Transcription factors for the production of cellulose degrading enzymes
A transcription factor, a technology encoding transcription factors, applied in the field of cellulose degradation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0315] Example 1: Induction of cellulolytic enzymes in wild-type Neurospora crassa
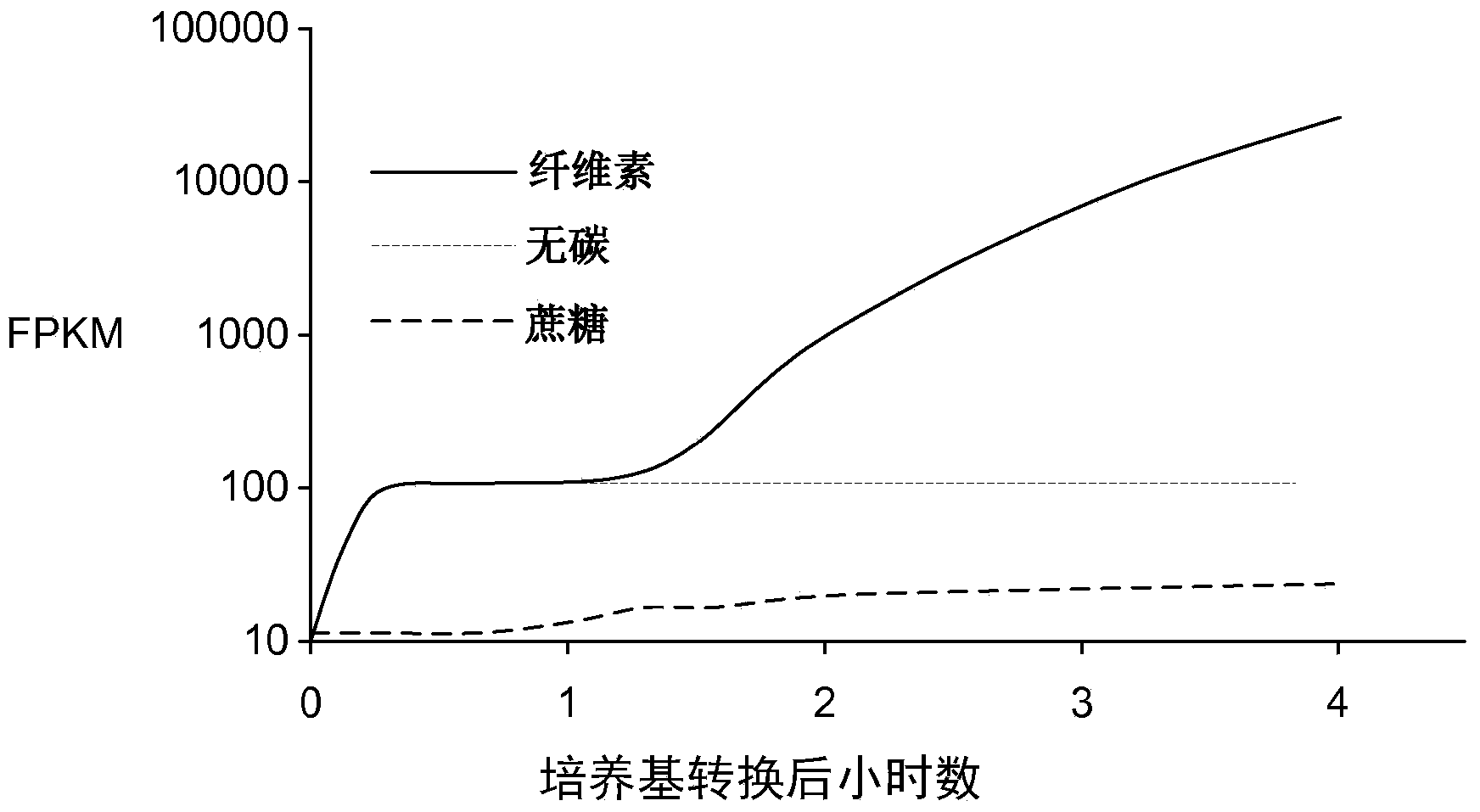
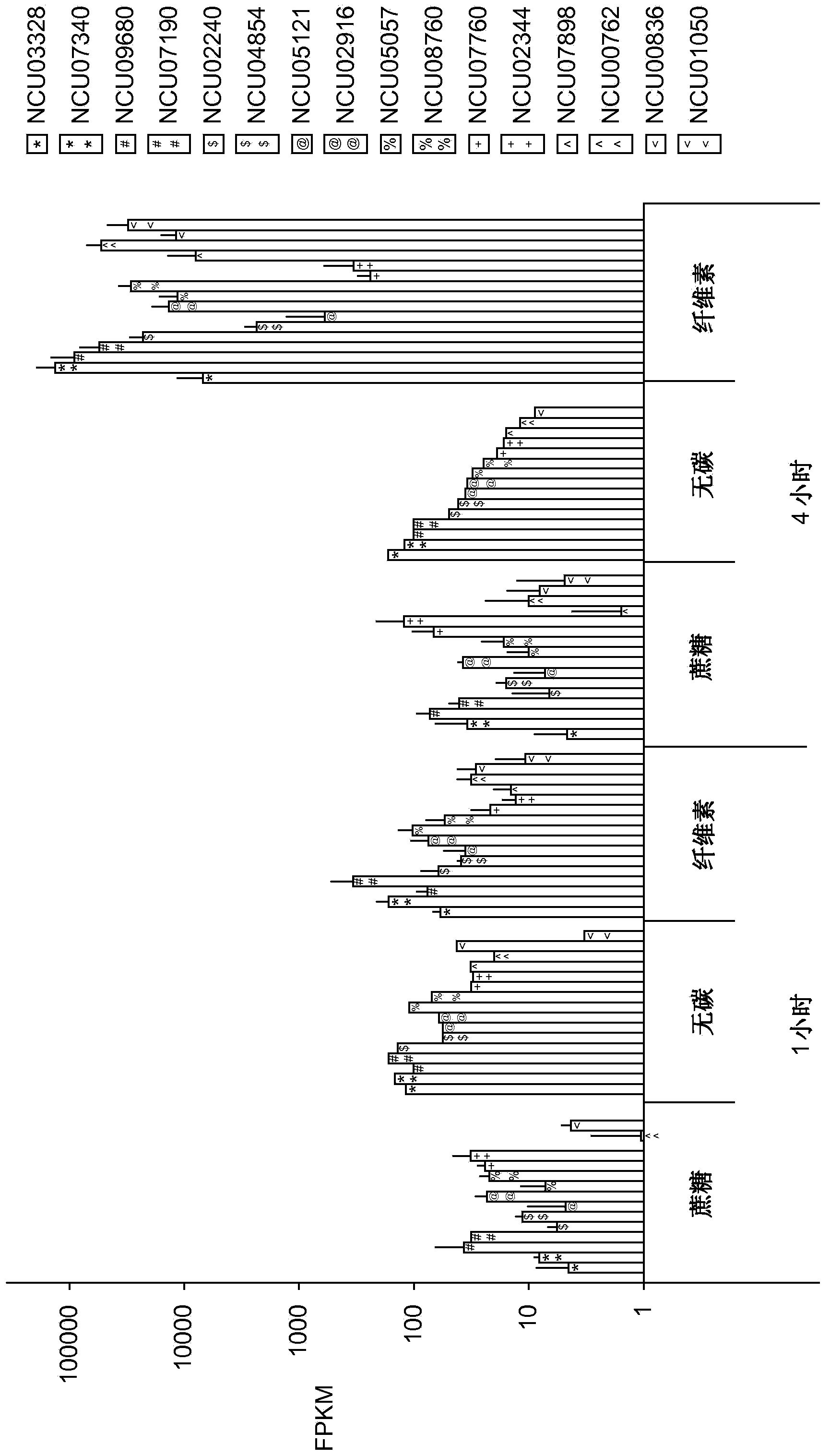
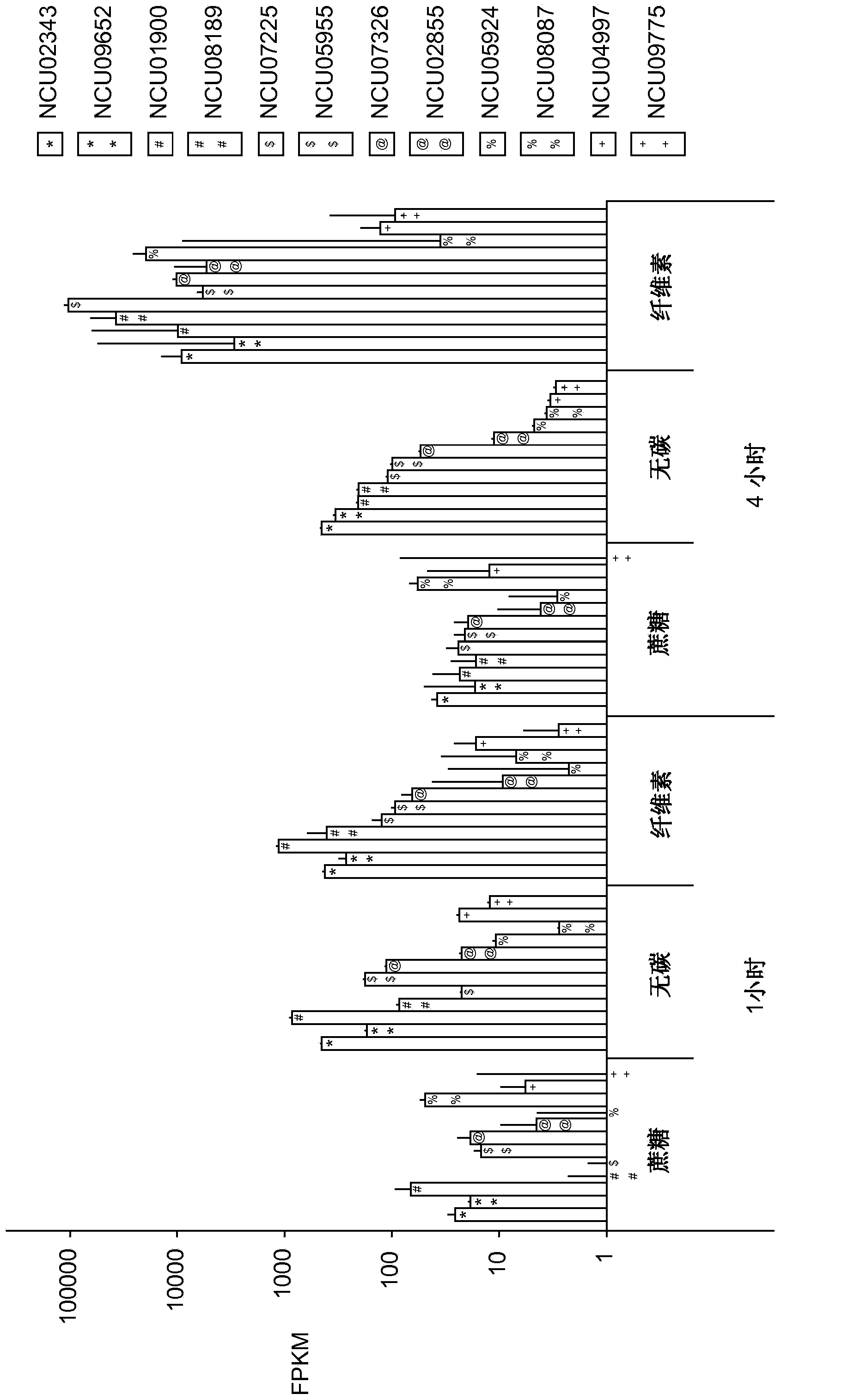
[0316] To better understand how filamentous fungi sense and respond to cellulose in their environment, next-generation RNA sequencing was used to profile genome-wide mRNA abundance in Neurospora crassa. For these experiments, cultures grown for 16 hours in sucrose minimal medium (SMM; linear growth phase) and then transferred from SMM to cellulose-only carbon source medium (CMM; cellulose minimal medium); RNA samples were taken at 30 min, 1 hr, 2 hr and 4 hr after transfer from SMM to CMM and compared to cultures transferred to SMM at the