Method for recycling nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste
A technology of neodymium iron boron and nickel plating, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic materials, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problems of power consumption, unqualified coating, time-consuming, etc., save energy consumption and working hours, and facilitate production arrangements , The effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
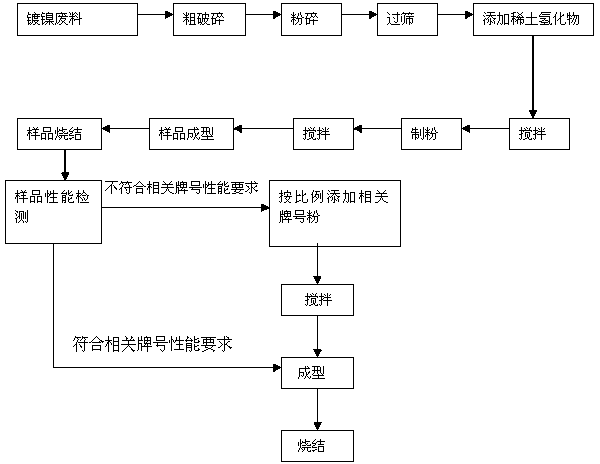
[0016] Use a jaw crusher to roughly crush the collected nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste into particles below 25mm, and then use a secondary crusher to crush the material into powder with a particle size below 3mm. peeling off;
[0017] The powder is then sieved through a 30-60 mesh sieve in a sealed nitrogen glove box to remove most of the nickel plating flakes;
[0018] Add 2wt% praseodymium neodymium hydride to the sieved powder, stir for 1-3 hours to make the ingredients uniform, then use a jet mill to prepare the powder into a fine powder of 3-5 μm, and stir again for 1-3 hours, every Add 1wt‰—5wt‰ milling additive before the first stirring;
[0019] After the powder is fully stirred and mixed, take an appropriate amount of powder for compression molding and sintering to make 5-20 NdFeB magnet samples for performance testing. The test data is: Br: 12.8—13.2KGS, Hcb: 11.8-12.5 KOe, Hcj: 14.2-15.3KOe, (BH) max: 40.5-43.0MGOe, according to GB / T 13560-2000, its performanc...
Embodiment 2
[0021] Use a jaw crusher to roughly crush the collected nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste into particles below 25mm, and then use a secondary crusher to crush the material into powder with a particle size below 3mm. peeling off;
[0022] The powder is then sieved through a 30-60 mesh sieve in a sealed nitrogen glove box to remove most of the nickel plating flakes;
[0023] Add 2wt% iron gadolinium hydride to the sieved powder, stir for 1-3 hours to make the ingredients uniform, then use a jet mill to prepare the powder into a fine powder of 3-5 μm, and stir again for 1-3 hours, every Add 1wt‰—5wt‰ milling additive before the first stirring;
[0024] After the powder is fully stirred and mixed, take an appropriate amount of powder for compression molding and sintering to make 5-20 pieces of 52×52×27 NdFeB magnet samples for performance testing. The test data is: Br: 12.2—12.6KGS , Hcb: 11.5-12.2KOe, Hcj: 13.4-14.7KOe, (BH) max: 36.7—38.4MGOe, according to GB / T 13560-2000, it...
Embodiment 3
[0026] Use a jaw crusher to roughly crush the collected nickel-plated sintered NdFeB waste into particles below 25mm, and then use a secondary crusher to crush the material into powder with a particle size below 3mm. peeling off;
[0027] The powder is then sieved through a 30-60 mesh sieve in a sealed nitrogen glove box to remove most of the nickel plating flakes;
[0028] Add 3wt% praseodymium neodymium hydride to the sieved powder, stir for 1-3 hours to make the ingredients uniform, then use the jet mill to prepare the powder into a fine powder of 3-5 μm, and stir again for 1-3 hours, every Add 1wt‰—5wt‰ milling additive before the first stirring;
[0029] After the powder is fully stirred and mixed, take an appropriate amount of powder for compression molding and sintering to make 5-20 pieces of 52×52×27 NdFeB magnet samples for performance testing. The test data is: Br: 12.6—12.9KGS , Hcb: 11.5-12.2KOe, Hcj: 14.8-16.1KOe, (BH) max: 38.8—41.3MGOe, according to GB / T 13560...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com