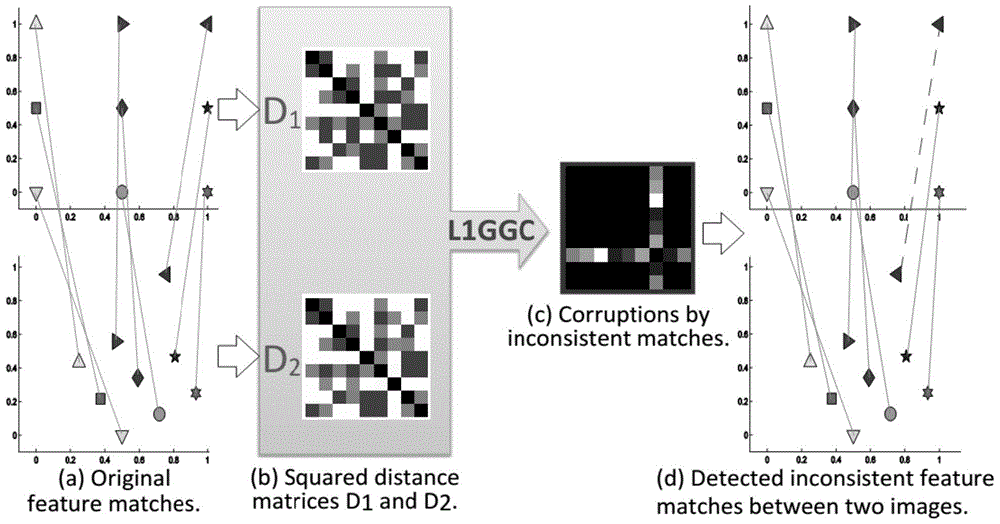
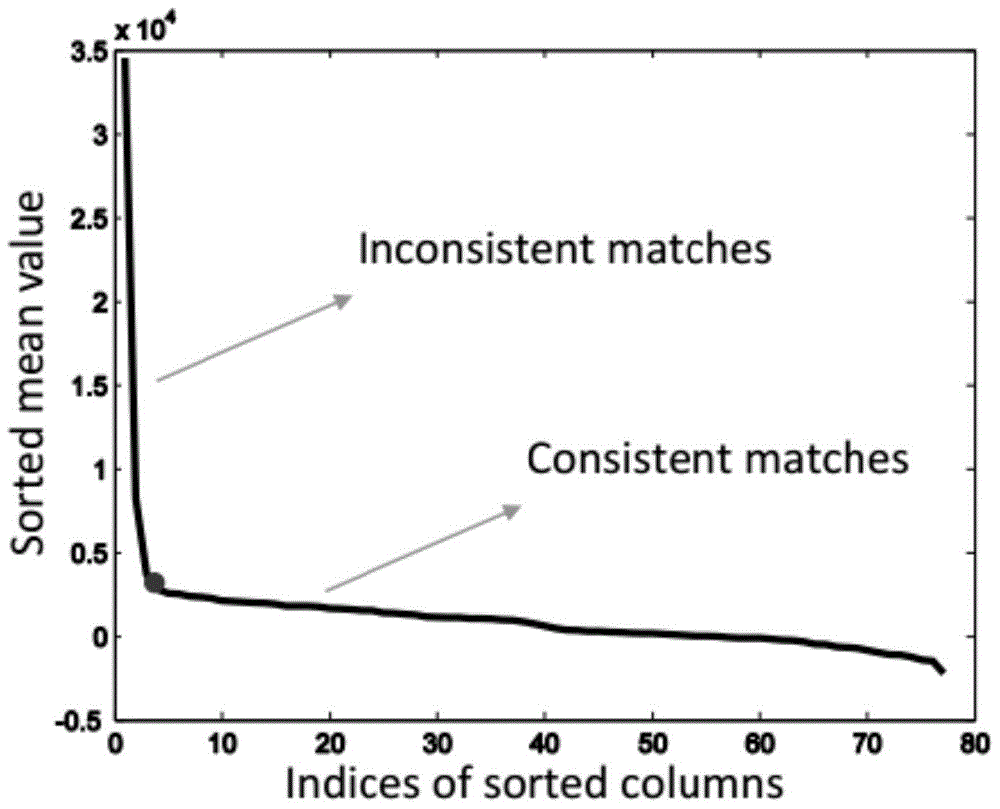
False Match Detection Method Based on L1 Norm Global Geometric Consistency Test
A technology of error matching and L1 norm, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, special data processing applications, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of time-consuming calculation, time-consuming, time-consuming and unfavorable retrieval, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
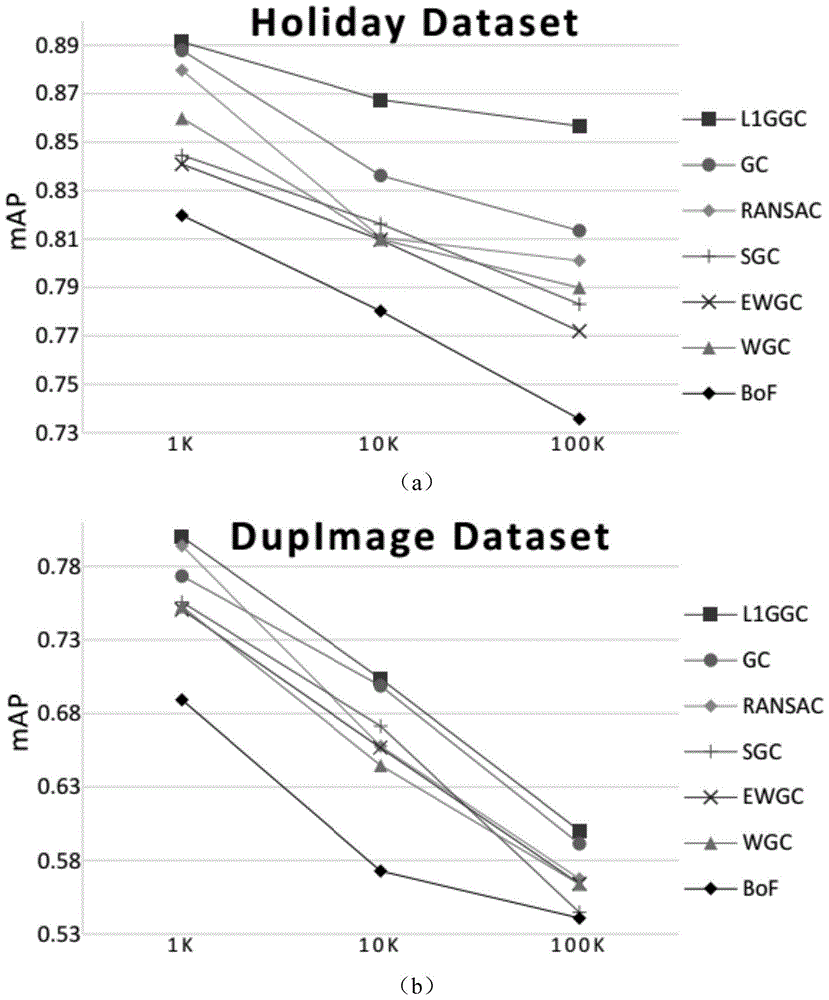
[0037] Datasets: Two popular datasets are used as the retrieved datasets, namely the Holiday dataset and the DupImage dataset. Among them, the Holiday dataset contains a total of 1491 images, and the approximate number of repeated image groups is 500; while the DupImage dataset contains a total of 1104 partially repeated images, with a total of 33 groups. In addition, in order to make the example more realistic, this embodiment also specially adopts the confusing image dataset MIRFlickr1M, which contains one million irrelevant images downloaded from web pages. In this embodiment, a picture in each retrieved data set is used as a target picture, and other pictures of the same group are mixed into the confused picture, so as to test the retrieval effect.
[0038] Evaluation indicators: In this embodiment, the general average retrieval accuracy (mAP) and average retrieval time that can reflect the performance of image retrieval are used to test and compare the present invention w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com