Mestin modulators and uses thereof
A moesin, a technology for use in the fields of molecular biology and medical research, can solve problems such as undiscovered duration or phase correlation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0140] Example 1 Preparation of anti-moesin antibody
[0141] Monoclonal antibodies against the C-terminal tail domain of Moesin were prepared using conventional hybridoma methods. To generate a C-terminal tail domain having the sequence SEQ ID NO: 1, PCR was used to amplify a cDNA fragment corresponding to the C-terminal tail domain described above (see SEQ ID shown in Figure 1 NO: 4, where the underlined part is the cDNA sequence of the C-terminal tail domain).
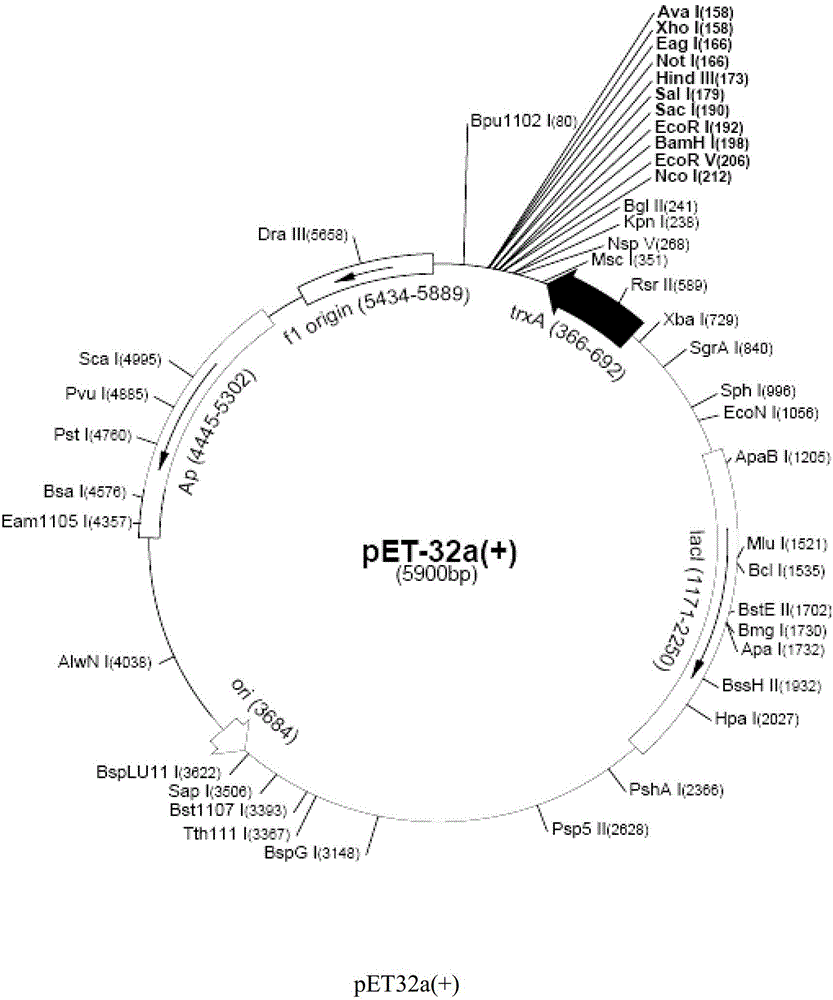
[0142] The PCR amplified moesin DNA fragment was cloned into an expression vector selected from pET32a(+) and pET28a(+). Then the constructed vector was used to transform the Escherichia coli host cell line BL21(DE3) for culture and expression. The restriction and cloning profiles of pET32a(+) and pET28a(+) are shown in Figure 2(a) and 2(b) . The expression system constructed for the C-terminal domain was validated using a restriction enzyme reaction by sequencing to confirm the correct reading frame for exp...
Embodiment 2
[0147] Example 2 Evaluating the Ability of Moesin Inhibitors to Inhibit Cell Proliferation
[0148]The ability of Moesin inhibitors to inhibit or reduce cell proliferation is assessed by this assay.
[0149] Cell proliferation assays were performed using a human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cell line (HPMEC). cells by 10 6 cells / cm 2 The density was seeded on six-well plates and the cells were cultured at room temperature in the presence of various test and control reagents as described below. After culturing for a defined period of time, cells are harvested and labeled for flow cytometry analysis. By dividing the OD of the test group 570 Mean value divided by the OD of the group with the same number of cells as the test group at the beginning of cell culture 570 Average values were used to determine proliferation rates at 2 hours, 24 hours, and 36 hours.
[0150] The test and control groups are as follows:
[0151] 1) TNF-α only;
[0152] 2) Antibodies agai...
Embodiment 3
[0158] Example 3 Cell-to-cell expression and apoptosis analysis of moesin
[0159] Cell cultures were subjected to apoptosis assays and surface antigen assays in the presence of the anti-moesin antibody described in Example 1 to assess the antibody's effect on endothelial cell apoptosis and intercellular expression of moesin (indicating that the the active form of the protein).
[0160] Apoptosis was studied using Annexin V assay. The collected cells were washed with PBS, centrifuged, and 70% ethanol, RNAs (200 mg / l) and PI (20 mg / l) were added sequentially. Cells were then stained using the Annexin-V FITC / PI kit, which is used for double staining of FITC and PI, since live cells are negative for both FITC and PI, while early apoptotic cells are positive for FITC but negative for PI , Late apoptotic or dead cells were positive for both FITC and PI. Stained cells were analyzed using flow cytometry to determine the number of apoptotic cells in the presence of different dete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com