Detection method for trace free acid in electrolyte lithium salt
A detection method, free acid technology, which is applied in the direction of material analysis by observing the influence of chemical indicators, and analysis by making materials undergo chemical reactions. Long time and other problems, to achieve the effect of wide application range, simple and easy method, high accuracy of results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Embodiment 1, the present embodiment detects the method for the acidity of lithium hexafluorophosphate, comprises the following steps:
[0025] (1) Take 100g of deionized water at a temperature of 0°C, add 1-3 drops of bromothymol blue indicator, use 0.05mol / L sodium hydroxide as the titrant, and titrate to blue-green with a digital titrator (deduct reagent blank);
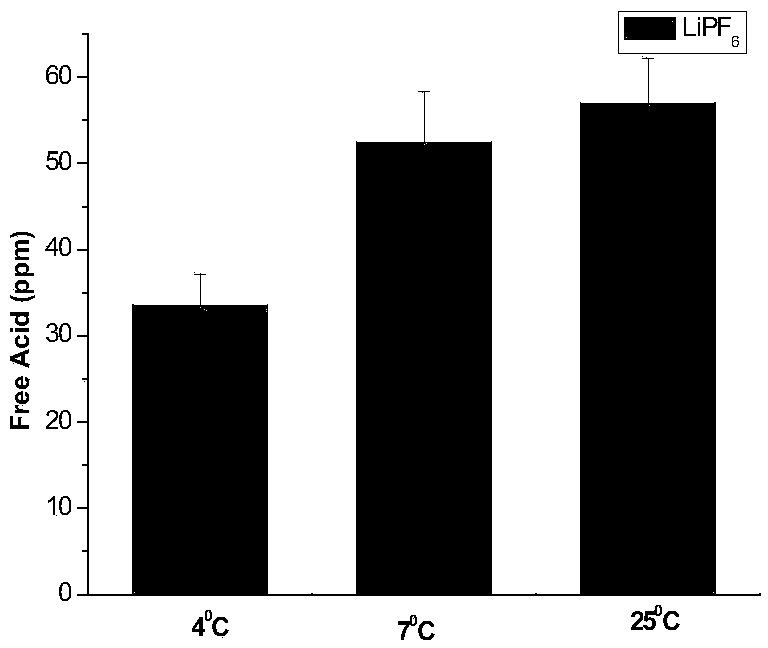
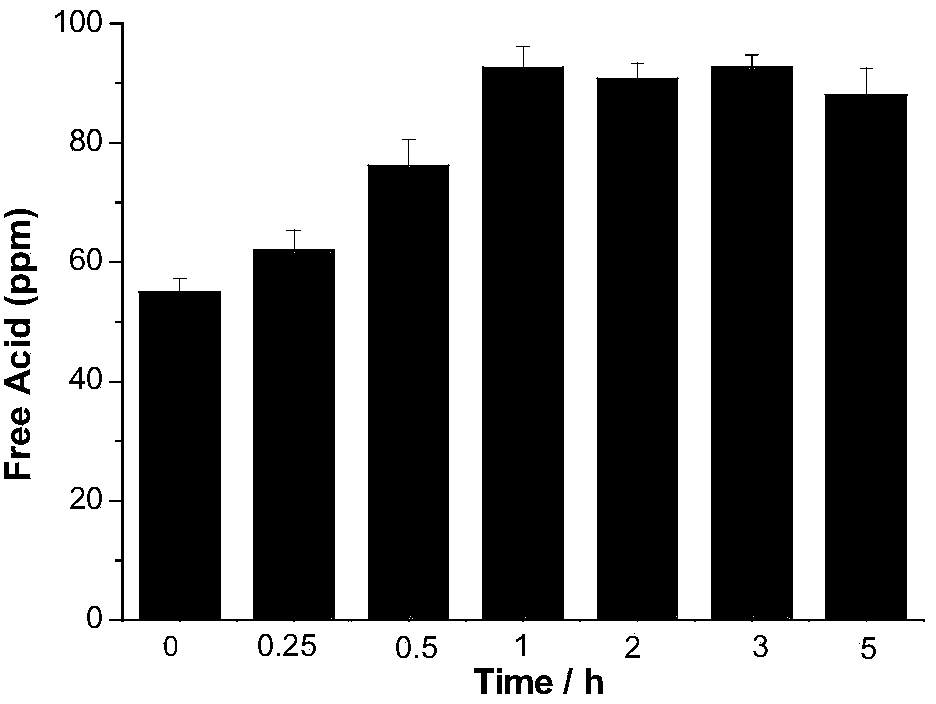
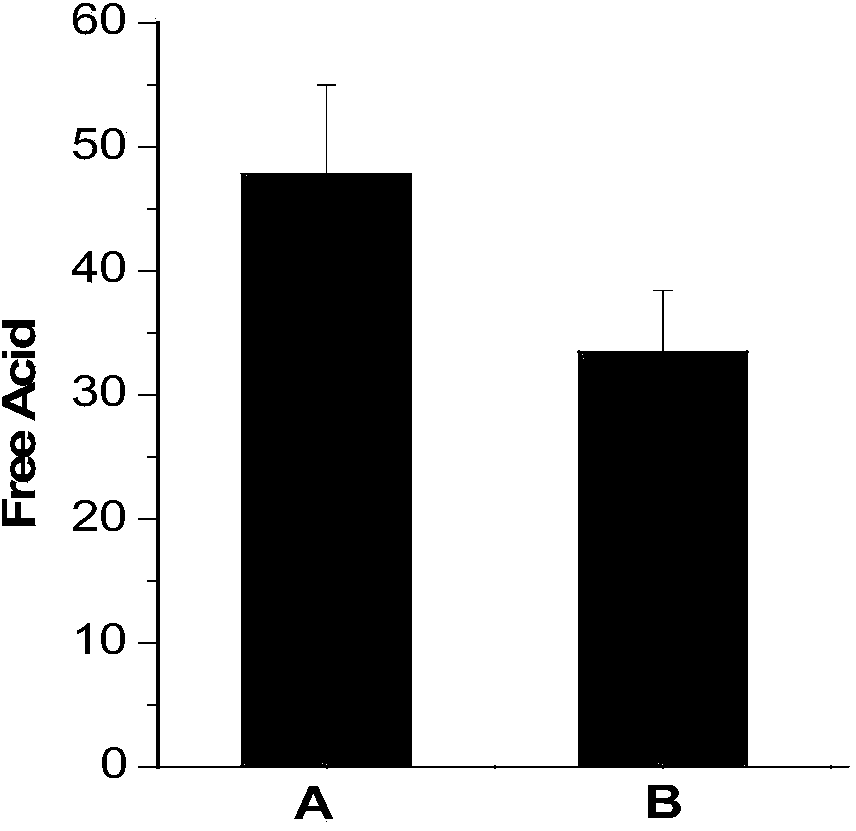
[0026] (2) Weigh 5g of lithium hexafluorophosphate, add it to the deionized water titrated in step (1), let it stand for 0min after dissolving, use 0.05mol / L sodium hydroxide as titrant, and titrate to blue-green with a digital titrator, The whole titration process is completed within 1 min, and the content of free acid in lithium hexafluorophosphate is calculated by the volume of sodium hydroxide consumed. The corresponding results are shown in Table 1. Intermediate precision data such as figure 1 shown.
[0027] (3) The calculation formula is as follows:
