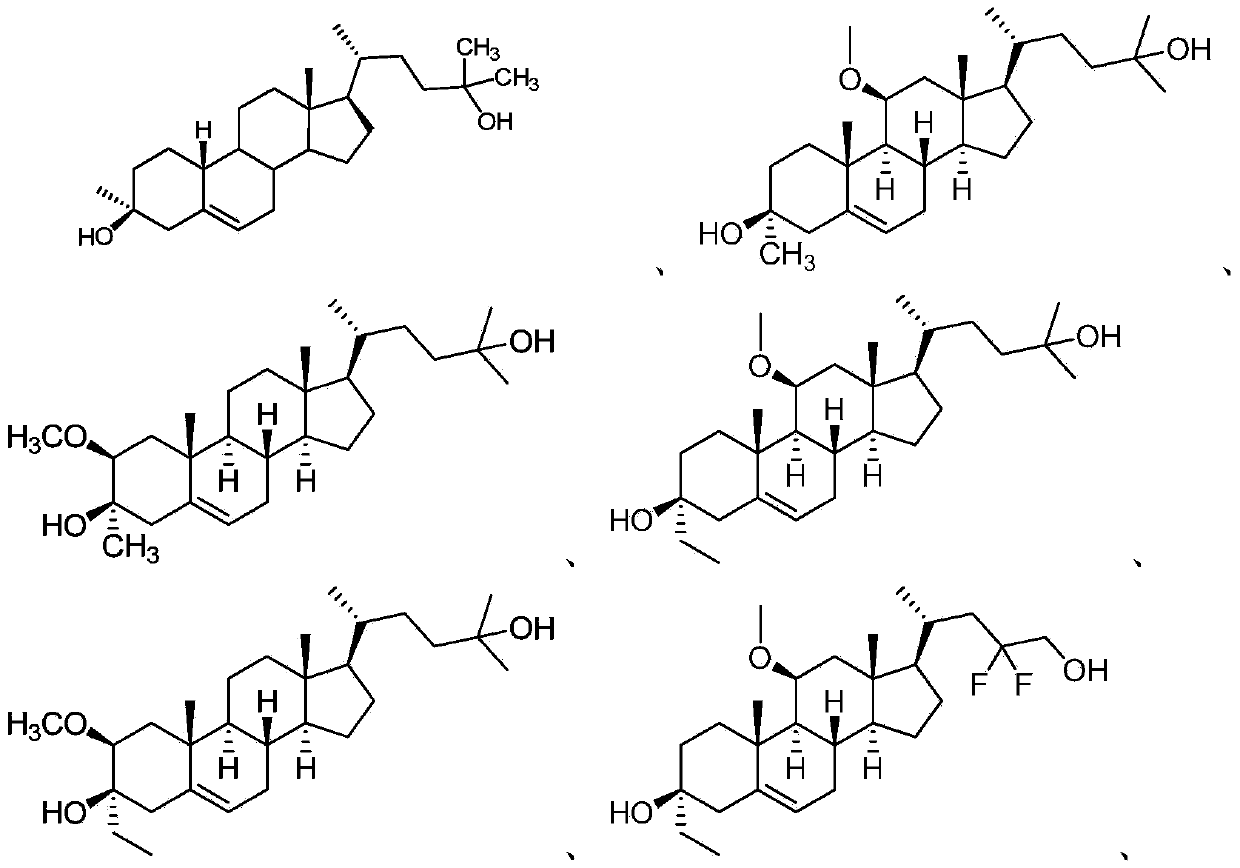
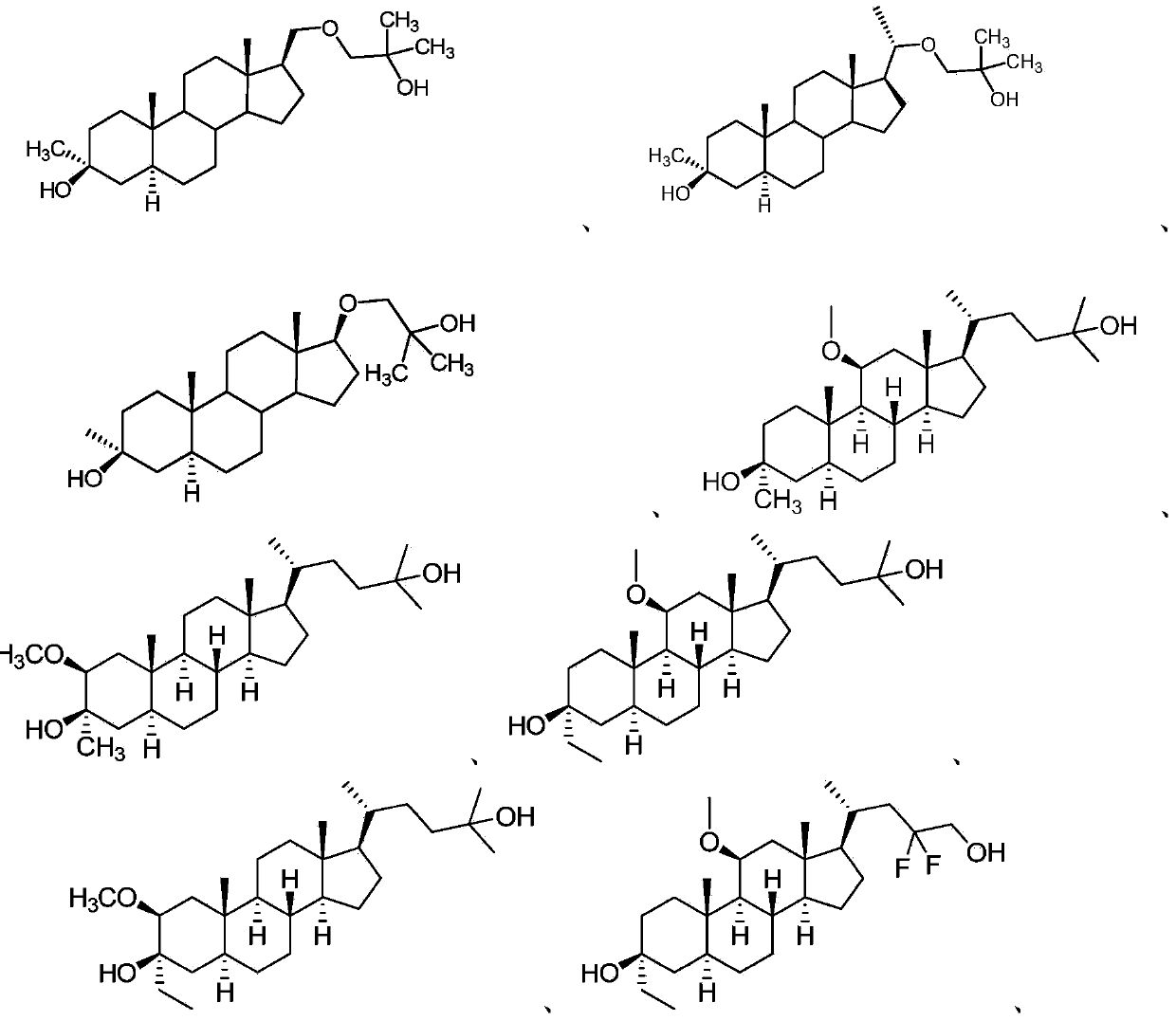
Neuroactive steroids, compositions, and uses thereof
A compound, unsubstituted technology, used in the preparation of steroids, drug combinations, steroids, etc., and can solve problems such as changes in the degree of regulation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0532] Embodiment 1. Preparation of Compound ST-200-A-001
[0533]
[0534]
[0535] Preparation of compound 2: To a solution of ketone 1 (50.0 g, 0.17 mol, 1.0 eq) and ethylene glycol (62 mL) in toluene (600 mL) was added p-toluenesulfonic acid (1.4 g, 7.28 mmol). The reaction mixture was heated at reflux overnight using a Dean-Stark trap. LCMS showed complete consumption of starting material. The mixture was cooled to room temperature, diluted with ethyl acetate (500 mL), and washed with saturated aqueous sodium bicarbonate (300 mL×2) and brine (300 mL×2). The organic phase was dried over sodium sulfate and concentrated in vacuo to obtain crude product 2 (64.0 g, 100%), which was directly used in the next step without further purification. 1 H NMR: (400MHz, CDCl3 )δ5.35(d, J=5.6Hz, 1H), 3.97-3.82(m, 4H), 3.59-3.47(m, 1H), 2.34-2.21(m, 2H), 2.06-1.94(m, 2H) , 1.90-1.74(m, 3H), 1.73-1.64(m, 1H), 1.63-1.33(m, 10H), 1.32-1.19(m, 1H), 1.14-1.03(m, 1H), 1.01(s, 3H), 0.99...
Embodiment 2
[0545] Embodiment 2. Preparation of Compound ST-200-A-003
[0546]
[0547] Preparation of compound A_003_1: at 0°C in N 2 Down to Ph 3 A solution of PEtBr (12.25 g, 33.00 mmol, 10.0 eq) in dry THF (15 mL) was added dropwise to a solution of t-BuOK (3.70 g, 33.00 mmol, 10.0 eq) in dry THF (10 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 1.5 