Method for dissolving cellulose and method for preparing regenerated fiber
A technology of regenerated cellulose and cellulose, applied in the direction of artificial filaments in cellulose solution, can solve the problems of lower quality of cellulose products, short time, uneven solution, etc., to avoid cellulose degradation and increase cellulose concentration , The effect of environmental protection in the manufacturing process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
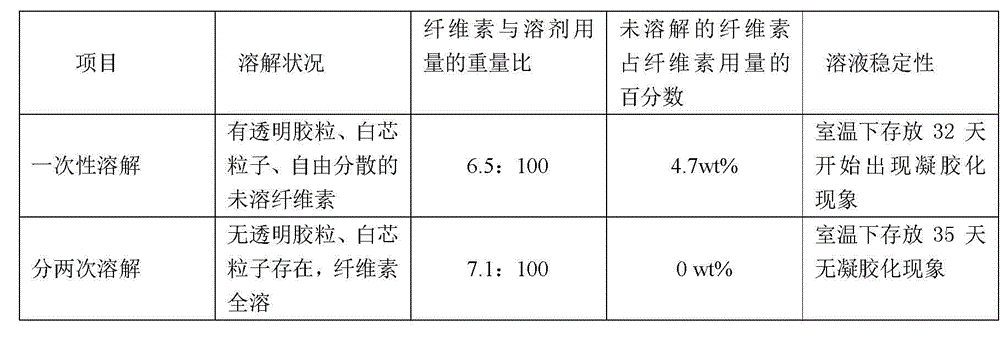
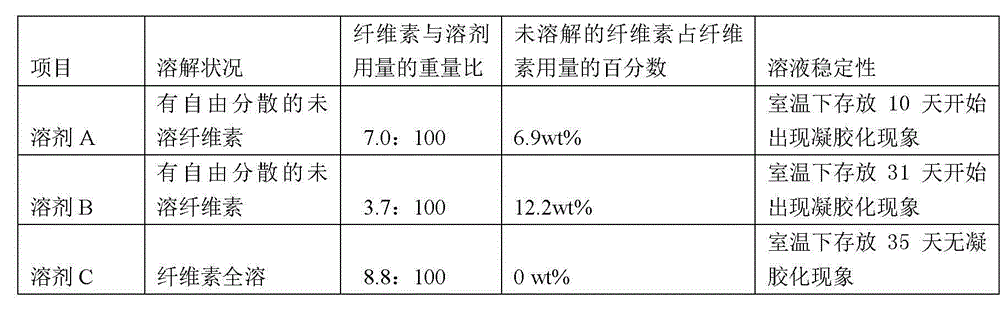
[0052] 3.6g of dried wood pulp (polymerization degree 400) and 40g of 7.5 wt% sodium hydroxide / 11.0 wt% urea / 1.5 wt% polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 800) mixed aqueous solution were kneaded and sheared at 8 °C to mix evenly, Then add 60g of 7.5 wt% sodium hydroxide / 11.0 wt% urea / 1.5 wt% polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 800) mixed aqueous solution with a temperature of -15°C, and place it at 25°C for kneading and shearing to mix evenly, and the fibers The element can be completely dissolved to obtain a uniform and transparent cellulose solution. The cellulose solution was stored at room temperature for 35 days without significant gelation.
Embodiment 2
[0054] 3.8g dry bamboo pulp (polymerization degree 400) and 30g 9.2 wt% sodium hydroxide / 4.5 wt% thiourea / 0.4 wt% polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 4000) mixed aqueous solution were kneaded and sheared at 25°C , and then add 70g of 9.2wt% sodium hydroxide / 4.5wt% thiourea / 0.4wt% polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 4000) mixed aqueous solution at a temperature of -8°C, and place it at -2°C for kneading and shear mixing Evenly, the cellulose can be completely dissolved to obtain a uniform and transparent cellulose solution. The cellulose solution was stored at room temperature for 35 days without significant gelation.
Embodiment 3
[0056] 5.0 g of dry cotton pulp (polymerization degree 500) and 70 g of 5.0 wt% lithium hydroxide / 12.0 wt% urea / 5.5 wt% polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 150) mixed aqueous solution were kneaded and sheared at 0 °C to mix evenly, Then add 30g of 5.0wt% lithium hydroxide / 12.0wt% urea / 5.5wt% polyethylene glycol (molecular weight 150) mixed aqueous solution at a temperature of -15°C, and knead and shear at -8°C to mix evenly. The cellulose can be completely dissolved to obtain a uniform and transparent cellulose solution. The cellulose solution was stored at room temperature for 35 days without significant gelation.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| degree of polymerization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com