Distribution method for sub carriers in cognitive OFDM network
An allocation method and sub-carrier technology, applied in network planning, network traffic/resource management, electrical components, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing length, satisfying sub-carrier allocation constraints, and reducing search space
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
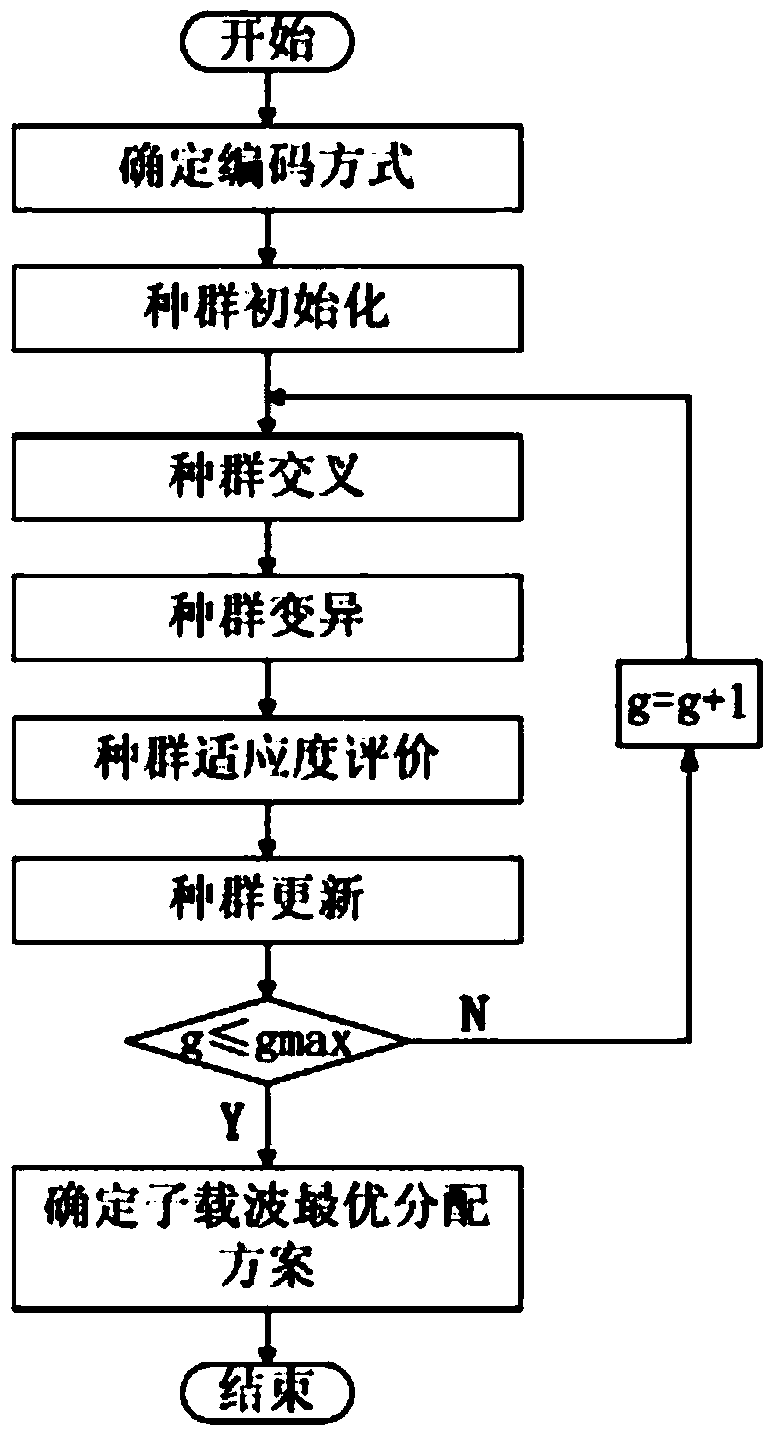
[0058] In order to improve spectrum utilization and solve the defects of existing methods for resource allocation in cognitive wireless networks, this embodiment proposes a method for allocating subcarriers in cognitive OFDM networks.
