Method for predicting ion diffusion coefficients of damaged cement based composite materials
A technology of ion diffusion and composite materials, which is applied in the field of cement-based composite materials, can solve problems such as changes in the transmission properties of cement-based composite materials that are difficult
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0034] The technical scheme of the present invention is described in detail below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
[0035] The method for predicting the ion diffusion coefficient of the damaged cement-based composite material of the present invention specifically comprises the following steps:
[0036]Step 1. Construct the three-dimensional lattice ion transport network of the damaged cement-based composite material, as follows:
[0037] Step 1-1, obtaining the microscopic / microscopic continuous structure of the non-destructive cement-based composite material;
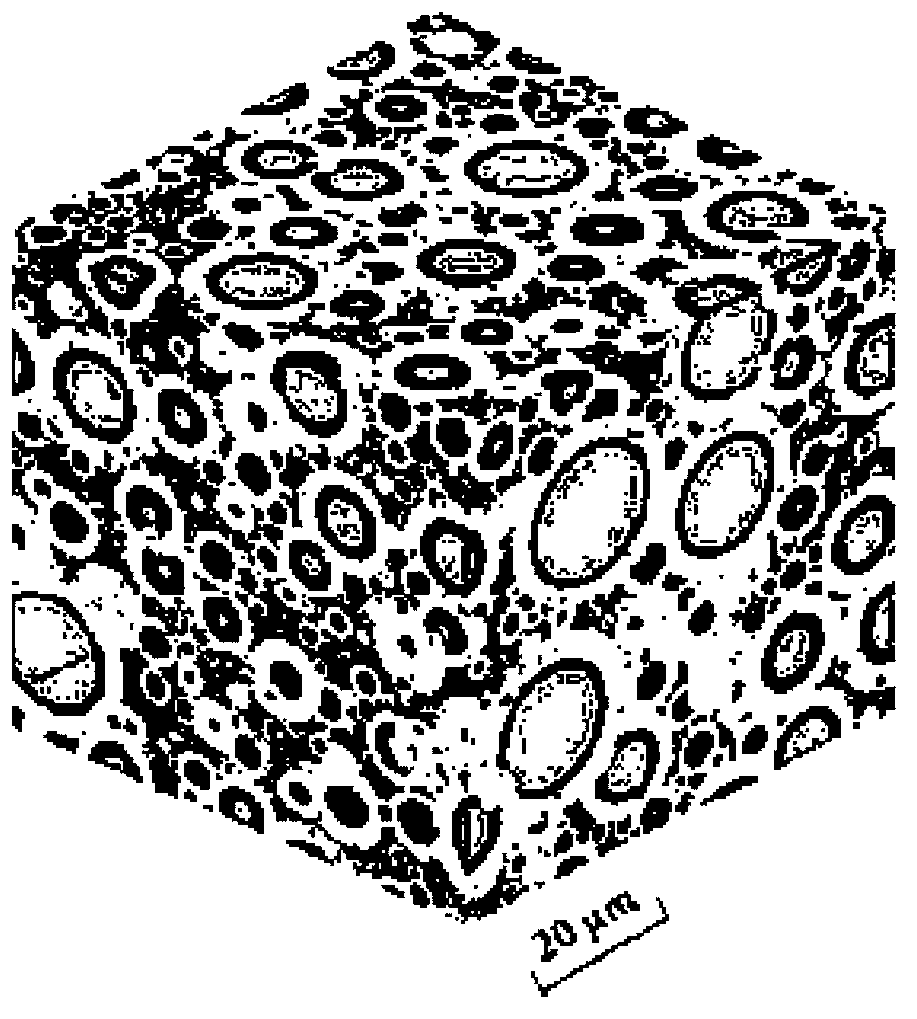
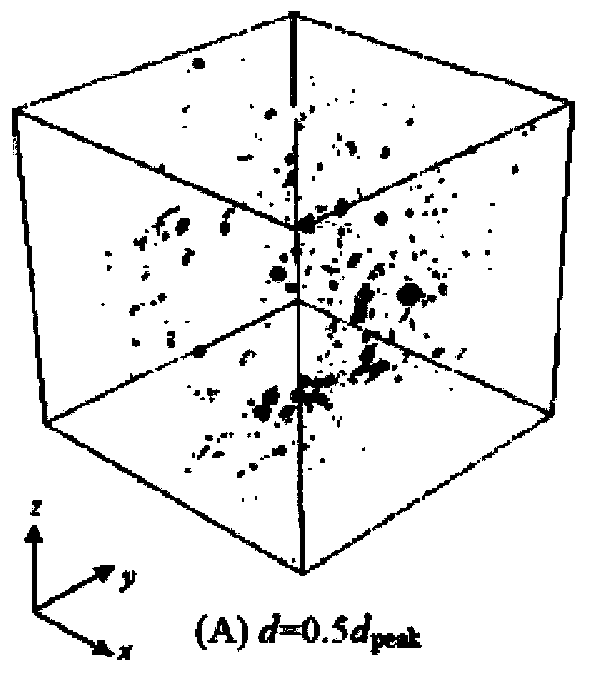
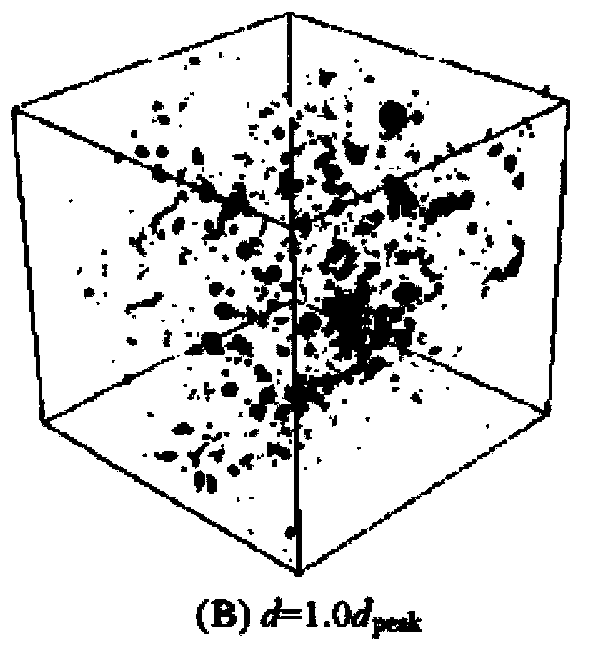
[0038] The micro / meso continuous structure of non-destructive cement-based composites can be obtained using various existing micro / meso models, such as the microstructure generative model for simulating cement paste: HYMOSTRUC3D, μic, and the mesostructure generative model for simulating concrete : SPACE, HADES, etc. figure 1 It shows the HYMOSTRUC3D model (see [van Breugel K.Simulation of hydration and for...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com