Time detection circuit, ad converter, and solid state imaging device
A time detection and circuit technology, which is applied in time-to-digital converters, analog-to-digital converters, electric solid-state devices, etc., to achieve the effect of shortening the operating time and reducing the current consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach )
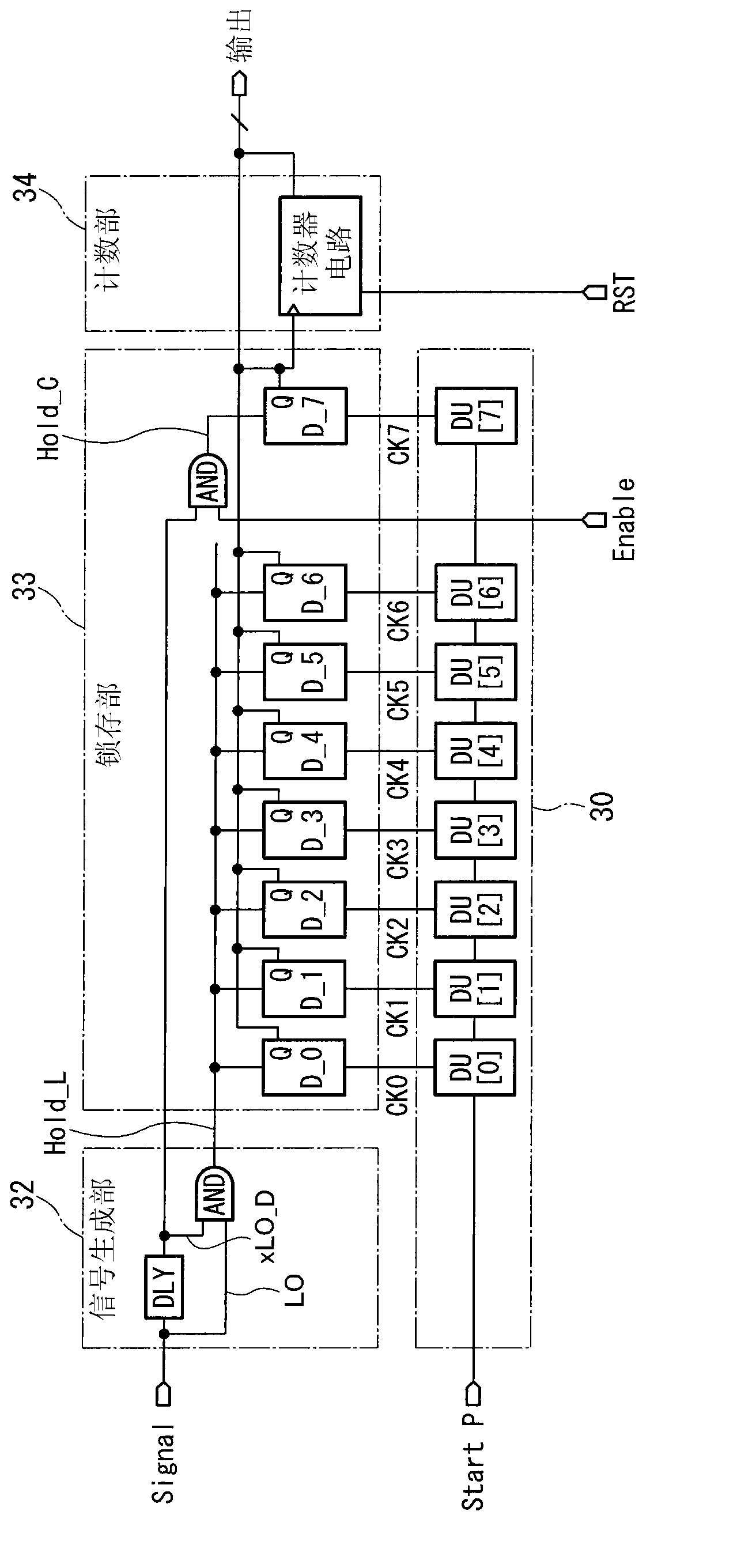
[0048] First, a first embodiment of the present invention will be described. figure 1 An example of the configuration of the time detection circuit of this embodiment is shown. Hereinafter, the configuration of this example will be described. figure 1 The shown time detection circuit is composed of a delay unit 30 , a signal generation unit 32 , a latch unit 33 , and a count unit 34 .
[0049] The delay unit 30 has a plurality of delay units DU[0] to DU[7] that delay an input signal and output it. Input the start pulse (=StartP) to the first delay unit DU[0].