[0028] w = ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Embodiment 2, the method for detecting the acidity of lithium tetrafluoroborate in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0034] (1) Take 100g of deionized water at a temperature of 1°C, add 1-3 drops of bromothymol blue indicator, use 0.01mol / l sodium hydroxide as the titrant, and titrate to blue-green with a digital titrator (deduct reagent blank);
[0035] (2) Weigh 2g of lithium tetrafluoroborate, add it to the deionized water titrated in step (1), dissolve it and let it stand for 1min, use 0.01mol / l sodium hydroxide as the titrant, and titrate with a digital titrator To blue-green, calculate the free acid content in lithium tetrafluoroborate from the volume of sodium hydroxide consumed. The corresponding results are shown in Table 1.
[0036] (3) The calculation formula is the same as step (3) of Example 1.
Embodiment 3
[0037] Embodiment 3, the method for detecting the acidity of lithium hexafluoroarsenate in this embodiment comprises the following steps:
[0038] (1) Take 100g of deionized water at a temperature of 4°C, add 1-3 drops of bromothymol blue indicator, use 0.1mol / l sodium hydroxide as the titrant, and titrate to blue-green with a digital titrator (deduct reagent blank);
[0039] (2) Weigh 10g of lithium hexafluoroarsenate, add it into the deionized water titrated in step (1), dissolve it and let it stand for 1min, use 0.1mol / l sodium hydroxide as the titrant, and titrate to the end point, The free acid content in lithium hexafluoroarsenate was calculated by the volume of sodium hydroxide consumed. The corresponding results are shown in Table 1.
[0040] (3) The calculation formula is the same as step (3) of Example 1.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com