I/Q unbalance correction method and device used for wireless local area network device
A wireless local area network, balance correction technology, applied to the shaping network, baseband system components, multi-frequency code system and other directions in the transmitter/receiver, can solve the problems affecting the dynamic range and receiving performance of the quadrature receiver.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
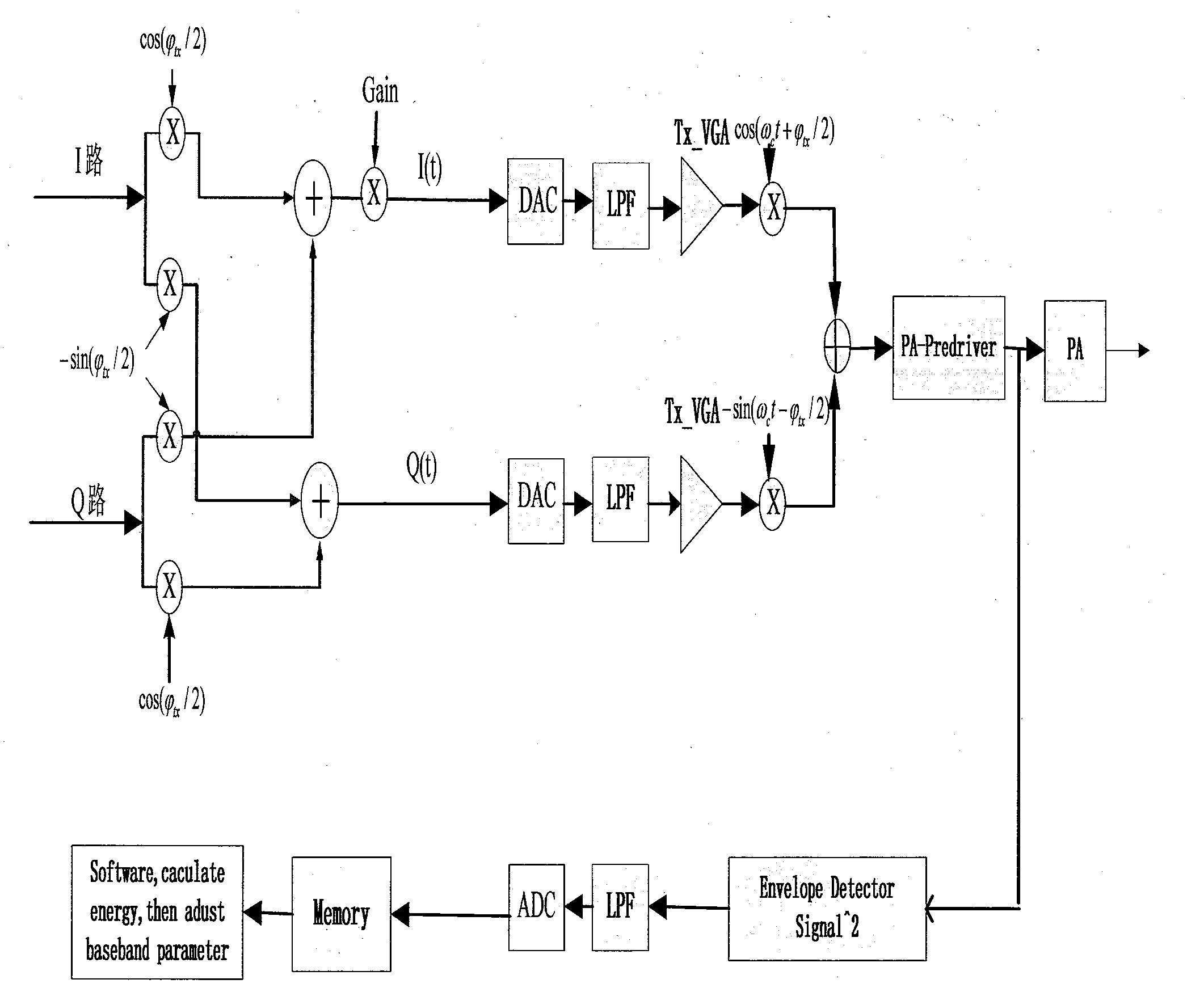
[0019] Transmitter IQ imbalance model:
