Superconducting cable cooling system
一种冷却系统、超导电的技术,应用在超导电性器件、冷却机、超导/高导导体等方向,能够解决难以制冷剂入口温度控制为恒定等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
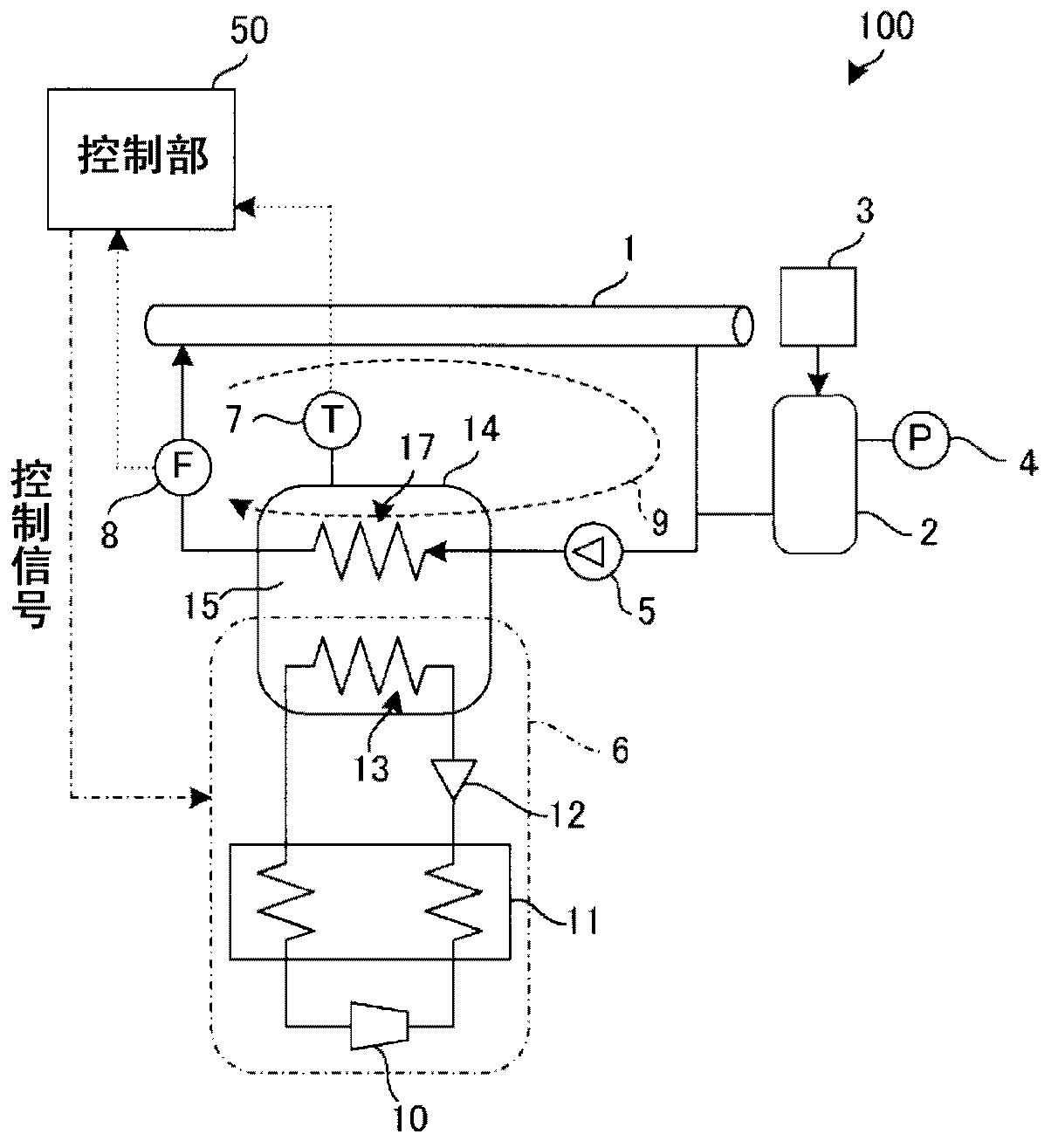
[0039] figure 1 It is a configuration diagram briefly explaining the overall configuration of the superconducting cable cooling system 100 according to the first embodiment. It should be noted that, for the reference Figure 10 DESCRIPTION OF THE BACKGROUND ART Common parts are assigned common symbols, and descriptions of details are appropriately omitted.
