Corynebacterium glutmicum synthase gene cloning and L183Q site directed mutagenesis method
A technique of Corynebacterium glutamicum and site-directed mutagenesis, which can be used in genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, botany equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem that the catalytic activity has not been improved, and increase the amount of substrate biosynthesis and enhance catalytic activity. Active, enhanced metabolic flux effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
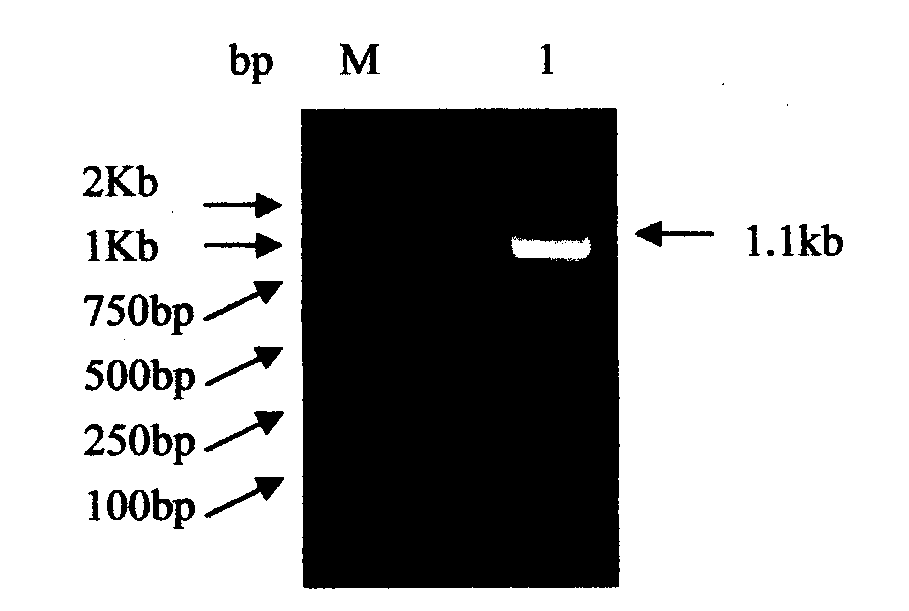
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0041] The gene cloning of Corynebacterium glutamicum DAHP synthetase and the L183Q site-directed mutation method are realized in the following manner: the materials used in the method are Corynebacterium glutamicum LG-332 and Escherichia coli DH5α;
[0042]The gene cloning of described Corynebacterium glutamicum DAHP synthetase, this gene cloning step is as follows:
[0043] 1) Extracting the genomic DNA of Corynebacterium glutamicum LG-332, inoculating a single colony of Corynebacterium glutamicum LG-332 in 10ml LB liquid medium, culturing on a shaker at 30°C for 12h, and inserting 2% of the inoculation amount the next day 100ml LB liquid medium; the genome extraction steps are as follows:
[0044] (1) 100ml bacterial overnight culture solution, centrifuged at 5000rpm for 10 minutes, and removed the supernatant.
[0045] (2) Add 9.5ml TE to suspend the precipitate, add 0.5ml 10% SDS, 50μl 20mg / ml (or 1mg dry powder) proteinase K, mix well, and incubate at 37°C for 1 hour. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com