[0020] The transmitted baseband complex signal can be expressed as:
[0021] v bb (t)=I(t)+jQ(t)
[0022] Assuming that there is no DC bias, the output signal after the mixer can be expressed as:
[0023]
[0024]
[0025]
[0026] Gain is the transmitter IQ amplitude imbalance coefficient;
[0027] is the transmitter IQ phase imbalance coefficient;
[0028] Therefore, the corresponding IQ-mismatched baseband signal is:
[0029]
[0030]
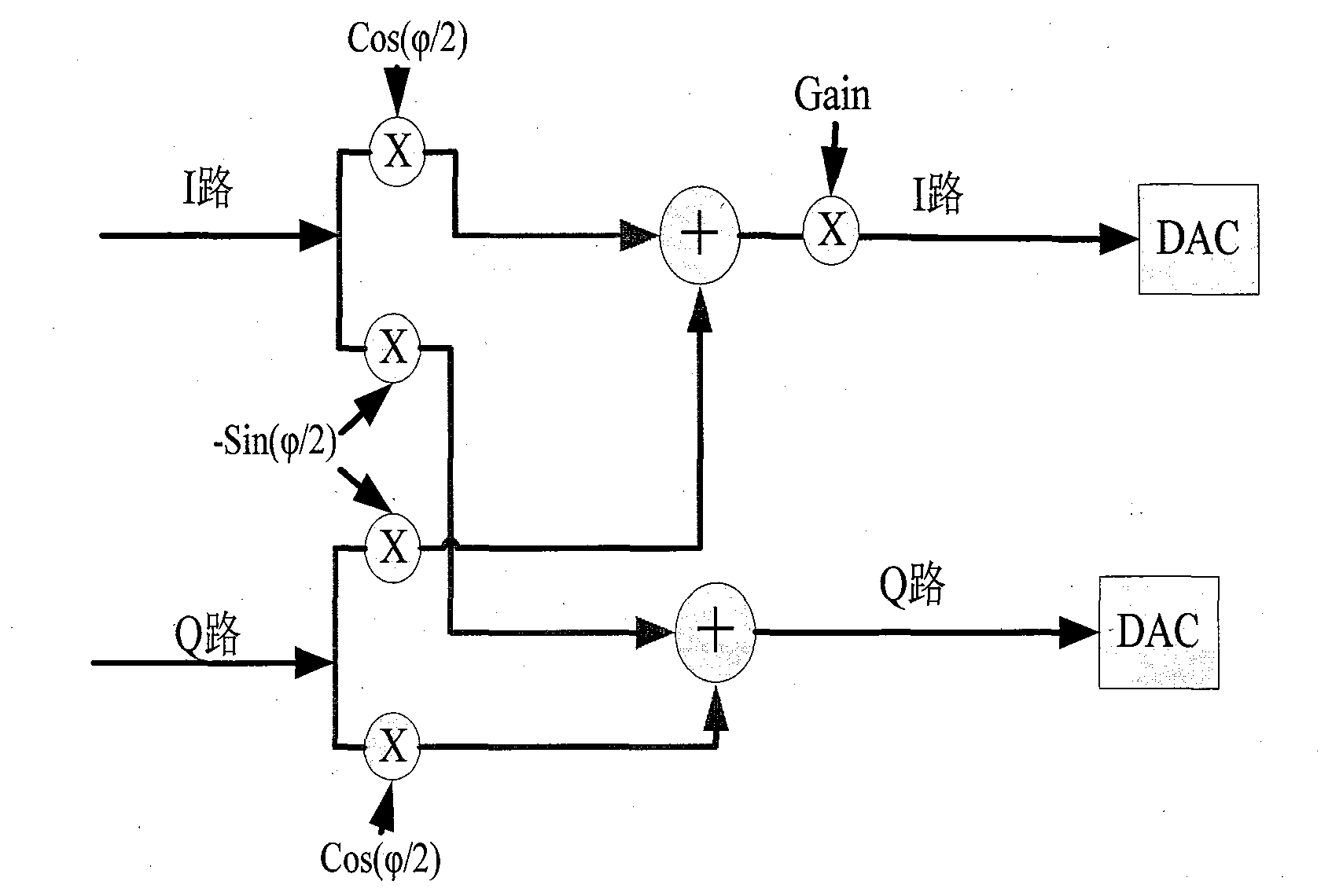
