Molecular markers closely linked to major gene loci for moisture resistance traits in sesame and their applications
A technology of molecular markers and main effect genes, applied in the field of molecular biology and genetic breeding, can solve the problems of narrow genetic basis, large difference in moisture resistance, unusability, etc., achieve clear selection goals, improve selection efficiency, and save production costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
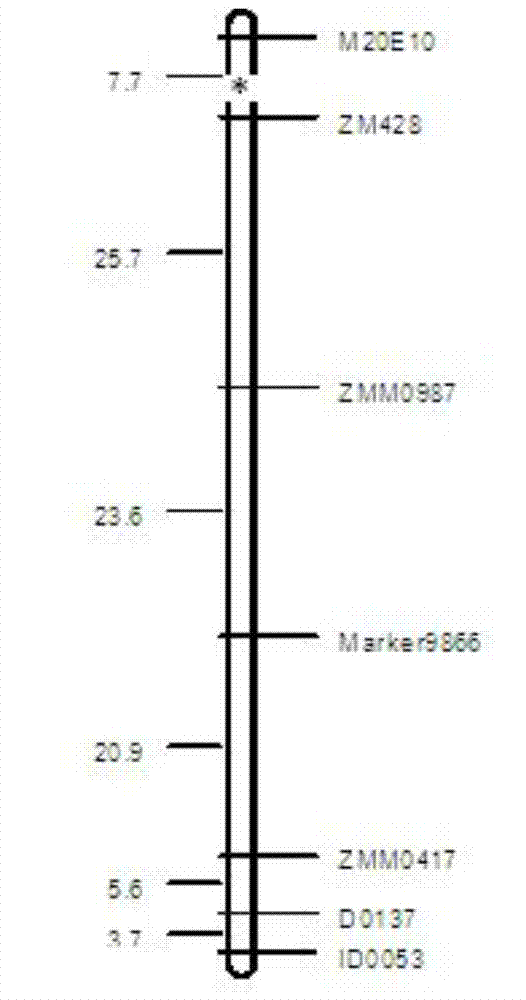
[0038] Example 1 Excavation of main effect gene loci of sesame moisture resistance traits
[0039] (1) Construct a moisture-tolerant / sensitive sesame recombinant inbred line (RIL) population and identify moisture tolerance
[0040] F1 seeds were obtained by crossing the moisture-resistant sesame variety Zhongzhi 13 (84% surviving plant rate after wet damage) and the sensitive germplasm Yiyangbai (31% surviving plant rate after wet damage), and the F1 plants were self-crossed to produce F2 generation seeds. The F2 plants are self-crossed to produce the seeds of the F3 generation, and the F3 generation is planted in rows and self-crossed to produce seeds. Only one seed of a single plant is harvested in each row, and it is planted to become a row of the next generation, and so on, and finally Obtain the F6 generation segregation population, that is, the recombinant inbred line (RIL) population;
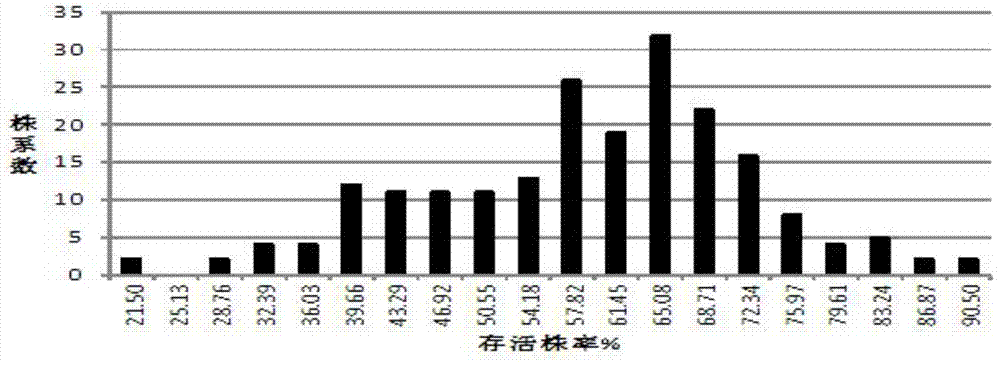
[0041] Identify the moisture resistance of the parents and RIL strains at the full ...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2 Application of the Molecular Marker ZM428 Tightly Linked to the Main Effect Gene Locus qWHCHL09 in Sesame Humidity-tolerant Breeding
[0072]After crossing Zhongzhi 13 with another sensitive variety Zhongzhi 7, 265 F2 individual plants were obtained. In addition, because the moisture resistance of F2 individual plants cannot be identified, 265 F2 individual plants were planted to obtain the corresponding 265 F2: 3 families, F2: The moisture resistance of the 3 families represents the moisture resistance of the F2 single plant. Molecular identification of F2 individual plants at the seedling stage, the specific steps include the extraction of total leaf DNA (specifically as the DNA extraction method in Example 1) and molecular identification using the molecular marker ZM428 closely linked to the major moisture resistance gene locus qWHCHL09, That is, through PCR amplification, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis test and band type statistics (specifically as PCR...
Embodiment 3
[0076] Example 3 Application of the Molecular Marker ZM428 Tightly Linked to the Main Gene Locus qWHCHL09 in the Screening and Early Prediction of Sesame Germplasm Resources for Moisture Tolerance
[0077] Plant 186 copies of sesame core germplasm resources, extract the DNA of each material at the seedling stage (specifically, the DNA extraction method in Example 1), and use the molecular marker ZM428 closely linked to the main moisture resistance gene locus qWHCHL09 for molecular identification, that is, by PCR Amplification, polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis test and band type statistics (specifically as the PCR amplification, gel electrophoresis and band type statistical method in embodiment 1), and carry out moisture resistance to 186 parts of sesame germplasm resources in full flowering stage The identification results showed that among the core germplasm resources of sesame obtained through molecular marker-assisted selection, 62% of the resources survived plant rates af...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com