Chemical and biological synthesis method for large-scale preparation of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
A technology for synthesizing nicotinamide adenine and nicotinamide adenine, which is applied in fermentation and other directions, can solve problems such as hindering the development of biocatalysis technology, difficulty in extraction, and low yield, and achieve the goals of promoting development, increasing yield, and reducing costs Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
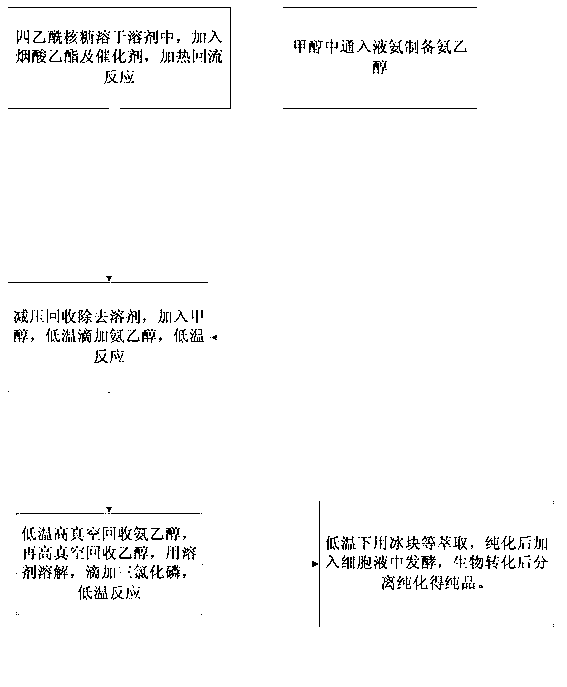
[0024] Add 20 kg of tetraacetylribose to No. 1 reactor, dissolve it with 200 kg of tetrahydrofuran, then add 10 kg of ethyl nicotinate, and directly add 5 kg of methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. The temperature was raised to produce reflux, and timing was started after reflux, and the reaction was carried out for 3 hours. After the reaction, the solvent was recovered under reduced pressure, and after recovery, 150 kg of ethanol was added for dissolution.
[0025] Pump 150 kg of ethanol into the No. 2 reaction kettle, turn on the freezer and cool down to -5°C. Open the decompression valve of the liquefied ammonia steel cylinder, start to pass through the ammonia, measure it, and after feeding 10 kilograms of ammonia, finish the flow through the ammonia. Freeze and cool down to below -10°C to obtain low-temperature ammonia ethanol. Drop the low-temperature ammonia ethanol into the No. 1 reaction kettle. After the dropwise addition, start timing, accurately control the reaction...
Embodiment 2
[0028] Add 100 kg of tetraacetylribose to No. 3 reactor, dissolve it with 1000 kg of dioxane, then add 50 kg of ethyl nicotinate, and directly add 25 kg of methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. The temperature was raised to produce reflux, and timing was started after reflux, and the reaction was carried out for 3 hours. After the reaction was completed, the solvent was recovered under reduced pressure, and after the recovery was completed, 750 kg of ethanol was added for dissolution.
[0029] Pump 750 kg of ethanol into the No. 4 reactor, turn on the freezer and cool down to -5°C. Open the decompression valve of the liquefied ammonia steel cylinder, start to pass through the ammonia, measure, after feeding 50 kilograms of ammonia, end the flow through the ammonia. Freeze and cool down to below -10°C to obtain low-temperature ammonia ethanol. Drop the low-temperature ammonia ethanol into the No. 3 reaction kettle. After the dropwise addition, start timing, accurately control the...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Add 200 kg of tetraacetylribose to No. 5 reactor, dissolve it with 2000 kg of tetrahydrofuran, then add 100 kg of ethyl nicotinate, and directly add 50 kg of methyl trifluoromethanesulfonate. The temperature was raised to produce reflux, and timing was started after reflux, and the reaction was carried out for 3 hours. After the reaction, the solvent was recovered under reduced pressure, and after recovery, 1500 kg of ethanol was added for dissolution.
[0033] Pump 1500 kg of ethanol into the No. 6 reactor, turn on the freezer and cool down to -5°C. Open the decompression valve of the liquefied ammonia steel cylinder, start to pass through the ammonia, measure it, and after feeding 100 kilograms of ammonia, finish the flow through the ammonia. Freeze and cool down to below -10°C to obtain low-temperature ammonia ethanol. Drop the low-temperature ammonia ethanol into the No. 5 reaction kettle. After the dropwise addition, start timing, accurately control the reaction ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com