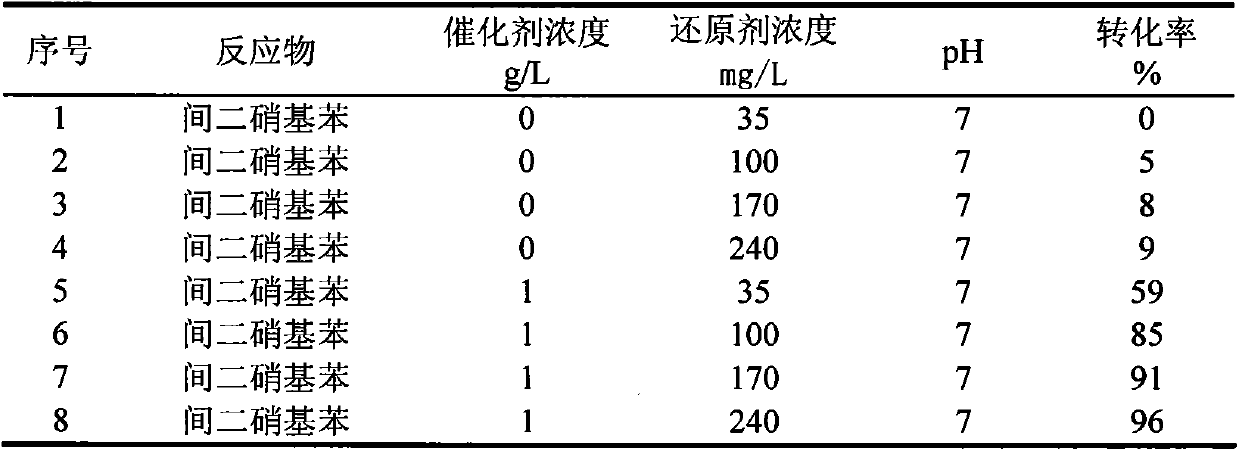
[0025] In 8 1L anaerobic simulated reactors, adding pH is 7 phosphate buffer solution and concentration is the m-dinitrobenzene waste water of 80mg / L, is filled with high-purity nitrogen in reactor (to remove reaction system Oxygen, form anaerobic environment), in reactor, add respectively 35mg / L, 100mg / L, 170mg / L, 240mg / L reducing agent sodium sulfide solution, then, do not add catalyst in No. 1-4 reactor, in 5 -Add 1g of black carbon (activated carbon used in this embodiment) as reaction catalyst in No. 8 reactor. The reactor is sealed and placed in a rotary oscillator, and the reaction is shaken at a speed of 150-200 rpm at normal temperature and pressure for 96 hours, and the reduced products after the reaction are anilines. The conversion rate of m-dinitrobenzene is shown in Table 1.
[0026] The conversion rate of m-dinitrobenzene under the reducing condition of sodium sulfide in table 1
[0027]
Embodiment 2
[0028] Embodiment 2: Reductive conversion of m-dinitrobenzene under different pH conditions
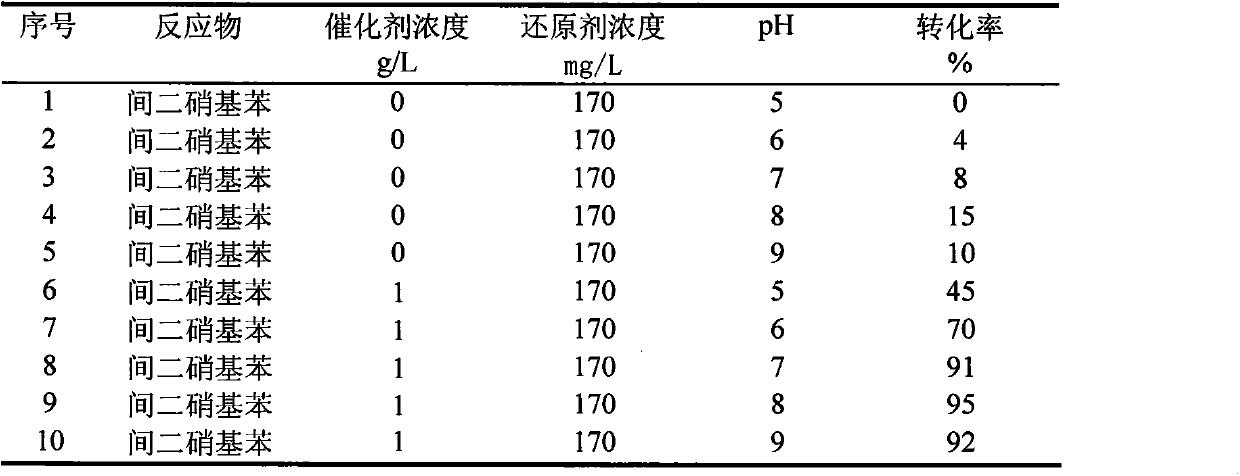
[0029] The difference from Example 1 is that 170mg / L reducing agent sodium sulfide was added to 10 reactors respectively. Then, no catalyzer was added in No. 1-5 reactors, and 1 g of black carbon (using activated carbon in this embodiment) was respectively added as a reaction catalyst in No. 6-10 reactors. . Different buffer solutions were added to different reactors, so that the pH of the reaction system was 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9 respectively. The conversion rate of m-dinitrobenzene after 96 hours of reaction is shown in Table 2.
[0030] The conversion rate of m-dinitrobenzene under different pH conditions in table 2
[0031]
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment 3: Reductive conversion of m-dinitrobenzene under different catalyst concentration conditions
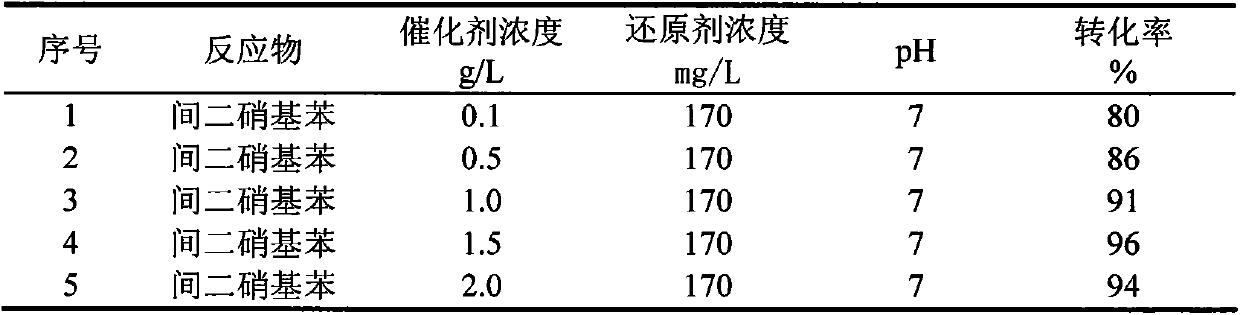
[0033] Different from Example 1, add 170mg / L reducing agent sodium sulfide respectively in 5 reactors, then, add a certain amount of black carbon (using gac in this embodiment) respectively in the reactors as reaction catalyst , so that the concentration is 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 1.0g / L. The reactor was sealed and placed in a rotary shaker, and the reaction was shaken at a speed of 150-200 rpm at normal temperature and pressure for 96 hours. The conversion rate of m-dinitrobenzene is shown in Table 3.
[0034] Table 3 Reductive conversion of m-dinitrobenzene under different catalyst concentrations
[0035]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com