Liquid crystal display device
A liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal layer technology, applied in nonlinear optics, instruments, optics, etc., can solve problems such as prolonging production time, increasing costs, and long exposure time, so as to solve the afterimage problem, save manufacturing costs, and shorten production time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] In order to describe the technical content, structural features, achieved goals and effects of the present invention in detail, the following will be described in detail in conjunction with the embodiments and accompanying drawings.
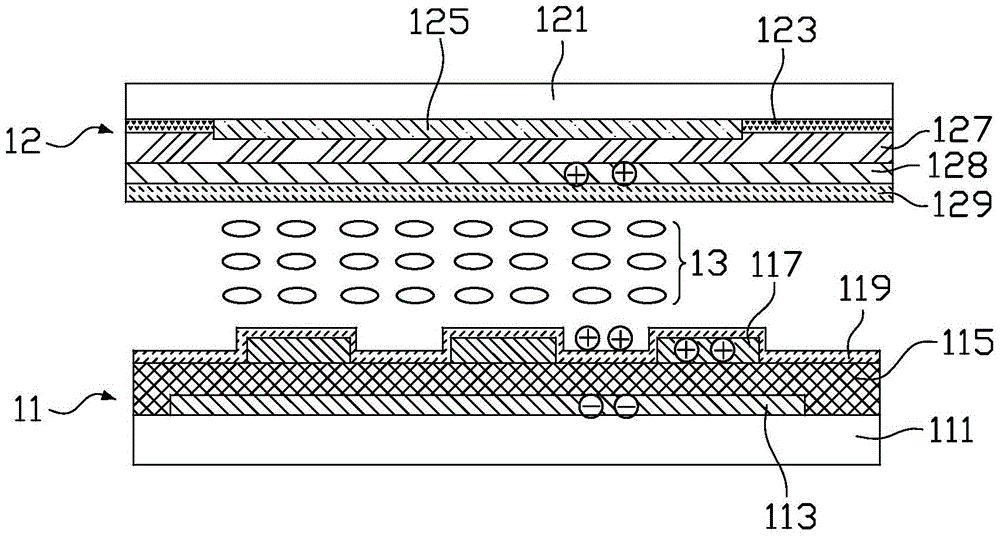
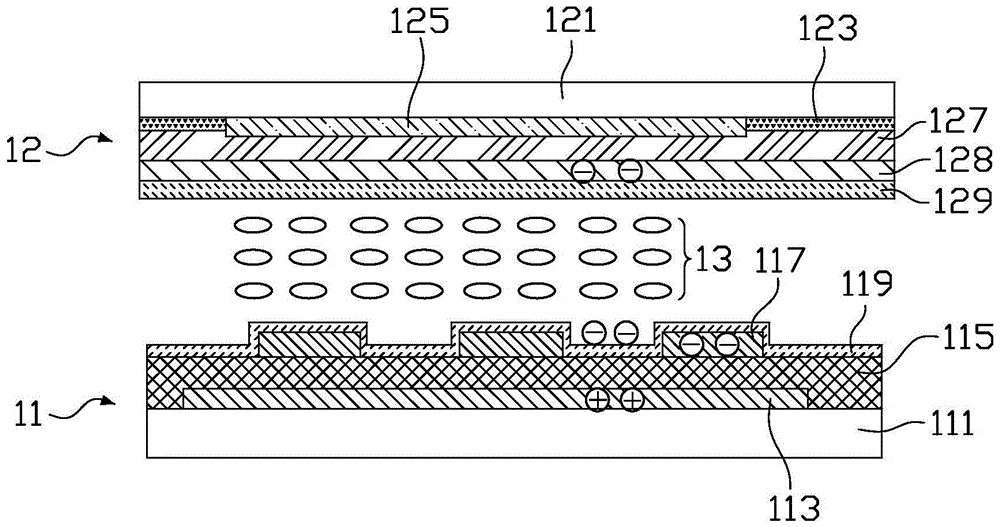
[0033] see Image 6 , Image 6 It is a schematic cross-sectional structure diagram of a liquid crystal display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention. The liquid crystal display device according to the first embodiment of the present invention includes an array substrate 31, a color filter substrate 32, and an array substrate 31 interposed between the array substrate 31 and the color filter substrate. 32 between the liquid crystal layer 33 . It should be noted that, for the sake of brevity, the figure only schematically shows the structure of one pixel area, and the drawing size and ratio of each component in the figure do not represent the actual size and ratio of the product.
[0034] The array substrate 31 i...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com