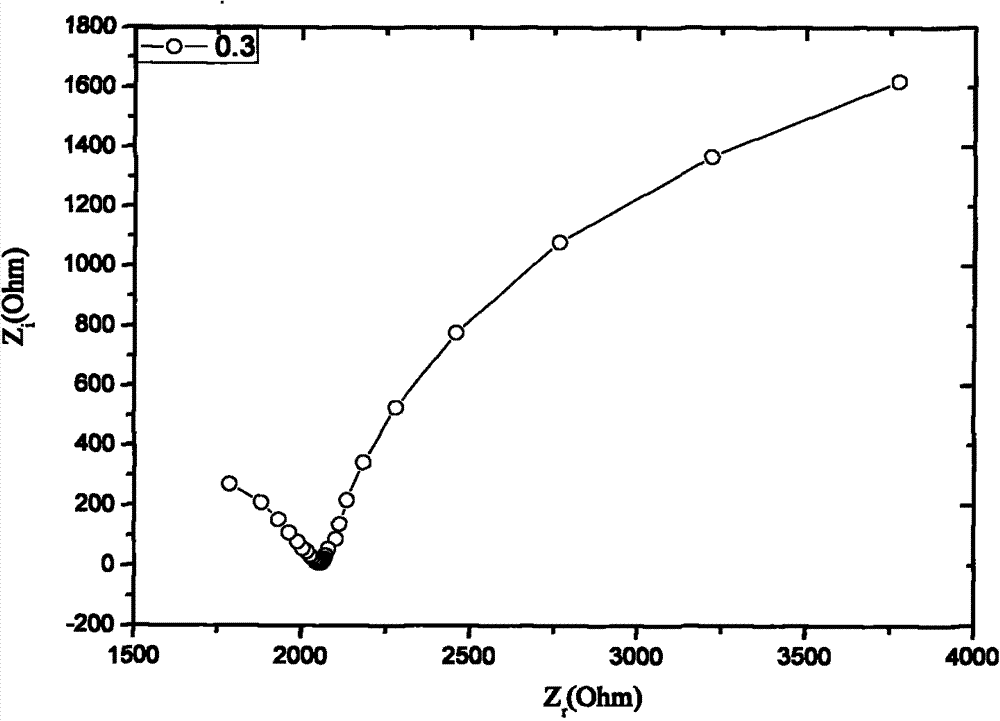
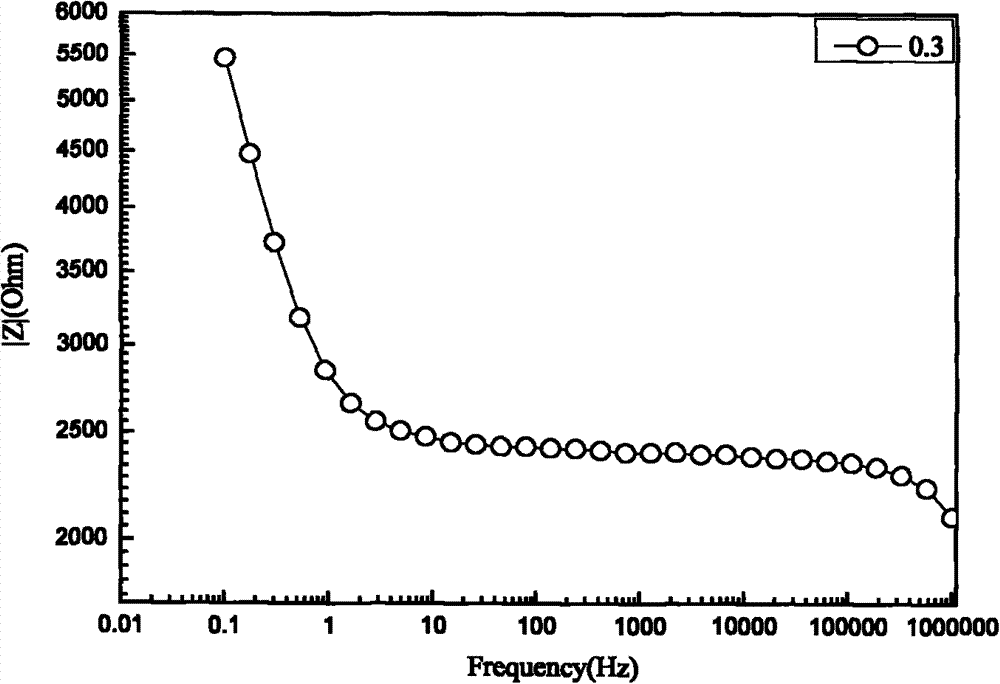
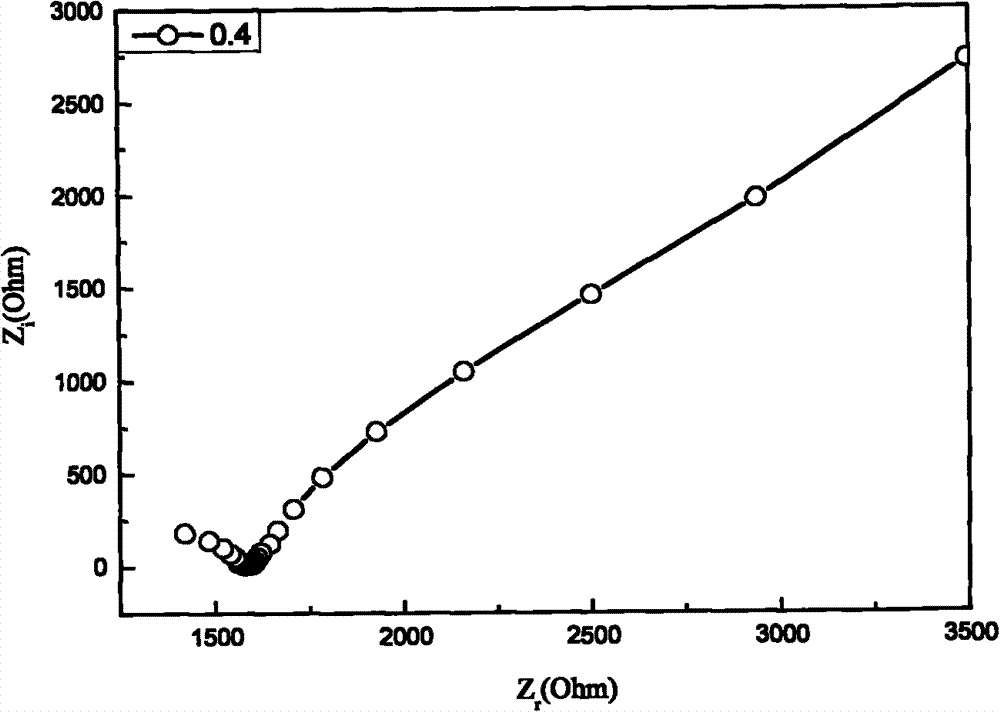
Method for testing sulfate radical erosion depth of cement-based material
A cement-based material, erosion depth technology, applied in the direction of suspension and porous material analysis, measurement devices, permeability/surface area analysis, etc., can solve the mold and cement specimens are easily damaged, can not be repeatedly detected, inconvenient to operate, etc. problems, achieve high sensitivity, save test manpower and time, and test time is short
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] A method for testing the depth of sulfate radical erosion of cement-based materials, comprising the following specific steps:
[0036](1) Inject the composite Portland cement into the mold disclosed by the patent No. ZL201120473976.2 for cement specimen curing, remove the electrode plates at both ends of the mold and place the mold in sulfate solutions with different sulfate concentrations for infiltration .
[0037] In step (1), the 525 composite Portland cement produced by Shenzhen Starfish Onoda Cement Co., Ltd. is injected into the mold disclosed by the patent No. ZL201120473976.2 (see the use disclosed in the third page of the embodiment of the specification part of the patent document for details) The mold used for the online test of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in the cement hydration process, the model specification of the mold is specifically described in the paragraph 0030 of the embodiment: "The material of the bottom plate 1, the side plate 2 and t...
Embodiment 2
[0063] A method for testing the depth of sulfate radical erosion of cement-based materials, comprising the following specific steps:
[0064] (1) Inject the composite Portland cement into the mold disclosed by the patent number ZL 201120473976.2 for cement specimen curing, remove the electrode plates at both ends of the mold and place the mold in sulfate solutions with different sulfate concentrations for infiltration.
[0065] In step (1), the 525 composite Portland cement produced by Shenzhen Starfish Onoda Cement Co., Ltd. is injected into the mold disclosed by the patent No. ZL 201120473976.2 (see for details the method disclosed in the third page embodiment of the specification part of the patent document for The mold for online testing of electrochemical impedance spectroscopy in the cement hydration process. The model specifications of the mold are specifically described in paragraph 0030 of the embodiment: "The materials of the bottom plate 1, the side plate 2 and the c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com