[0050] The signal generation unit 32 generates control signals for controlling the operations of the latch unit 33 and the counter unit 34 . The signal generating section 32 has: an inversion delay circuit DLY that inverts and delays an analog signal Signal that is an object of time detection; and an AND circuit that outputs a signal that takes an input L0 (= Signal) and the logical product (AND) of the output xL0...
no. 2 approach )
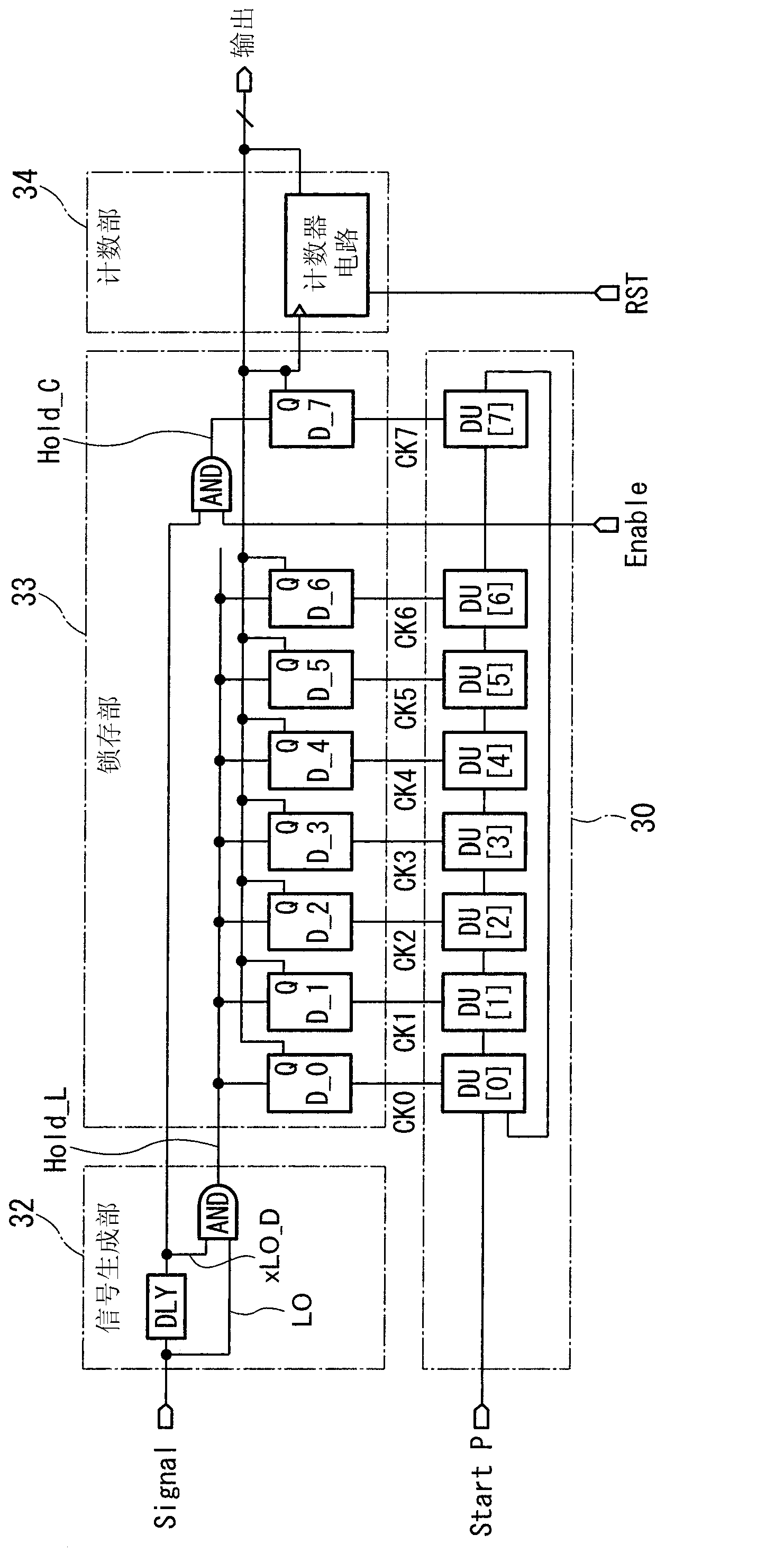
[0063] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. image 3 An example of the configuration of the time detection circuit of this embodiment is shown. The configuration diagram of this example will be described below. and figure 1 The structure shown in is different from the structure of the delay section 30 . In the present embodiment, a ring delay circuit is realized by connecting a plurality of delay units DU[*] (* is 0 to 7) constituting the delay unit 30 in a ring shape. In addition to figure 1 The same, so the description is omitted.
