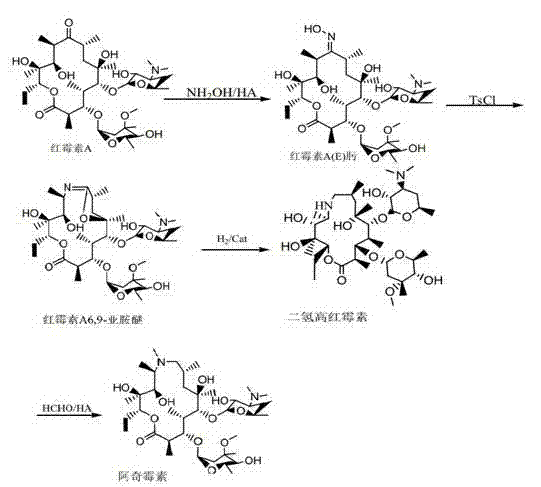
One-pot process for preparing azithromycin
A technology of azithromycin and process method, which is applied in the field of preparation of azithromycin, can solve problems such as low yield, cumbersome operation, and harsh reaction conditions, and achieve the effects of shortening production time, reducing procedures, and reducing the discharge of three wastes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] step one: Same as step 1 of the control example
[0024] Step two: Add 7.5g (0.110mol) sodium formate to the feed liquid, filter to remove the solid, dry the feed liquid under reduced pressure, add acetone 50ml, sodium formate 3.75g (0.0551mol), drop formaldehyde 8ml (0.1207mol), 5 ~ 8ml (0.1109mol ~0.1774mol) formic acid to adjust the pH to 4.5~5.0, keep it warm at 40°C for 24 hours, point the plate to monitor until there is no reductant residue, after the reaction is completed, adjust the pH to 10.2~10.7 with alkali, separate the layers after stirring, extract the water layer with 15ml acetone, Combine the acetone layers, add 300ml of water for crystallization, cool down to 20°C, filter with suction to obtain crude azithromycin, recrystallize from 50ml of acetone to obtain 25.12g (0.0320mol) of azithromycin dihydrate, calculated as erythromycin A6,9-imine ether, yield It was 77.9%, and the HPLC content was 98.07%.
Embodiment 2
[0026] step one: Same as step 1 of the control example
[0027] Step two: Add 3g (0.0441mol) sodium formate to the feed liquid, remove the solid by filtration, recover the feed liquid to dryness under reduced pressure, add acetone 60ml, formaldehyde 8ml (0.1207mol), sodium formate 9.7g (0.143mol), 5 ~ 8ml (0.1109mol ~ 0.1774 mol) formic acid to adjust the pH to 4.5-5.0, keep warm at 40°C for 24 hours, spot plate monitoring until no reducing substance remains, after the reaction is completed, adjust the pH to 10.2-10.7 with alkali, separate layers after stirring, extract the water layer with 15ml acetone, and combine the acetone layer, add 300ml of water for crystallization, lower the temperature to 20°C, and filter with suction to obtain crude azithromycin, recrystallize from 50ml of acetone to obtain 25.75g (0.0328mol) of azithromycin dihydrate, calculated as erythromycin A6,9-imine ether, the yield It was 79.8%, and the HPLC content was 97.79%.
Embodiment 3
[0029] step one: Same as step 1 of the control example
[0030] Step two: Add 9.7g of sodium formate (0.143mol) to the feed liquid, remove the solid by filtration, recover the feed liquid to dryness under reduced pressure, add 50ml of acetone, 8ml of formaldehyde (0.1207mol), 2.46g of sodium formate (0.0362mol), mol) formic acid to adjust the pH to 5.0-5.5, keep it warm at 40°C for 24 hours, point the plate to monitor until there is no reductant residue, after the reaction is completed, adjust the pH to 10.2-10.7 with alkali, separate the layers after stirring, extract the water layer with 15ml acetone, and combine the acetone After adding 300ml of water for crystallization, cool down to 20°C, suction filter to obtain crude azithromycin, recrystallize with 50ml of acetone to obtain azithromycin dihydrate, and dry under reduced pressure to obtain 24.85g (0.0317mol) of azithromycin. Calculated, the yield was 77.1%, and the HPLC content was 98.6%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com