Lubricating agent, friction pair and method for controlling friction coefficient between friction pair
A friction coefficient and lubricant technology, applied in the field of lubricants, friction pairs and the friction coefficient control between friction pairs, can solve the problems of metal friction parts prone to corrosion, easily corroded, aqueous solution precipitation reaction, etc., to achieve electrochemical stability The effect of wide potential window, stable electrochemical properties, and large load speed range
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach
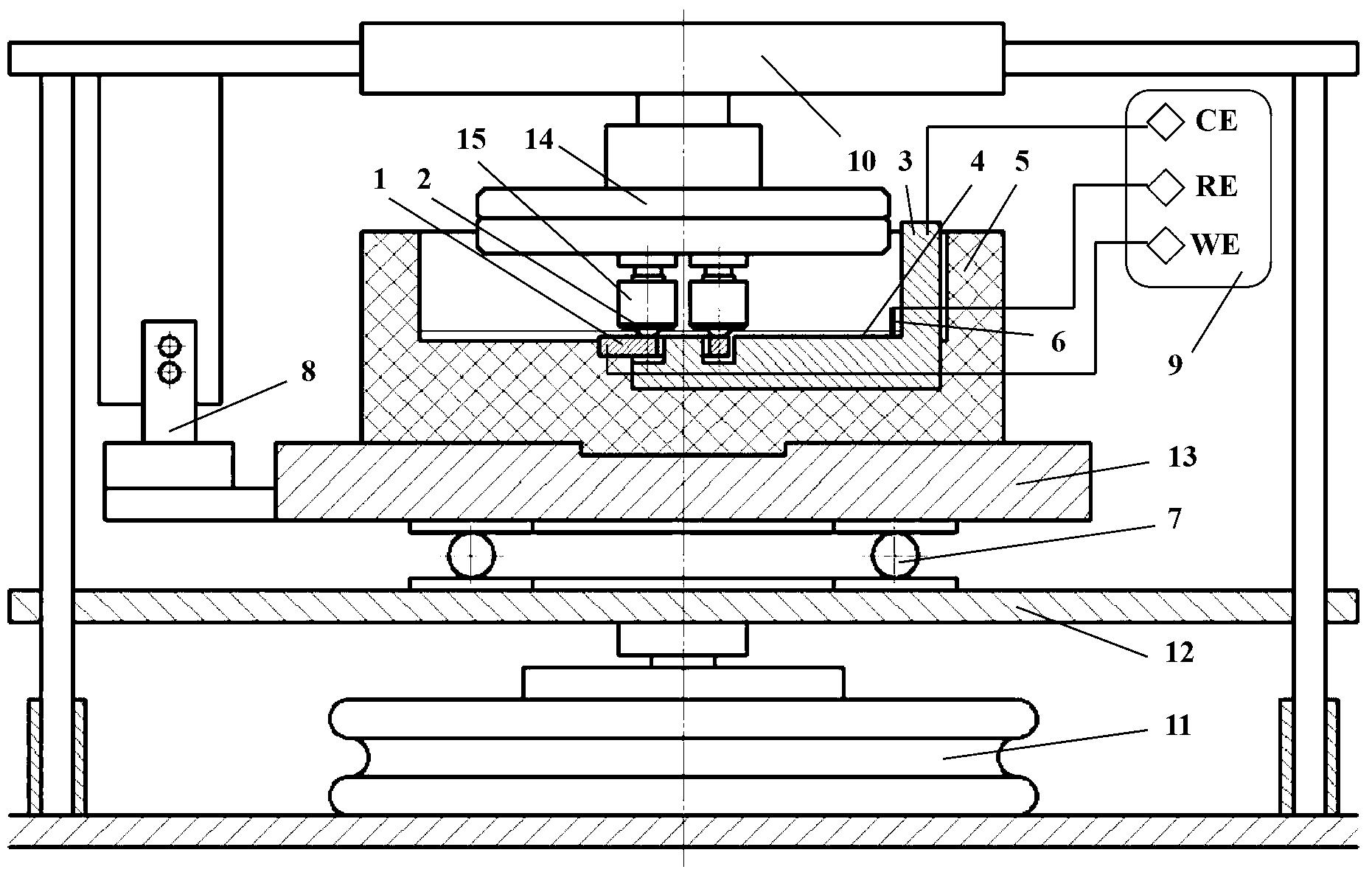
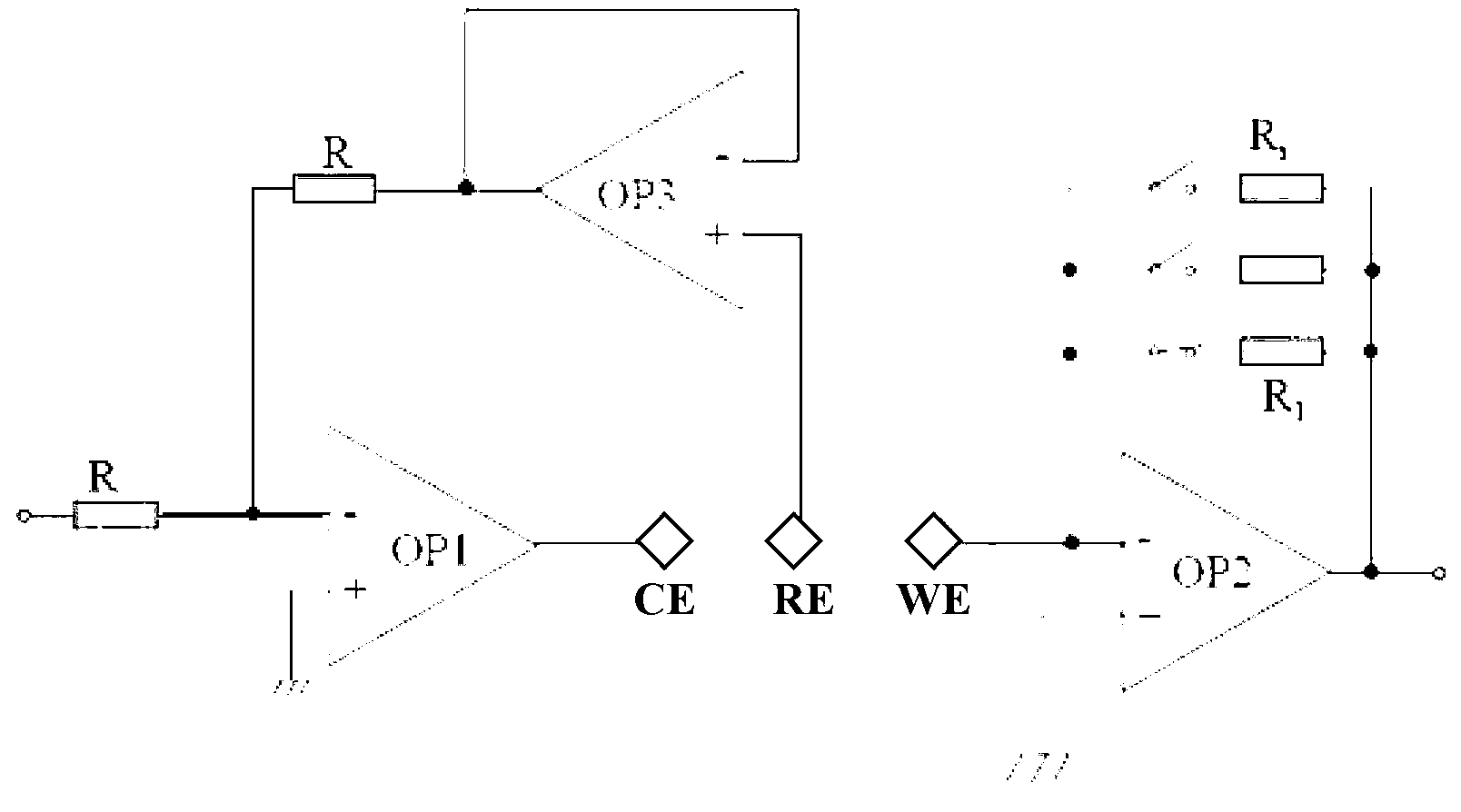
[0058] Such as figure 1 As shown, the device 1000 for implementing the method for controlling the friction coefficient between friction pairs of the present invention includes: a first friction member 1, a second friction member 2, a counter electrode 3, a lubricant 4, a lubrication pool 5, a reference electrode 6, Thrust ball bearing 7, force sensor 8, potentiostat 9, speed control system 10, loading device 11, lifting table 12, lubrication pool base 13, coupling 14 and clamp 15, of which 4 is lubricant, first friction The piece 1 and the second friction piece 2 form a friction pair.
[0059] Among them, the first friction piece 1 is a metal piece and serves as a working electrode, and the second friction piece 2 may be a ceramic or metal piece.
[0060] Specifically, the main components in the device and their connection relationship are as follows: the lower test piece of the friction pair, that is, the first friction piece 1 is a stainless steel disc, which is placed in the lub...