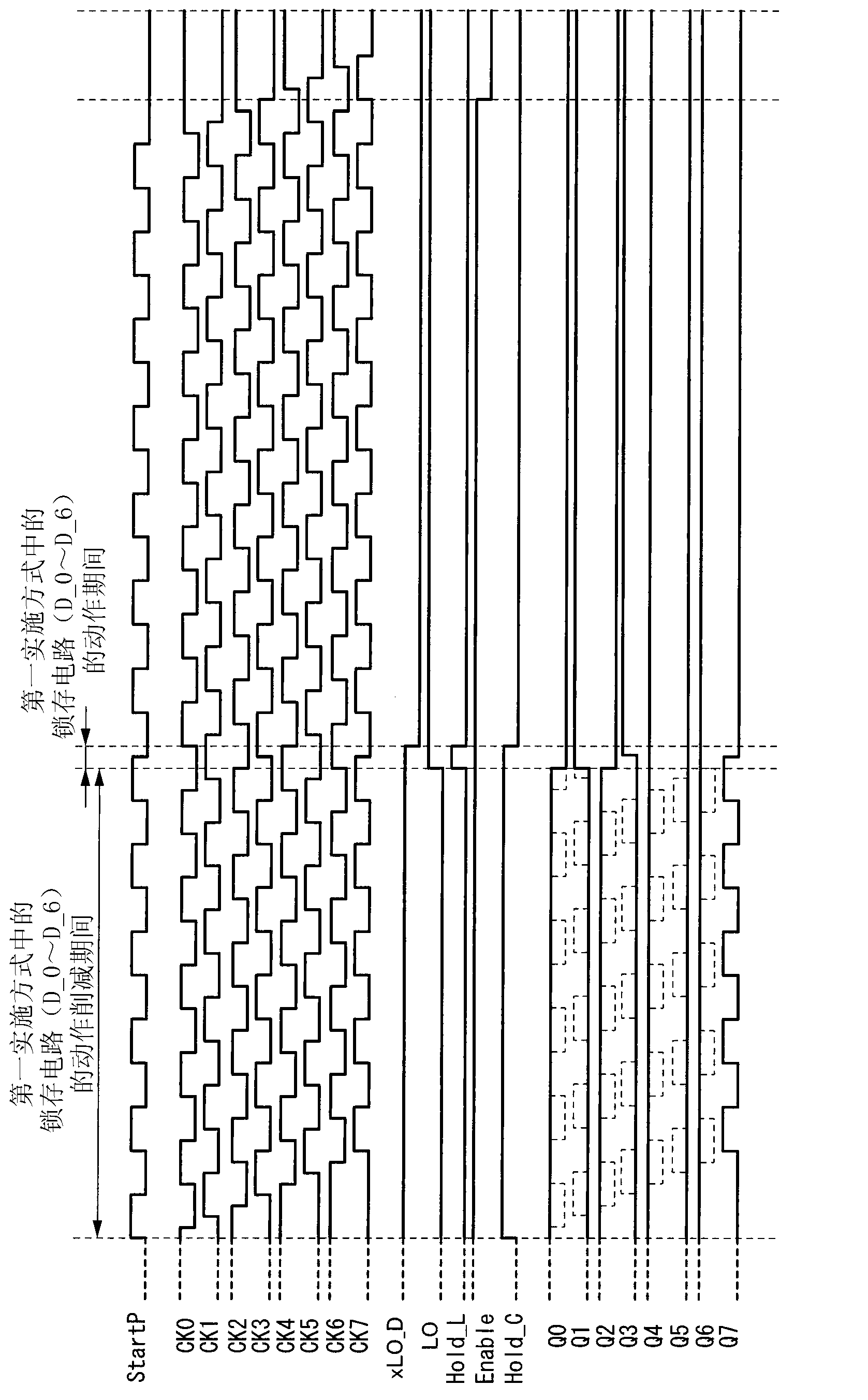
[0064] Next, the operation of this example will be described. Figure 4 The operation of the time detection circuit of this embodiment is shown. and figure 2 The difference is the start pulse (=StartP), the logic state of the start pulse (=StartP) changes from low level to high level, thus, the delay part 30 starts to operate, and according to the output CK7 from the delay part 30, The counting operatio...
no. 3 approach )
[0067] Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. Figure 5 An example of the configuration of the time detection circuit of this embodiment is shown. Hereinafter, the configuration diagram of this example will be described. exist Figure 5 The illustration of the delay unit 30 is omitted. and image 3 The structure shown in is different in that a comparison unit 31 is added. The comparator 31 is composed of a voltage comparator which receives an analog signal Signal which is the object of time detection and a ramp wave Ramp which increases or decreases with the passage of time, and outputs a signal indicating a comparison between the analog signal Signal and the ramp wave Ramp. signal of the result. Thus, a time interval corresponding to the analog signal Signal (equivalent to figure 2 "Detected time" in the description of the ). In addition to image 3 The same, so the description is omitted.
[0068] Next, the operation of this example wi...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com