Phase change inks containing crystalline trans-cinnamic diesters and polyterpene resins
A technology of trans-cinnamic acid ester and cinnamic acid diester, which is applied in the field of phase change ink composition, and can solve problems such as poor image firmness, image cracking, and poor scratch resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0071] ink preparation
[0072] The ink compositions can be prepared by any desired or convenient method. For example, the components of the ink vehicle may be mixed together and the mixture subsequently heated to at least its melting point. The colorant may be added before the ink composition is heated or after the ink composition is heated. The molten mixture can optionally be milled in an attritor, ball mill, or media mill, or subjected to high shear mixing to disperse the colorant in the ink vehicle. The heated mixture is then stirred to obtain a homogeneous molten ink, and the ink is then cooled to ambient temperature. The ink is solid at ambient temperature.
[0073] The nature of the ink
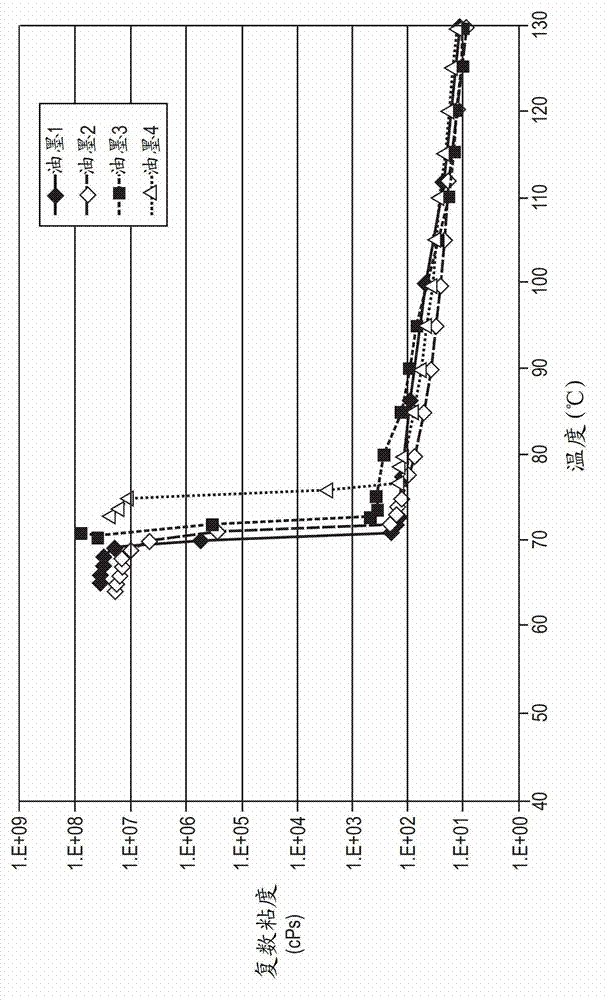
[0074] The melting and crystallization temperatures of phase change ink compositions can be determined by Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) using, for example, a TA Instruments Q100 apparatus, using a temperature gradient of heating and cooling of 10°C per minute and between...
Embodiment I
[0113] Synthesis of Butane-1,4-trans-Cinnamate
[0114]
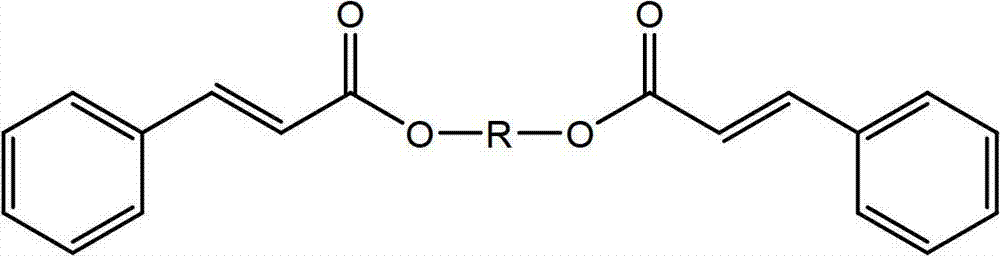
[0115]To a 500 mL three-neck round bottom flask equipped with a Dean-Stark trap and condenser, thermocouple and argon inlet was added trans-cinnamic acid (100 g, 674 mmol, purchased from Sigma-Aldrich), 1 , 4-butanediol (30.4 g, 337 mmol, purchased from Sigma-Aldrich) and FASCAT 4201 dibutyltin oxide catalyst (0.12 g, 0.1 wt%, purchased from Arkema Inc.). The mixture was heated slowly to 120°C under argon, during which time the trans-cinnamic acid melted. The temperature was then increased to 180°C and condensation started at about 150°C. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight (about 20 hours) at 180°C. Subsequently, vacuum (1-2 mmHg) was applied for about 20 minutes. A total of 5.3 ml of water was collected in the Dean-Stark trap. The reaction mixture was cooled to about 100°C under argon and drained into an aluminum pan and cooled to room temperature to yield 110 g of product as an off-white solid. The p...
Embodiment II
[0117] Synthesis of propane-1,3-trans-cinnamate
[0118]
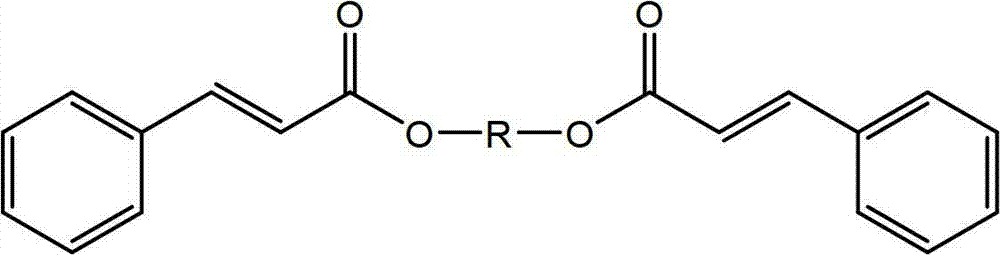
[0119] The procedure of Example 1 was repeated except that 1,4-butanediol was replaced with 1,3-propanediol. T 熔融 (DSC)=89.9°C; T 结晶 (DSC) = 72°C (measured by DSC at 5°C / min).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| crystallization temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melt viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com