hours. A solution of INTA (1.00 g, 3.31 mmol, 1.0 eq) in THF (10 mL) was then added dropwise and the resulting mixture was stirred at 70°C for 4 hours. TLC (PE:EA=3:1) indicated complete consumption of starting material. The reaction was saturated with NH 4 Aqueous Cl solution (50 mL) was quenched and extracted with EA (30 mL x 2). Pass the combined organic phases through Na 2 SO 4 Dry and concentrate in vacuo. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel (eluent: PE:EA=12:1) to give the product (900 mg, 90.9%) as a white powder. 1 H NMR: (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ5.32(d, J=5.2Hz, 1H), 5.15-5.12(m, 1H), 2.44-2....
Embodiment 3
[0551] Example 3. Preparation of Compound ST-200-A-007
[0552]
[0553] Preparation of Compound INT E: To a solution of 9-BBN (0.5M in THF, 133mL, 66.6mmol, 10.0eq) was added dropwise A_001_1 (2.0g, 6.66mmol, 1.0eq) in THF (10mL) under ice bath The solution. The reaction mixture was heated to 60 °C and stirred for 20 hours. The mixture was cooled to 0 °C and 10% aqueous NaOH (20 mL) was added followed by 30% H 2 o 2 Aqueous solution (30%, 10 mL). The mixture was stirred at 0 °C for 2 hours, then extracted with EA (30 mL x 3). The combined organic layers were washed with brine (30 mL), passed through Na 2 SO 4 Drying and concentration in vacuo gave the crude product, which was purified by flash column chromatography eluting with PE / EA (10 / 1 ) to afford INT E (1.0 g, 47%) as a white solid. 1 H NMR: (400MHz, CDCl 3 )δ5.30 (d, J=5.2Hz, 1H), 3.75-3.71 (dd, J 1 =10.4Hz,J 2 =6.8Hz, 1H), 3.58-3.53 (dd, J 1 =10.4Hz,J 2 =7.6Hz, 1H), 2.43-2.41(d, J=10.4Hz, 1H), 2.02-1.96(...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com