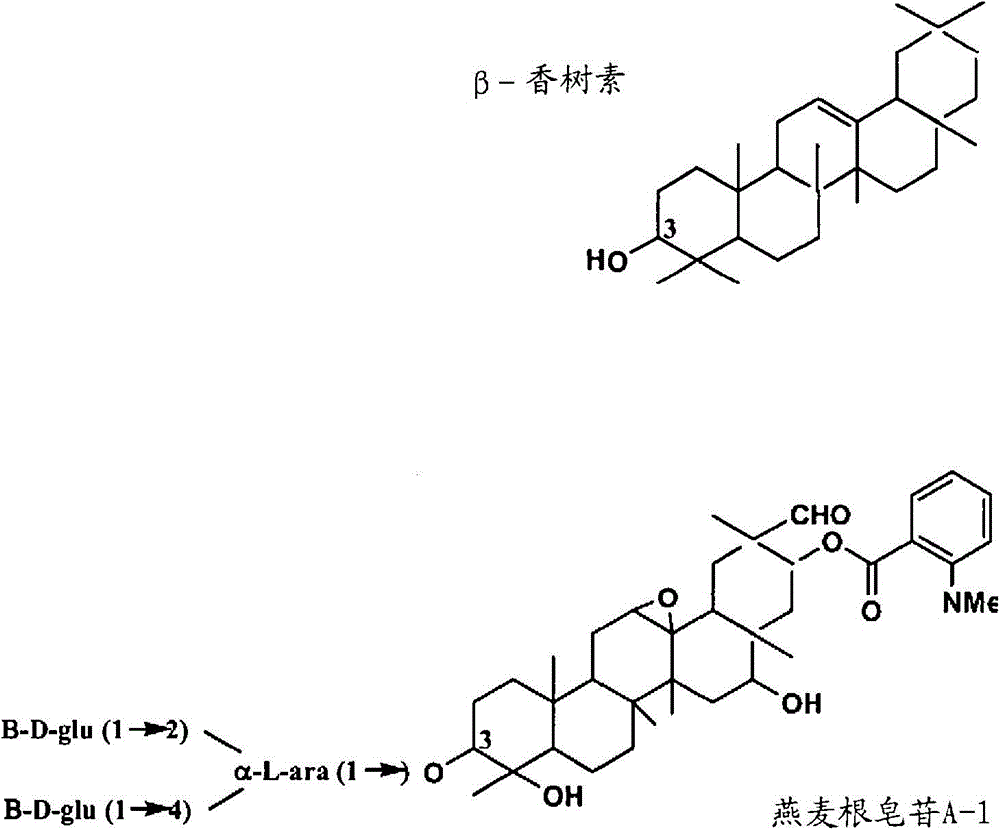
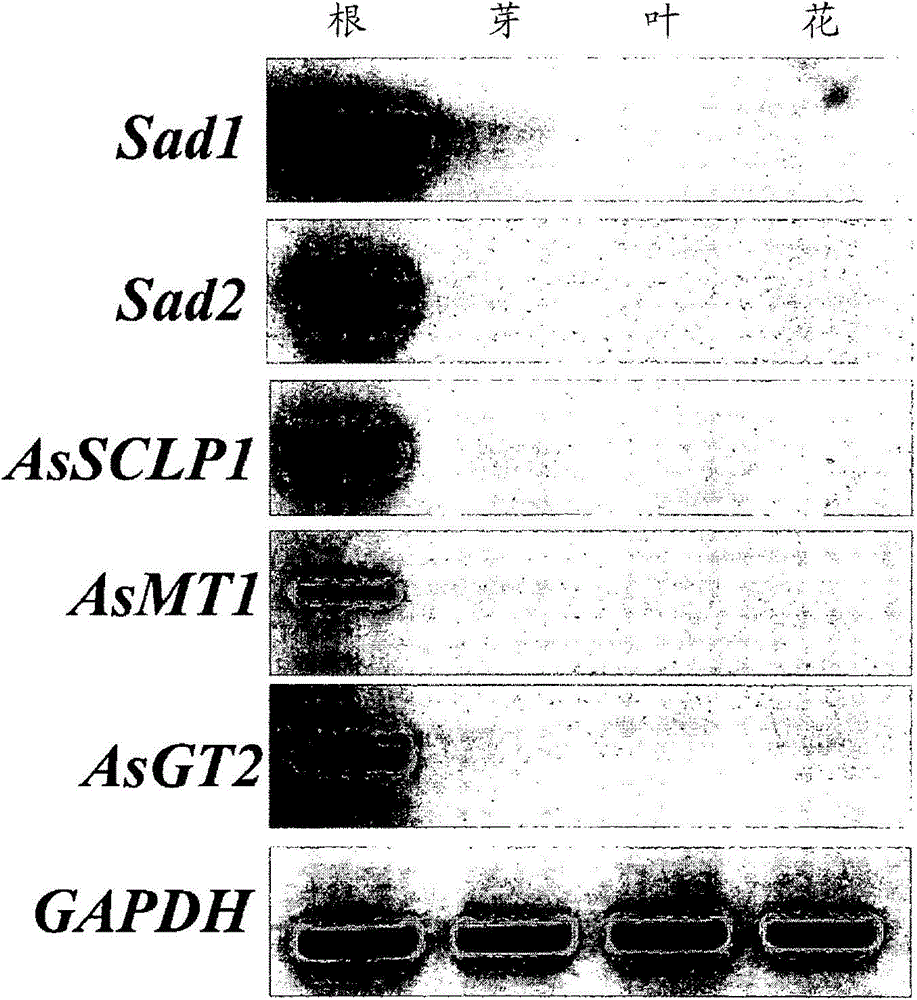
Enzymes involved in triterpene synthesis
A technology of amyrin synthase and methyltransferase, which is applied in the direction of transferase, cells modified by introducing foreign genetic material, angiosperms/flowering plants, etc., and can solve the problem of lack of peptidase activity and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0161] Isolation of Genomic and cDNA Fragments of Serine Carboxypeptidase-Like Protein (AsSCPL1), Methyltransferase (AsMT1) and Glucosyltransferase (AsGT2)
[0162] Genomic polynucleotide fragments encoding genes affected by serine carboxypeptidase-like protein (AsSCPL1), methyltransferase (AsMT1) and glucosyltransferase (AsGT2) were isolated from the BAC library derived from the accession number S75 genomic DNA and cDNA libraries were prepared from oats as follows.
[0163] The BAC library was constructed from the black oat accession number S75 genomic DNA ((Qi X. et al., 2006, Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A103:18848-18853). The DNA probe was derived from Sad1 (Osbourn et al., 2007 On March 6th, US, 7,186,884B2) and Sad2 (people such as Osbourn, US2006-0112448A1), this probe is used for screening complete BAC library.Construction spans a gene cluster (Qi X. et al., 2004, Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.U.S.A.101:8233-8238) BAC contig. BAC fingerprint and BAC end sequence analysis allowed us ...
Embodiment 2
[0172] Isolation and characterization of Sad7 oat mutants
