Large-scale complicated target model oriented electromagnetic wave shadow processing method
A complex target and target model technology, applied in the field of electromagnetic wave shadow processing for large-scale complex target models, can solve problems such as difficult to obtain electromagnetic propagation paths, total error expansion, and regions that are not suitable for arbitrary distribution of target models, and achieve the goal of overcoming Boundary rounding error, the effect of overcoming human error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The specific implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments. The following examples are only used to illustrate the present invention, but not to limit the scope of the present invention.
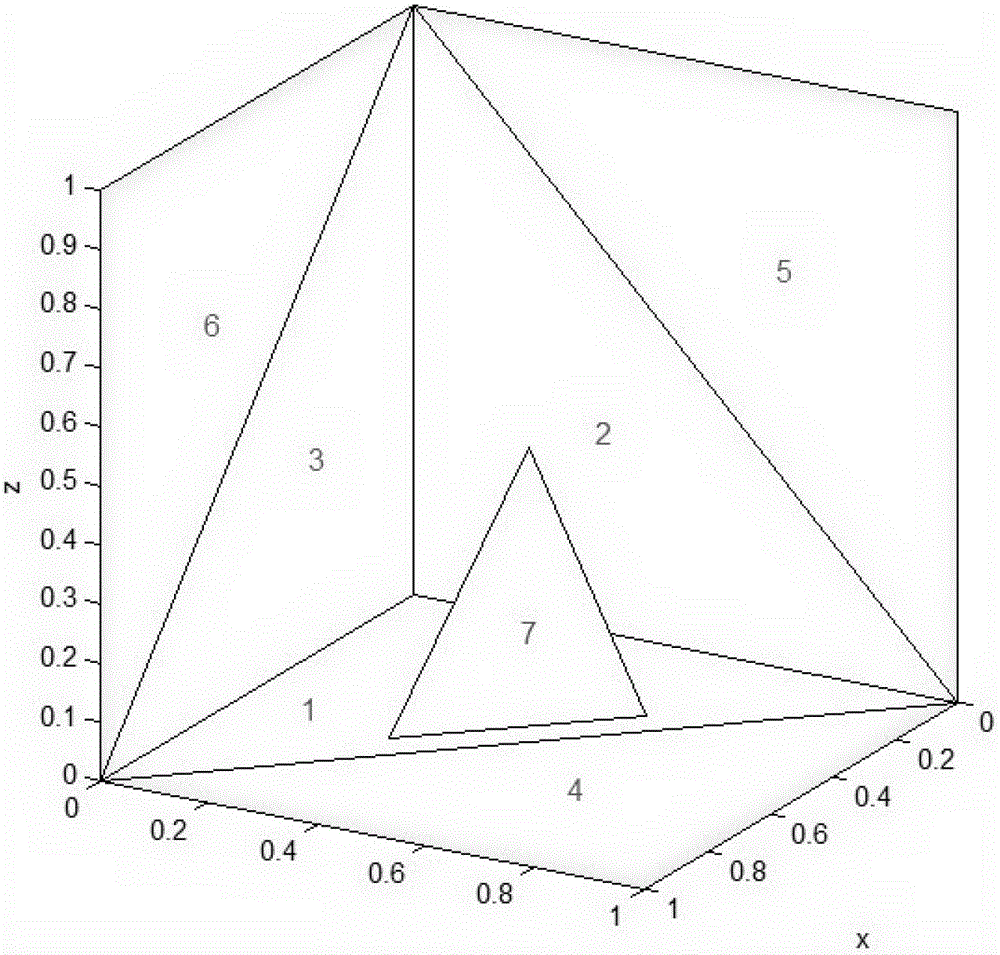
