Method for removing hexavalent chromium in water
A hexavalent chromium and water removal technology, which is applied in chemical instruments and methods, water pollutants, adsorbed water/sewage treatment, etc., can solve problems such as limited adsorption capacity, and achieve the effect of low cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
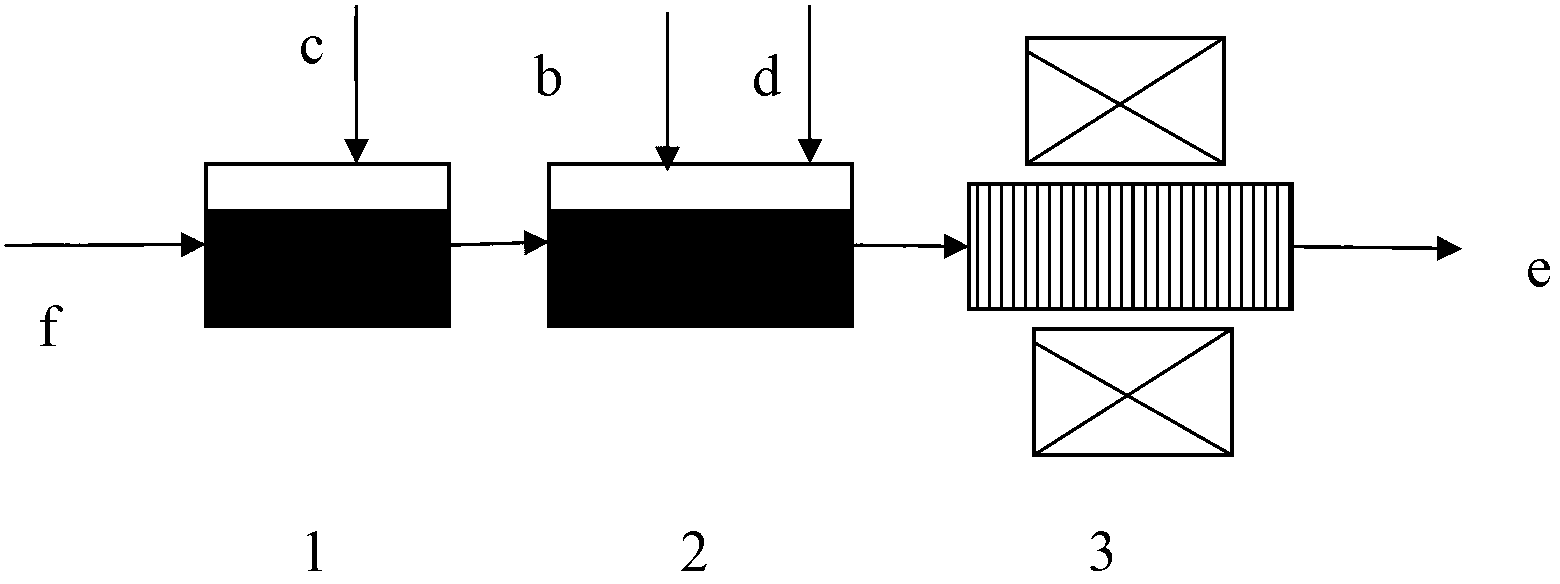
[0039] 1.1 Wash the corn stalks, dry them in an oven at 105° C. for 24 hours, crush and sieve to obtain corn stalks with a particle size of 300 μm.
[0040] 1.2 Mix 10g of citric acid, 55ml of distilled water and 10g of the crushed corn stalks obtained in 1.1, stir magnetically in a 55°C water bath for 24h, then evaporate to dryness at 50°C, dry at 110°C for 24h, and then wash with sodium hydroxide Neutralize and wash, and dry at 45° C. for 14 hours to obtain modified corn stalks.
[0041] 1.3 The concentration of hexavalent chromium in water containing hexavalent chromium is 4.2mg / L, enter the acid adjustment pool, adjust the pH value to less than 3.0 with hydrochloric acid, and enter the mixing pool after 10 minutes of reaction, add 2g / L of the improved solution obtained in 1.2 Corn stalks and magnetite powder 1.0g / L, after stirring for 2 hours, enter the superconducting separator, and use the superconducting separator to separate the reacted modified corn stalk adsorbent an...
Embodiment 2
[0043] 2.1 Wash the corn stalks, place them in an oven to dry at 105° C. for 24 hours, then crush and sieve to obtain corn stalks with a particle size of 300 μm.
[0044] 2.2 Mix 10g of citric acid, 55ml of distilled water and 10g of the crushed corn stalks obtained in 2.1 thoroughly, stir magnetically in a water bath at 55°C for 24h, then evaporate to dryness at 50°C, dry at 110°C for 24h, then wash with sodium hydroxide Neutralize and wash, and dry at 45° C. for 14 hours to obtain modified corn stalks.
[0045] 2.3 The concentration of hexavalent chromium in water containing hexavalent chromium is 7.0mg / L, enter the acid adjustment pool, adjust the pH value to less than 3.0 with hydrochloric acid, and enter the mixing pool after 10 minutes of reaction, add 2g / L2. 1.0g / L of modified corn stalks and magnetite powder, stirred and reacted for 2 hours, then entered the superconducting separator, and the reacted modified corn stalk adsorbent and magnetite powder were separated fro...
Embodiment 3
[0047] 3.1 Wash the corn stalks, place them in an oven to dry at 105° C. for 24 hours, and then crush and sieve to obtain corn stalks with a particle size of 300 μm.
[0048] 3.2 Mix 10g of citric acid, 55ml of distilled water and 10g of the crushed corn stalks obtained in 3.1 thoroughly, stir magnetically in a water bath at 55°C for 24h, then evaporate to dryness at 50°C, dry at 110°C for 24h, then wash with sodium hydroxide Neutralize and wash, and dry at 45° C. for 14 hours to obtain modified corn stalks.
[0049] 3.3 The concentration of hexavalent chromium in the water containing hexavalent chromium is 14.7mg / L, enter the acid adjustment pool, adjust the pH value to less than 3.0 with hydrochloric acid, and after 10 minutes of reaction, enter the mixing pool, add 2g / L 3.2 of the improved 1.0g / L of modified corn stalks and magnetite powder, stirred and reacted for 2 hours, then entered the superconducting separator, and the reacted modified corn stalk adsorbent and magneti...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com