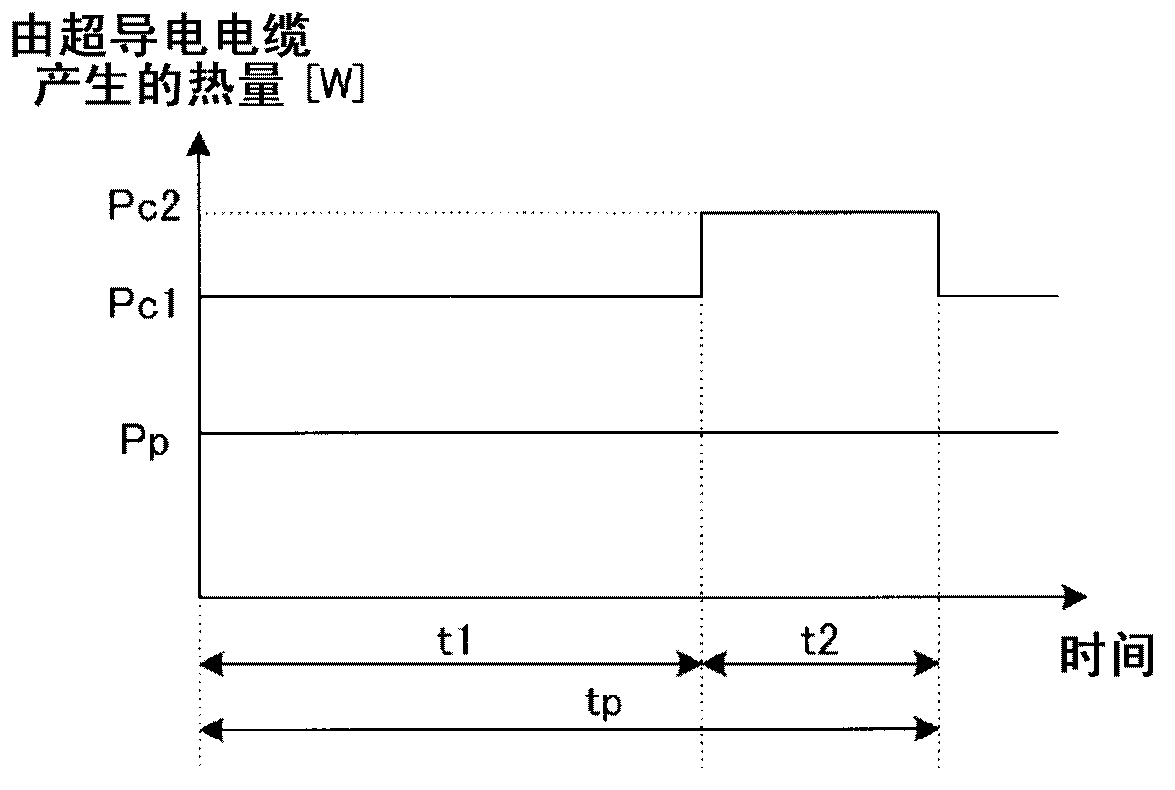
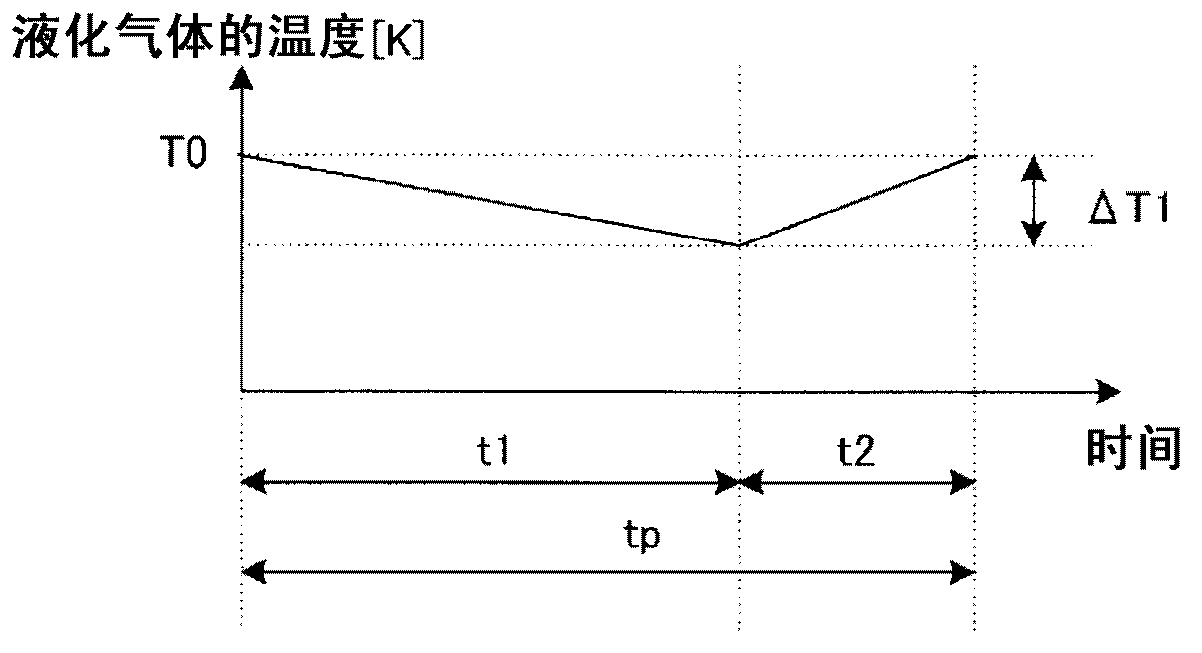
[0040] The cooling system 100 supplies the refrigerant used in the cooling process of the superconducting cable 1 to the heat exchange part 17 by the circulation pump 5 under pressure, cools it, and then supplies it to the superconducting cable 1 again, thereby forming a circulation path 9 and cooling the superconducting cable 1 . The conductive cable 1 is cooled. The superconducting cable 1 is formed of a high-temperature superconductor, and is cooled by a refrigerant (liquid nitrogen) flowing in the circulation path 9 . It should be noted that the refrigerant flowing in the circulation path 9 is figure 1 Although il...
no. 2 example
[0078] Figure 5 It is a configuration diagram schematically showing the overall configuration of a superconducting cable cooling system 100 according to the second embodiment. In addition, the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the same structure as Example 1, and repeated description is abbreviate|omitted suitably.
[0079] The superconducting cable cooling system 100 according to the second embodiment is characterized in that a plurality of superconducting cables such as the superconducting cable 1 a and the superconducting cable 1 b can be cooled by one Brayton cycle refrigerator 6 . Circulation pumps 5a and 5b, heat exchange units 17a and 17b, flow sensors 8a and 8b, storage tanks 2a and 2b are respectively provided in each of superconducting cables 1a and 1b, and independent circulation paths 9a and 9b are formed. Since the circulation paths 9a and 9b are independent, they are configured to be able to control pressure, flow rate, etc. in a state of being set sepa...
no. 3 example
[0090] Next, refer to Figure 6 , the superconducting cable cooling system 100 according to the third embodiment will be described. Figure 6 It is a configuration diagram schematically showing the overall configuration of a superconducting cable cooling system 100 according to the third embodiment. It should be noted that the same symbols are assigned to the same structures as those in the above-mentioned first embodiment, and repeated descriptions are appropriately omitted.
[0091] In the case of superconducting cables used for long-distance power transmission, such as Figure 6 As shown, the superconducting cables 1a and 1b are often connected in series to achieve a longer distance. In such a case, since the pressurization capability of the circulation pump 5 has a limit, independent circulation paths 9 a and 9 b are provided corresponding to the respective superconducting cables.
[0092] exist Figure 6In the example shown, the adjacent superconducting cables 1a and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com