[0031] The baseband signal for transmitter IQ mismatch can be corrected by the following transmitter correction model:
[0032]
[0033]
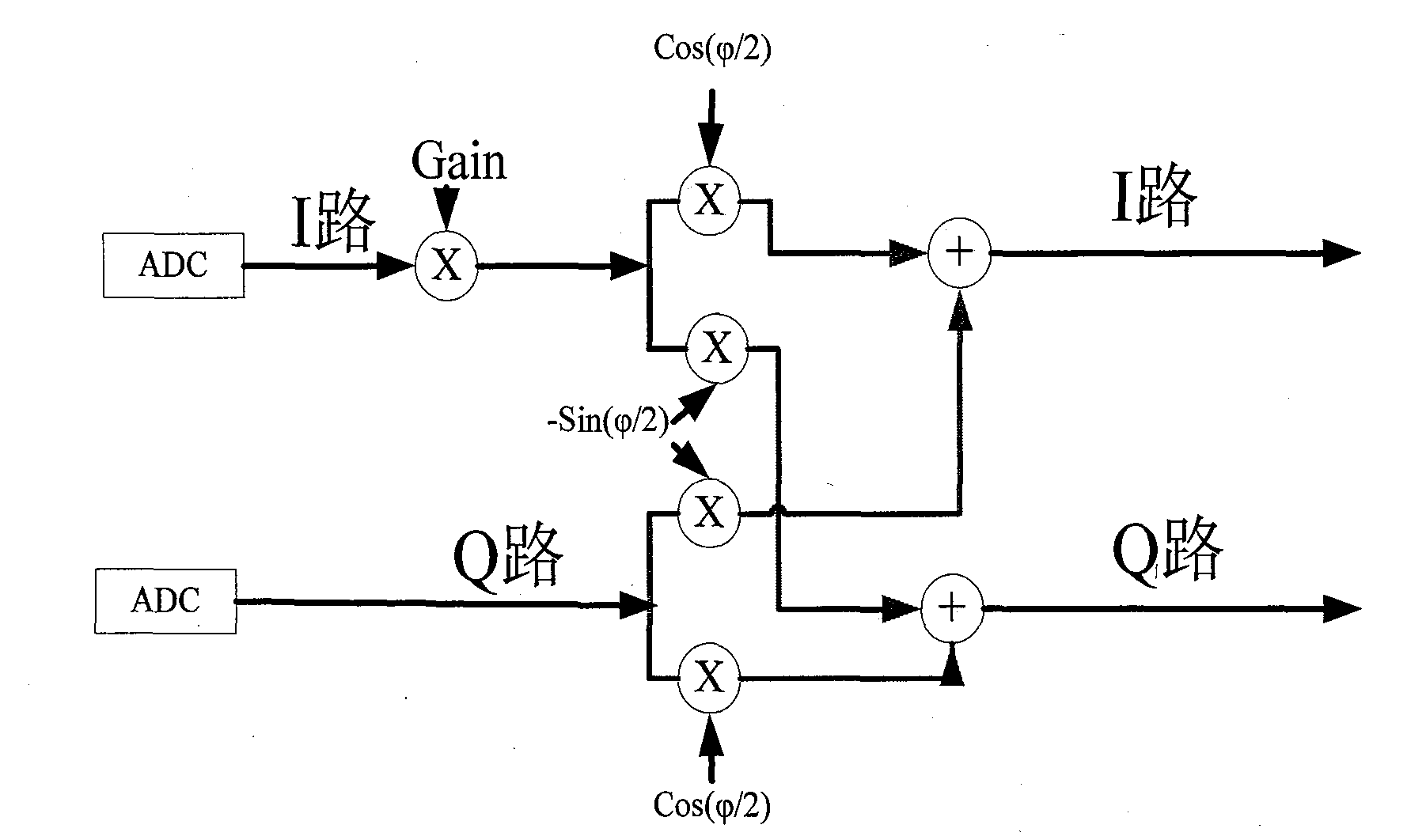
[0034] Receiver IQ imbalance model:
[0035] The signal received by the radio frequency can be expressed as:
[0036] v rf (t)=I(t)cos(ω RF t)-Q(t)sin(ω RF t)
[0037] Assuming that there is no DC bias, after down-conversion and low-pass filter, the baseband signal with IQ mismatch can be expressed as:
[0038]
[0039]
[0...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com