Method for performing fermentation production on gamma-aminobutyric acid by using high-concentration monopotassium phosphate as buffer salt
A technology of potassium dihydrogen phosphate and aminobutyric acid is applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, fermentation and other directions to achieve the effects of increased yield, simple operation and strong buffering capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
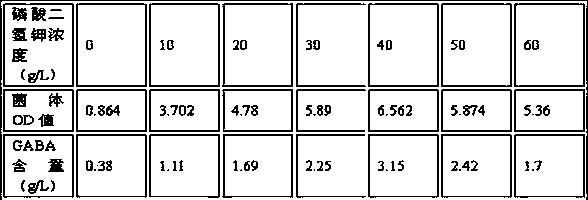
[0037] Example 1: Lactococcus lactis after two generations of activation by conventional methods was inoculated in a specific medium (glucose 30 g / L, yeast extract 40 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 20 g / L, Sodium glutamate 10 g / L, MgSO 4 0.6 g / L, MnSO 4 ·H 2O 0.1 g / L, Tween-80 0.5 mL / L, initial pH controlled at 6.8-7.0) in the fermenter. The culture temperature was 30 °C, the rotation speed was 50 r / min, and the culture was not ventilated. When the pH of the fermentation liquid dropped to 5.0 naturally, ammonia water or sodium hydroxide solution was added to maintain the pH at 5.0±0.5, and the fermentation liquid was added to the fermentation liquid after 24-48 h. Add sodium glutamate concentrate to maintain 5~15 g / L, add glucose during the whole fermentation process to maintain the concentration of fermentation liquid at about 5~20 g / L, and cultivate for 40~60 h to obtain high γ-amino Butyric acid lactic acid bacteria fermentation broth. After culturing for 48 hours...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2: Lactococcus lactis after two generations of activation by conventional methods was inoculated in a specific medium (glucose 30 g / L, yeast extract 40 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 30 g / L, Sodium glutamate 10 g / L, MgSO 4 0.6 g / L, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.1 g / L, Tween-80 0.5 mL / L, initial pH controlled at 6.8-7.0) in the fermenter. The culture temperature was 30 °C, the rotation speed was 50 r / min, and the culture was not ventilated. When the pH of the fermentation liquid dropped to 5.0 naturally, ammonia water or sodium hydroxide solution was added to maintain the pH at 5.0±0.5, and the fermentation liquid was added to the fermentation liquid after 24-48 h. Add sodium glutamate concentrate to maintain 5~15 g / L, add glucose during the whole fermentation process to maintain the concentration of fermentation liquid at about 5~20 g / L, and cultivate for 40~60 h to obtain high γ-amino Butyric acid lactic acid bacteria fermentation broth. After culturing for 48 hour...
Embodiment 3
[0039] Example 3: Lactococcus lactis after two generations of activation by conventional methods was inoculated in a specific medium (glucose 30 g / L, yeast extract 40 g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 40 g / L, Sodium glutamate 10 g / L, MgSO 4 0.6 g / L, MnSO 4 ·H 2 O 0.1 g / L, Tween-80 0.5 mL / L, initial pH controlled at 6.8-7.0) in the fermenter. The culture temperature was 30 °C, the rotation speed was 50 r / min, and the culture was not ventilated. When the pH of the fermentation liquid dropped to 5.0 naturally, ammonia water or sodium hydroxide solution was added to maintain the pH at 5.0±0.5, and the fermentation liquid was added to the fermentation liquid after 24-48 h. Add sodium glutamate concentrate to maintain 5~15 g / L, add glucose during the whole fermentation process to maintain the concentration of fermentation liquid at about 5~20 g / L, and cultivate for 40~60 h to obtain high γ-amino Butyric acid lactic acid bacteria fermentation broth. After culturing for 48 hour...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com