Embodiment 1
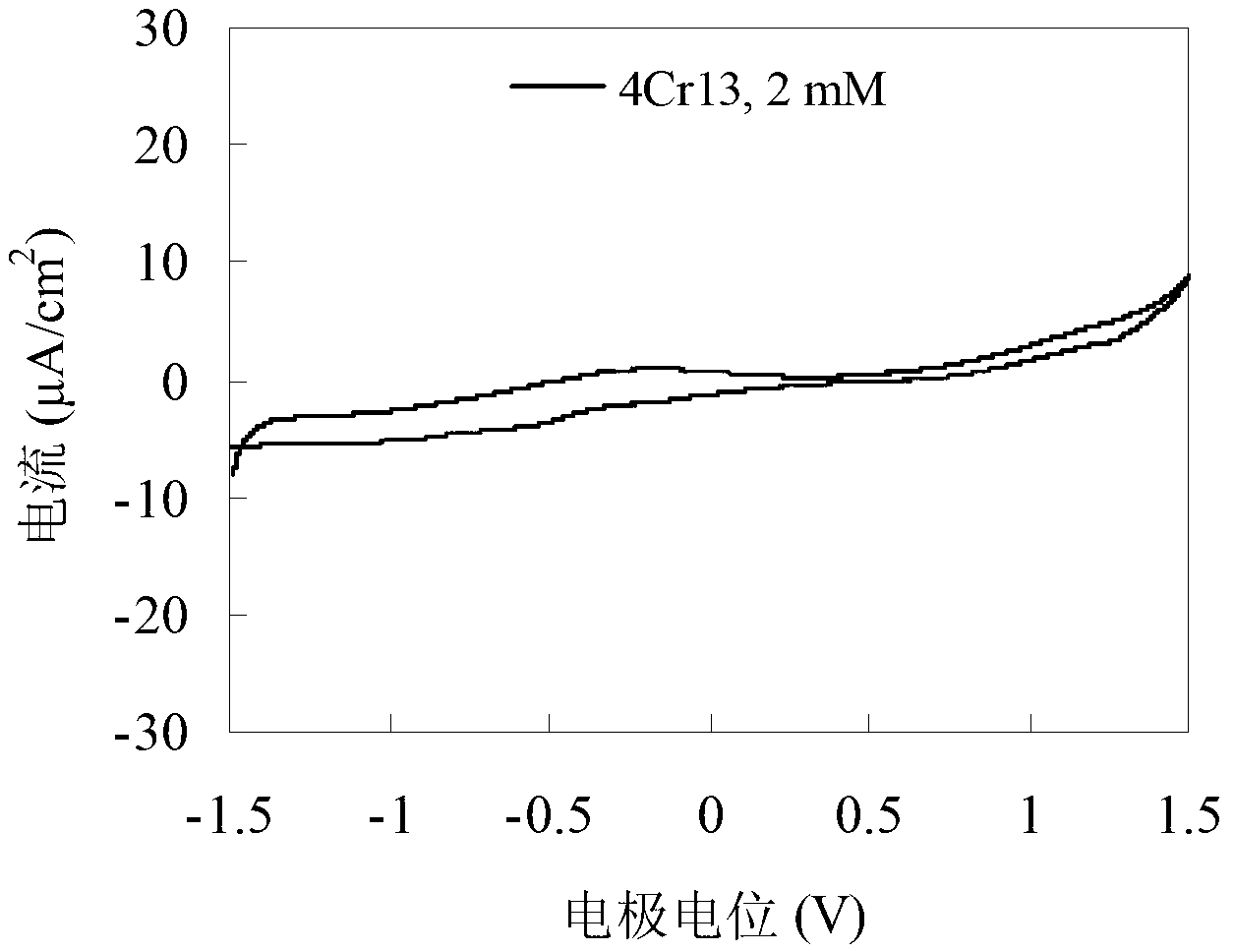
[0066] With reference to the above description of the specific embodiments of the method for controlling the friction coefficient between the friction pairs of the present invention, figure 1 The device shown is a platform that implements the method of controlling the friction coefficient between friction pairs of the present invention and detects the relationship between the friction coefficient and the electrode potential. Among them, such as figure 1 The first friction member 1 shown is a stainless steel (model 4Cr13) disc, the second friction member 2 is a zirconium dioxide ball (2 in total, with the same radius of gyration), and the lubricant 4 is sodium lauryl sulfate Propylene carbonate solution.
[0067] In this embodiment, the response result of the friction coefficient changing with the electrode potential is obtained, and the purpose of controlling the friction coefficient between the friction pairs is achieved. specifically, Figure 5 with Image 6 A schematic diagram...
Embodiment 2
[0070] Similarly, referring to the foregoing description of the specific embodiments of the method for controlling the friction coefficient between the friction pairs of the present invention, figure 1 The device shown is a platform that implements the method of controlling the friction coefficient between friction pairs of the present invention and detects the relationship between the friction coefficient and the electrode potential. Among them, such as figure 1 The first friction member 1 shown is a stainless steel (model 4Cr13) disc, the second friction member 2 is a zirconium dioxide ball (3 in total, with the same radius of gyration), and the lubricant 4 is sodium lauryl sulfate Propylene carbonate solution.
[0071] Figure 7-9 A schematic diagram of the response curve of the friction coefficient with the electrode potential of this embodiment is shown. among them, Figure 7 The working conditions involved are: the normal load of the friction pair is 500N, the rotation spee...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com