[0059] This embodiment takes the existing genetic algorithm flow as the basic framework, and redesigns the encoding method, mutation operation and population update operation according to the characteristics of subcarrier allocation in the cognitive OFDM network. The basic process includes: initial value setting, population coding, population initialization, population crossover, population variation, population fitness evaluation and population update, among which population crossover, population variation, population fitness evaluation and population update operations are iteratively performed alternately until the Obtain an optimal solution or iterate over a specified maximum number of times. The specific steps of the subcarrier allocation m...
Embodiment 2
[0094] In order to further illustrate the present invention, this embodiment elaborates the present invention on the basis of Embodiment 1.
[0095] Step 1: Construct the optimization problem model
[0096] Generally, when OFDM modulation technology is used in cognitive wireless networks, the allocation of subcarriers and power in the network can be modeled as an optimization problem with an objective function and multiple constraints. Considering that in general, subcarrier allocation needs to satisfy the assumption that the power allocated by secondary users on each subcarrier is equal, and the total transmission power of secondary users is less than the maximum power that the network equipment can provide. In addition, considering the transmission power of secondary users For the impact on the primary user, the subcarrier allocation algorithm should meet the following principles: (1) The interference to the primary user caused by the power transmitted by the secondary user ...
Embodiment 3
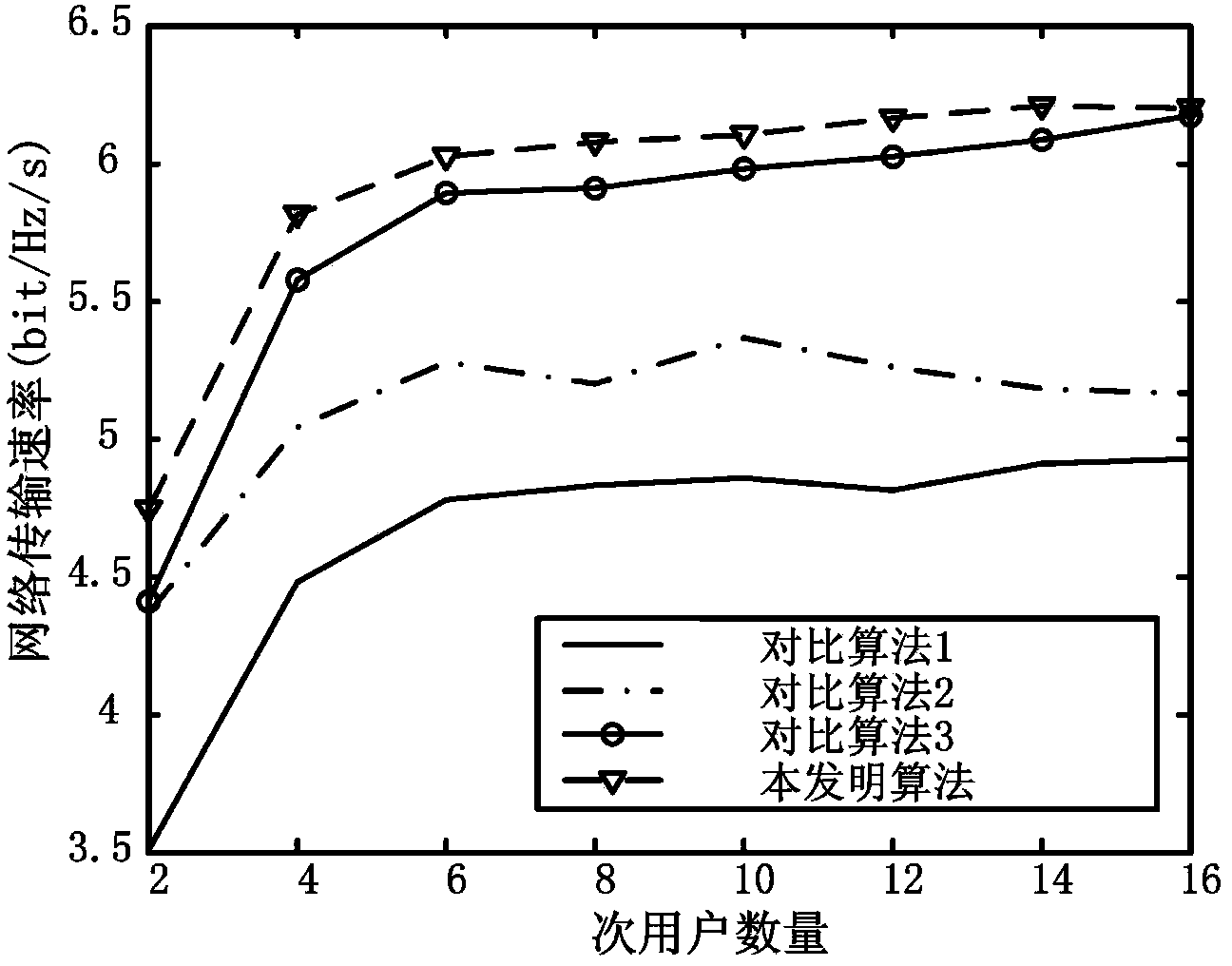
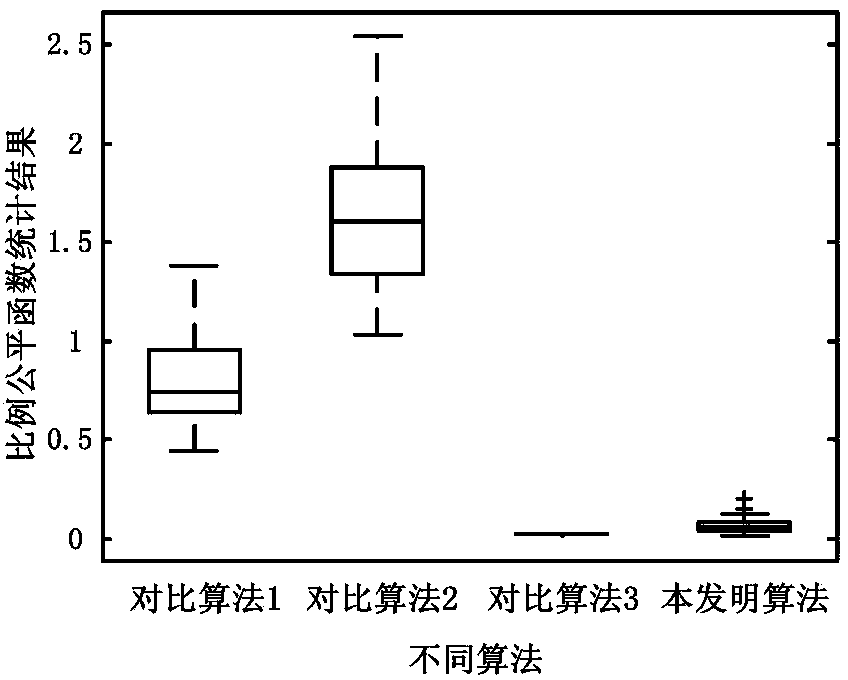
[0154] The effects of the present invention will be further described below in combination with simulation experiments.
[0155] 1. The comparison algorithm used in the experiment:
[0156] Compared with Algorithm 1, the penalty function method is used to transform the constrained problem into an unconstrained problem, and the immune clone selection algorithm is used to allocate subcarriers and power.
[0157] Compared with Algorithm 2, under the limitation of the total bandwidth and total power of the system, an effective and flexible spectrum sharing control algorithm using the least subcarriers is proposed, and then the power is allocated using the traditional water filling method.
[0158] Compared with Algorithm 3, a suboptimal but effective scheme design is proposed, which maximizes the total data transmission rate of users under the constraints of total user power and proportional fairness, and realizes adaptive and flexible data transmission rate among discrete users ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com