Agile elastic telescoping method in cloud environment
An elastic scaling, cloud environment technology, applied in the direction of climate sustainability, resource allocation, multi-programming devices, etc., can solve problems such as inability to guarantee service quality
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
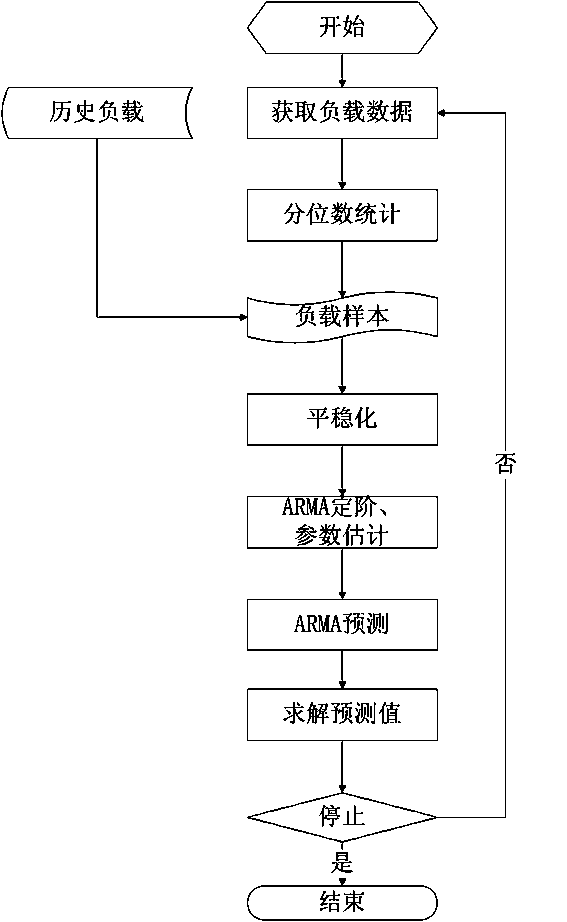
[0090] 1. A first-level prediction algorithm based on the ARIMA model, which uses the periodicity and trend of the application load to predict the load of the next time slice. The algorithm flow chart is as follows figure 1 As shown, the specific operation steps are as follows:
[0091] Step 1.1. Obtain application load data. It can be obtained directly from the load balancer, or obtained by analyzing log files.
[0092] Step 1.2, calculate the sample value. Sort the collected load data of the latest time slice, and use its quantile statistics as a new sample and put it into the historical load.
[0093] Step 1.3, sample stabilization. The load samples of the latest N time slices are taken out, and the periodic difference operation is performed according to the formula (10). Then follow the formula (5) to carry out the differential operation until W t is a stationary sequence.
[0094] Step 1.4, put W t As training data, ARMA is ordered according to the AIC criterion. ...
experiment example 1 2
[0109] Experimental Example 1 Validation of the effect of the second-level prediction algorithm
[0110] The original application load data records the number of requests per second, and we perform average and quantile statistics for different time periods. Such as image 3 As shown, we performed average, 90%, 95%, and 99% quantile statistics for each hour. It can be seen from the statistical chart that the quantile statistical value is much higher than the average value most of the time, which can better reflect the actual resource demand of the application in a certain period of time.
[0111] Figure 4 It is the data of a certain three hours in the above application load (the mean and quantile statistics are performed in units of 5 minutes). It can be seen that the load applied within 1 hour also fluctuates greatly. If the predicted load value is predicted in units of hours, the maximum required amount of resources will be allocated to this time period, resulting in was...