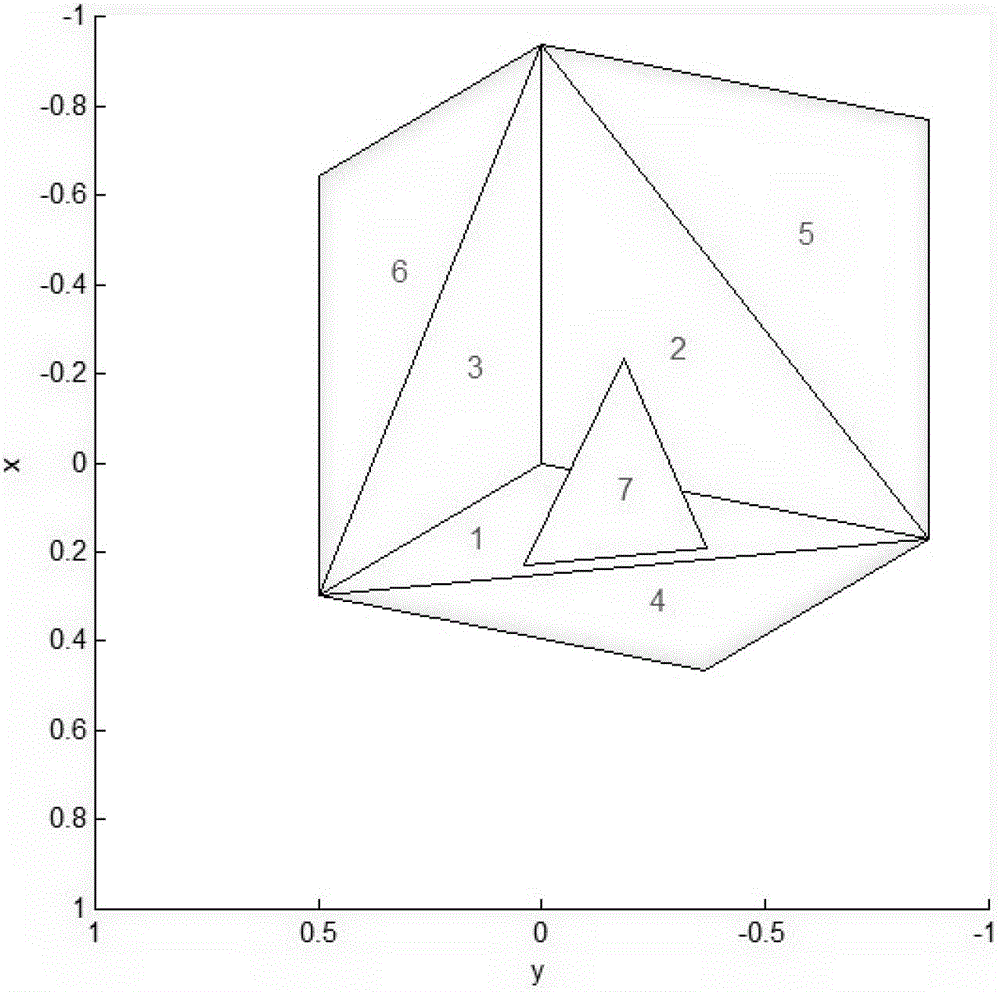
[0032] Below as figure 2 The target model shown in the figure is taken as an example for description. The target model shown in the figure is composed of 7 triangular base surfaces; assuming that the incident direction of electromagnetic waves is θ=70°, Due to the irradiation of electromagnetic waves, electromagnetic wave shadows may be generated on partial areas of other base surfaces behind the base surface 7.
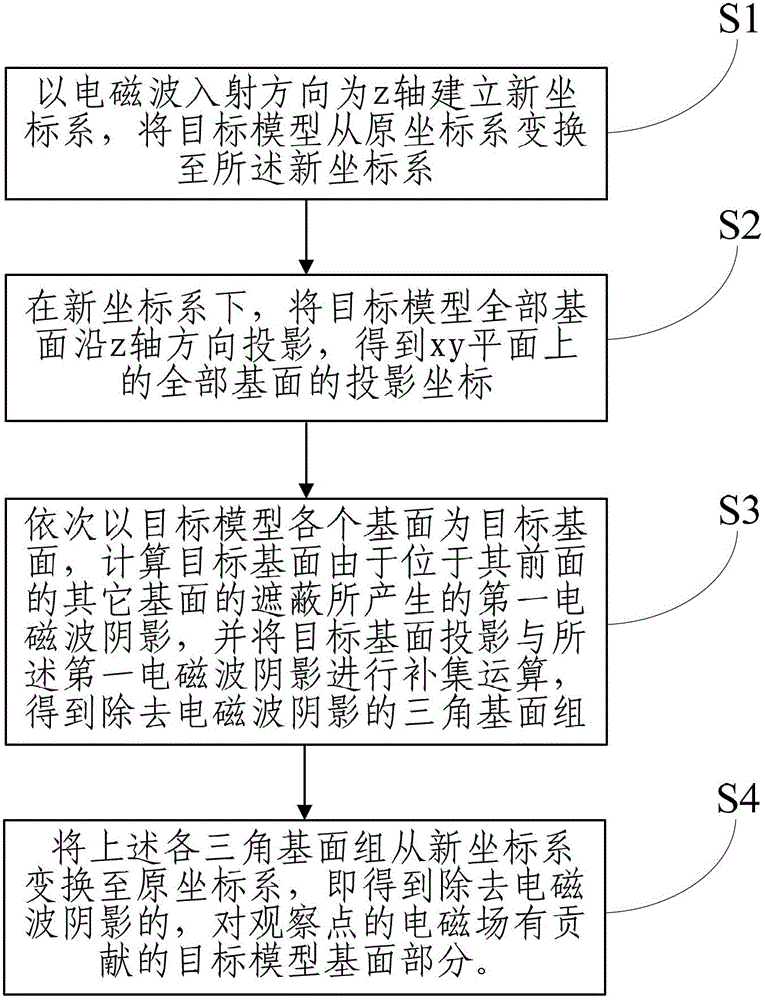
[0033] Flow chart as figure 1 An electromagnetic wave shadow processing method for large-scale complex target models shown in, mainly includes the following steps:
[0034] S1. In the incident direction of electromagnetic waves (θ=70°, ) Establish a new coordinate system for the z-axis, and transform the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com