[0173] Seeds of diploid oats (Oats black) were mutagenized with sodium azide and M2 seeds from individual M1 plants were germinated and root fluorescence assessed for primary screening to identify saponin-deficient or Sad oat mutants. Candidate avenantia root saponin-deficient mutants were identified based on reduced root fluorescence and confirmed by TLC and HPLC analysis of methanolic root extracts from homozygous M3 seedlings.
[0174] generate mutants
[0175] Seeds of diploid oats (Oats black) (accession number S75 from Institute of Grasslands and Environmental Research, Aberystwyth, Wales, UK) were mutagenized with sodium azide essentially as described (Rines, H.W., 1985, Env. Exp. Bot., 25:7-17). Briefly, mutagenesis was performed as follows. Seeds were presoaked in Erlenmeyer flasks sealed with rubber stoppers, using 0.5 mL of water per seed, and shaken at 120 cycles per minute in an orbital platform sh...
Embodiment 3
[0183] Isolation and characterization of Sad9 oat mutants
[0184] The original mutants #616, #825, #376 and #1243 (Papadopoulou et al. 1999. PNAS9612923-1928) did not contain any nucleotide changes in the AsMT1 and AsGT2 genes. The sequence analysis was extended to 82 new Sad mutants, which were isolated as described in Example 2. Three mutant M3 lines (#195, #961 and #1310) were identified as having point mutations in the AsMT1 gene (Table 2). No mutations were identified in the AsGT2 gene for any mutants in the pool. DNA sequence analysis confirmed a single nucleotide change in the coding sequence in three mutants (#195, #961 and #1310). Each of these nucleotide changes was predicted to result in an amino acid change (Table 2).
[0185]The roots of these three mutants lacked the bright blue fluorescence associated with avenantia root saponin A-1 and showed dark purple fluorescence under UV excitation. These mutants are called "purple mutants". A more purple mutant #8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com