experiment example 2
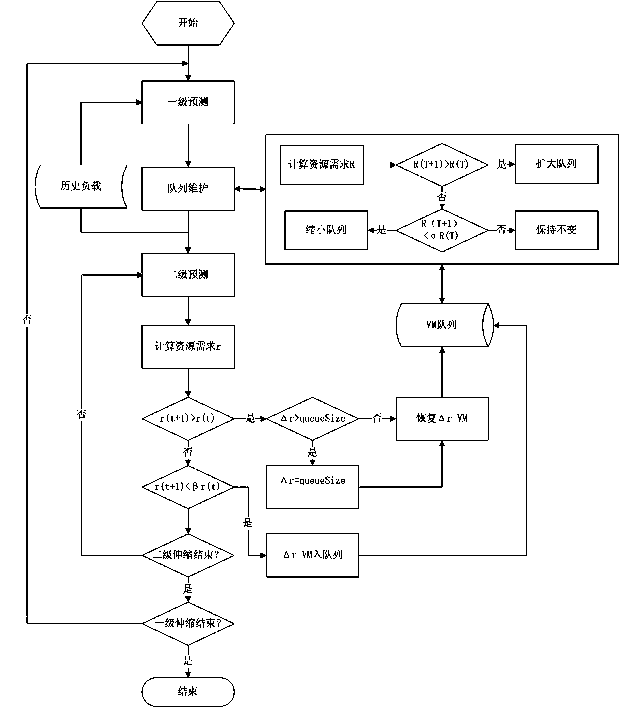
[0115] Experimental example 2 Verification effect of agile elastic scaling method
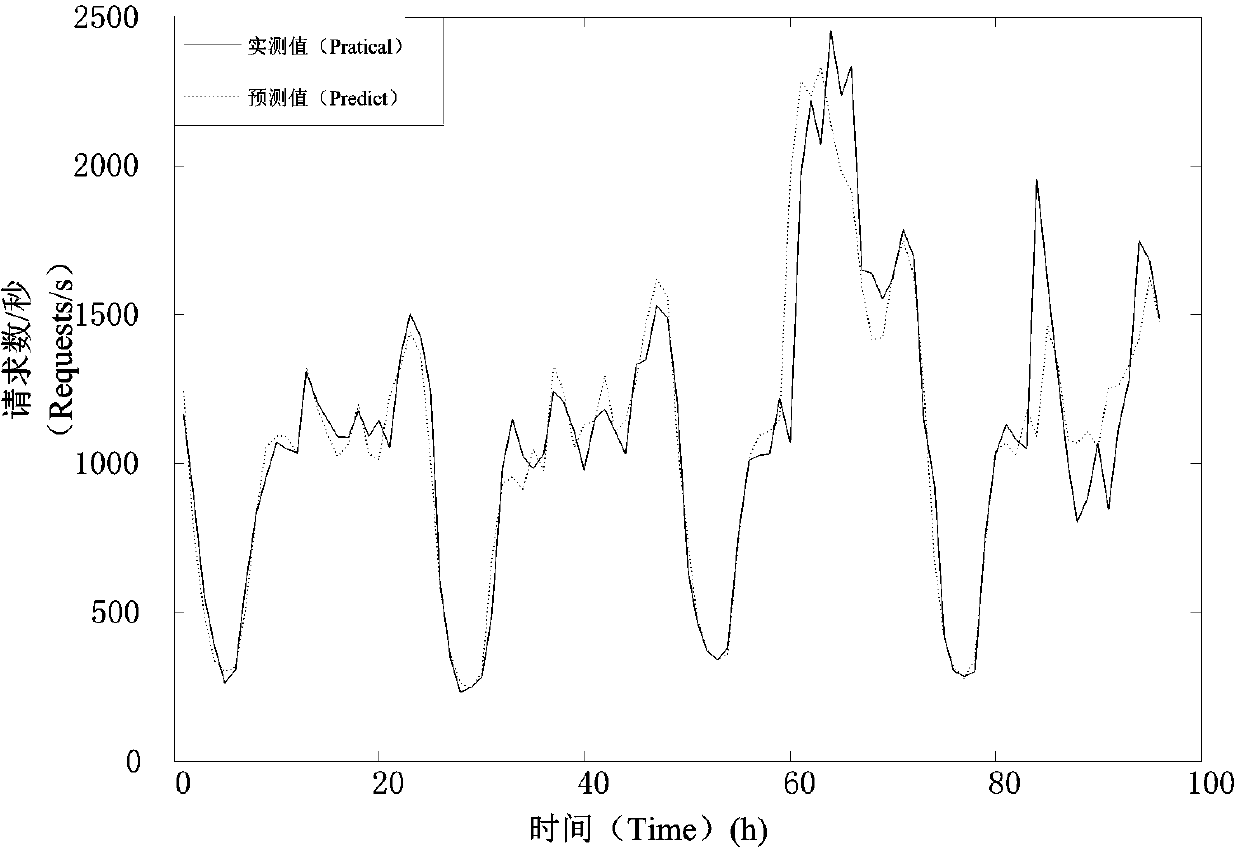
[0116] Using the first-level forecast (95% quantile) with a cycle T=1h, combined with the load / resource model, the resource allocation results are as follows Figure 9 , it can be seen that the forecast resource fits the load curve well. However, in order to reduce SLA errors caused by underestimation of resources, it is usually necessary to allocate some additional resources according to the forecast results. Figure 10 When adding additional resources in different proportions, the corresponding SLA error. It can be seen that when no additional resources are used, only 97.374% of the service quality can be guaranteed, and 99.5% of the service quality can be achieved by adding 50% of the additional resources.
[0117] However, for the coarse-grained resource allocation with a cycle T=1h, in order to ensure the quality of service, resources will be allocated with the maximum load in this time ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com