A kind of method for carrying out drying method for wet d-ribose crystallization
A ribose and crystallization technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, monosaccharides, sugar derivatives, etc., to achieve the effect of ensuring quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
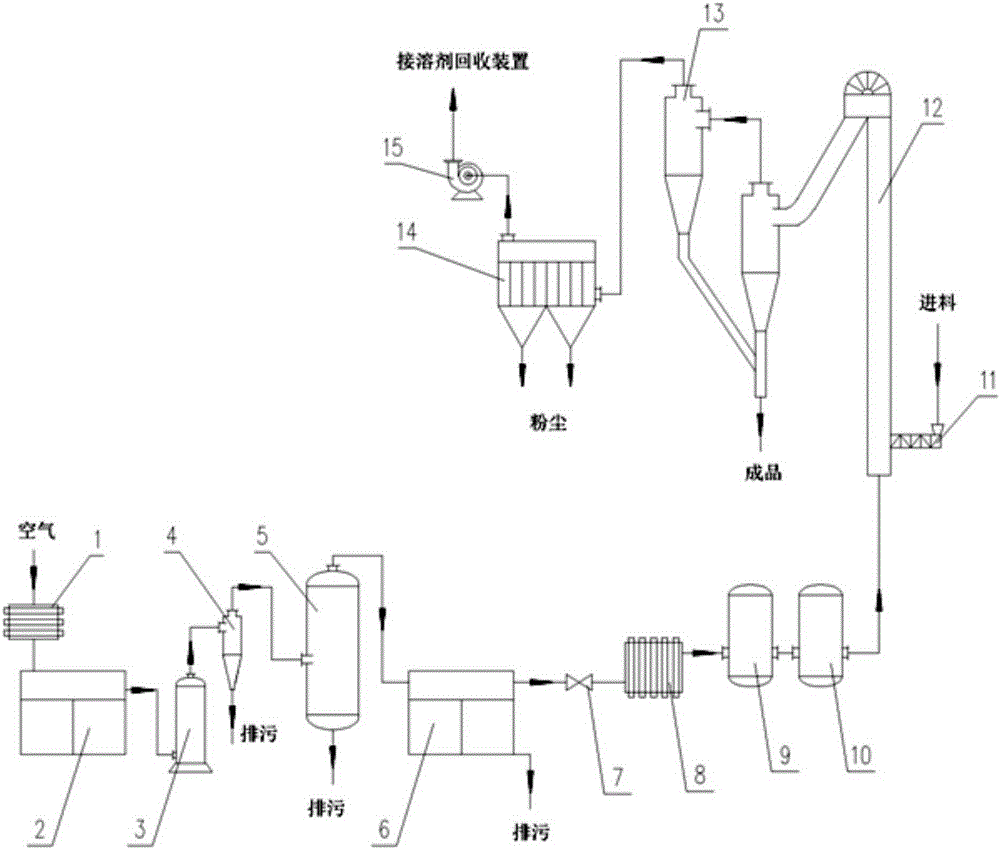
[0034] refer to figure 1 Schematic diagram of drying process and equipment connection for wet D-ribose crystallization, the ambient temperature is 25°C, and the relative air humidity is 40%.
[0035] A method for drying the wet D-ribose crystals obtained from the separation and extraction of the fermentation broth, the steps are:
[0036] (1) Use the primary filter to preliminarily remove impurities from the air to be dried, then use an air compressor to compress the air to 0.7MPa, then use a cooler to reduce the air to 30°C, and use a cyclone separator to remove the condensed oil in the air and water removal;
[0037] (2) Use a cold dryer and control the pressure dew point temperature of the cold dryer to 3°C, further cool down and condense the compressed air obtained in step (1), remove oil and water, and obtain dehumidified air;
[0038] (3) Adjust the air pressure after dehumidification (step 2) to 6.0KPa through the regulating valve, and then heat the depressurized air ...
Embodiment 2
[0044] The basic steps are the same as in Example 1, the ambient temperature is 33°C, and the relative air humidity is 60%.
[0045] Different from embodiment 1 in the step is:
[0046] Use an air compressor to compress the air to 0.6MPa, and then use a cooler to lower the air to 35°C;
[0047] Use a cold dryer and control the pressure dew point temperature of the cold dryer to 2°C;
[0048] Adjust the dehumidified air pressure to 5.0KPa through the regulating valve, then heat the depressurized air to 45°C through the heater, and then filter through the two-stage filter to obtain an almost dry temperature with a relative humidity of only 1.7%. Hot, clean, dry air.
[0049] Centrifuge solid-liquid separation to obtain D-ribose wet crystals 350kg, moisture content 6.5%. Wet crystals of D-ribose are fed into the drying column at a uniform speed from the feeder, and fully contact with dry air (the mixing ratio of air and wet D-ribose crystals is expressed in m 3 : Kg is 6:1), ...
Embodiment 3
[0052] The basic steps are the same as in Example 1, the ambient temperature is 36°C, and the relative air humidity is 70%.
[0053] Different from embodiment 1 in the step is:
[0054] Use an air compressor to compress the air to 0.5MPa, and then use a cooler to lower the air to 40°C;
[0055] Use a cold dryer and control the pressure dew point temperature of the cold dryer to 4°C;
[0056] Adjust the dehumidified air pressure to 5.5KPa through the regulating valve, and then heat the depressurized air to 50°C through the heater.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com