Power system weak link identification method based on risk evaluation
A power system and weak link technology, applied in the field of power system analysis, can solve problems such as the law of power flow distribution in the power system that does not take into account the size of the load, and the judgment deviation of weak links, so as to prevent large-scale power outages, reduce power outage risks, and improve The effect of the operational safety level
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
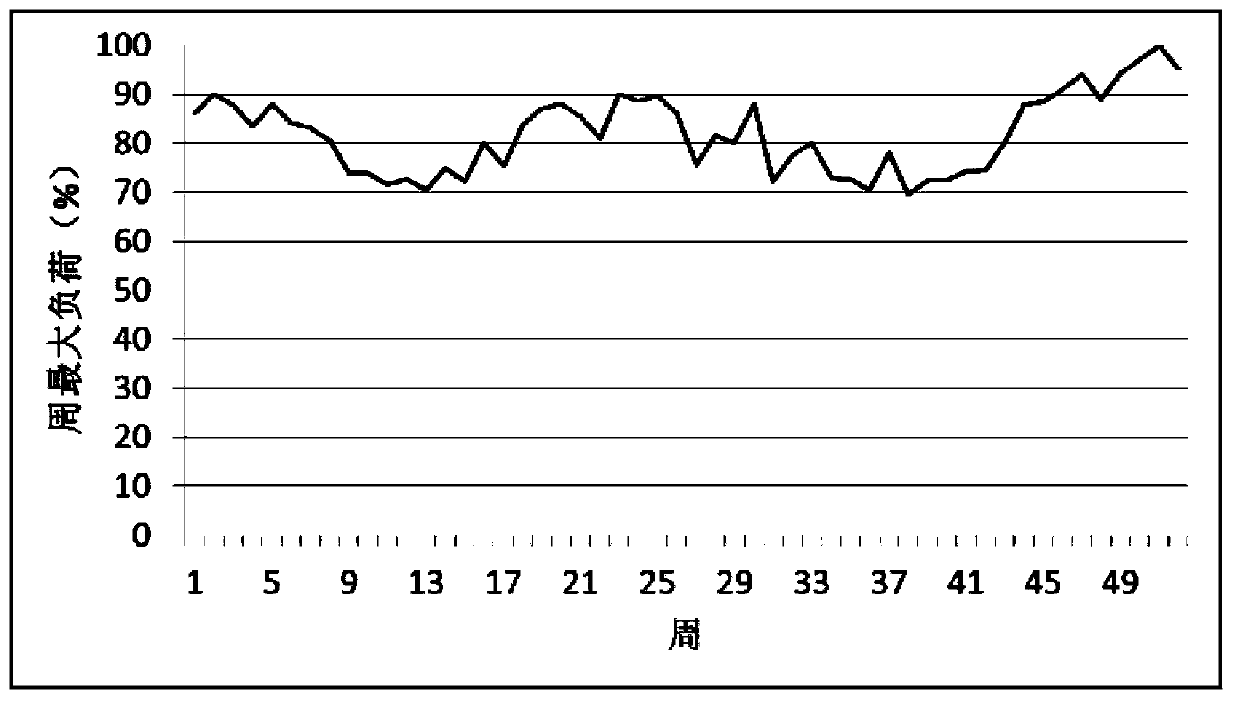
[0157] Taking the IEEE reliability standard test power system (IEEE RTS-79) as an example, the risk assessment-based power system weak link identification method proposed by the present invention is described, and the effect achieved by the present invention is verified. The IEEE RTS-79 power system includes a total of 24 nodes, 32 generator sets, and 38 branches, with a maximum load of 2850MW and an installed capacity of 3405MW. IEEE RTS-79 power system network topology diagram such as figure 2 As shown, the maximum load curve of the power system in each week in one year is as follows image 3 The generator parameters are shown in Table 1, the load ratio of each node is shown in Table 2, and the branch (line and transformer) parameters are shown in Table 3.
[0158] Table 1 IEEE RTS-79 generator set reliability data
[0159]
[0160]
[0161] Table 2 IEEE RTS-7 node load ratio
[0162]
[0163]
[0164] Table 3 IEEE RTS-79 branch circuit (line and transformer)...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com