same time points. Typical expression patterns of genes known to be involved in cellulose degradation are shown in Figure 1A middle. The expression level of genes in this subset increased by about 1 order of magnitude within 30 min after transfer. Transcript abundance remained constant for about 1 hour before increasing several orders of magnitude betwee...
Embodiment 2
[0320] Example 2: Necessary Regulators for Cellulose Degradation
[0321] To identify transcription factors required for cellulose degradation, we screened ~200 N. crassa transcription factor deletion sets for mutants with deletions grown on cellulose. Two mutants with severe growth defects on cellulose but normal growth on sucrose were identified. For cellulose degradation regulators 1 and 2, the corresponding genes NCU07705 and NCU08042 were tentatively named cdr-1 and cdr-2, respectively. However, it was later discovered that the prefix "cdr" was previously used for genes related to cadmium resistance in Neurospora crassa. Therefore, for cellulose degradation regulators 1 and 2, the genes NCU07705 and NCU08042 were renamed clr-1 and clr-2, respectively. It should be noted that although some figures may refer to cdr-1 and cdr-2, the descriptions of these figures in Examples 2-4 below refer to cdr-1 as clr-1 and cdr-2 as clr -2.
[0322] Deletion mutants of clr-1 and cl...
Embodiment 3
[0327] Example 3: Phylogenetic Analysis
[0328] A phylogenetic analysis of clr-1 and clr-2 was performed to gain insight into the evolutionary history of the two genes. The maximum likelihood phylogenetic tree of clr-1 and clr-2 homologues substantially recapitulates the previous fungal tree ( Figure 6 ). Trees generated using Bayesian inference also showed consistent trees (Fig. 9). The similarity between the two trees provides support for the idea that CLR-1 and CLR-2 may have co-evolved and the hypothesis that they may function together as a hybrid.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com