Power semiconductor device with antistatic discharge capacity and manufacturing method
A power semiconductor and discharge capability technology, applied in semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturing, semiconductor devices, electric solid-state devices, etc., can solve the problems of complex formation and increase cost, and achieve design flexibility, cost reduction, and improvement of ESD capability. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
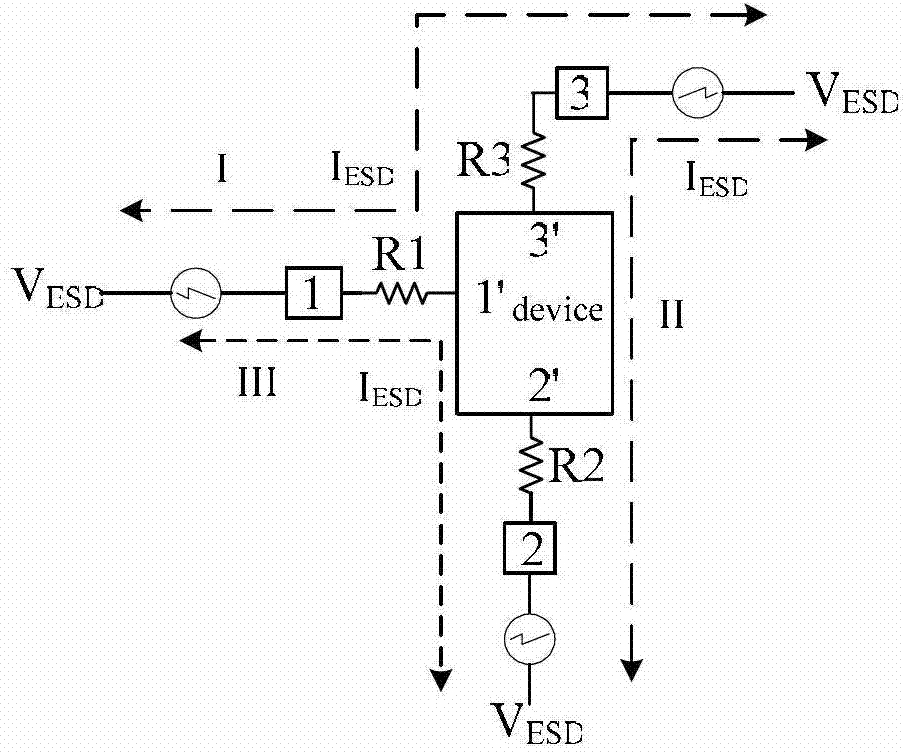
[0053] Figure 3 to Figure 5It shows that the present invention provides a power semiconductor device with anti-static discharge capability, and the gate terminal is connected in series with strip resistors to form a circular array layout structure of the gate.
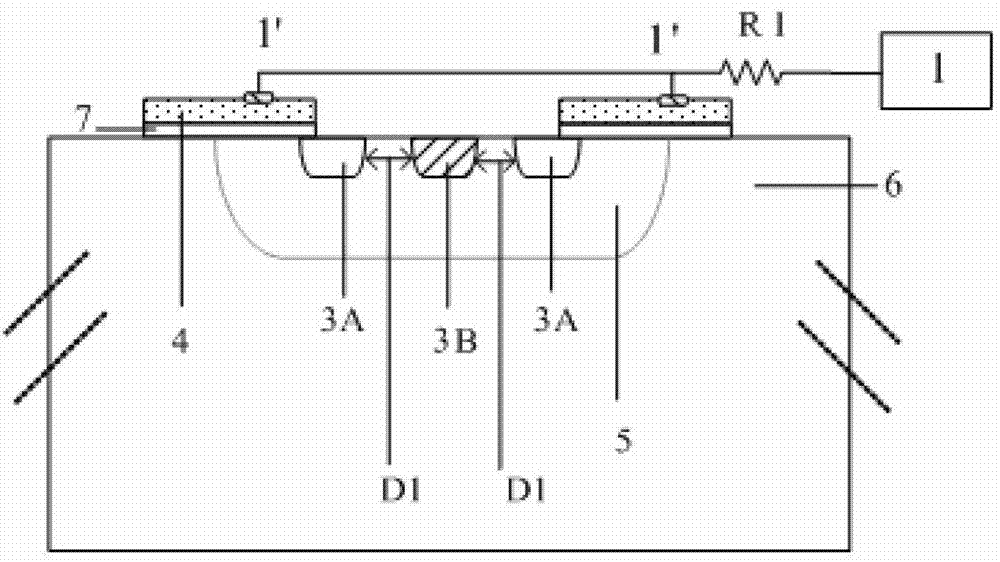
[0054] Such as Figure 3 to Figure 5 As shown, the steps for forming each of the cells 8 are as follows: provide an epitaxial layer (not shown in the figure, please refer to Figure 2A to Figure 2C In the mark 6); form a second-type lightly doped region in the epitaxial layer (not shown in the figure, please refer to Figure 2A to Figure 2C Mark 5 in the above); on the epitaxial layer, a gate dielectric layer is sequentially formed from bottom to top (not shown in the figure, please refer to Figure 2A to Figure 2C Mark 7) and the first polysilicon strip 4; etch the first polysilicon strip 4 and the gate dielectric layer to expose the second-type lightly doped region; in the second-type lightly doped A first type h...
Embodiment 2
[0061] Figure 8 to Figure 9 Shown is the circular array layout structure of the source terminal of the power semiconductor device with anti-static discharge capability of the present invention, which is connected in series with strip resistors to form the source.
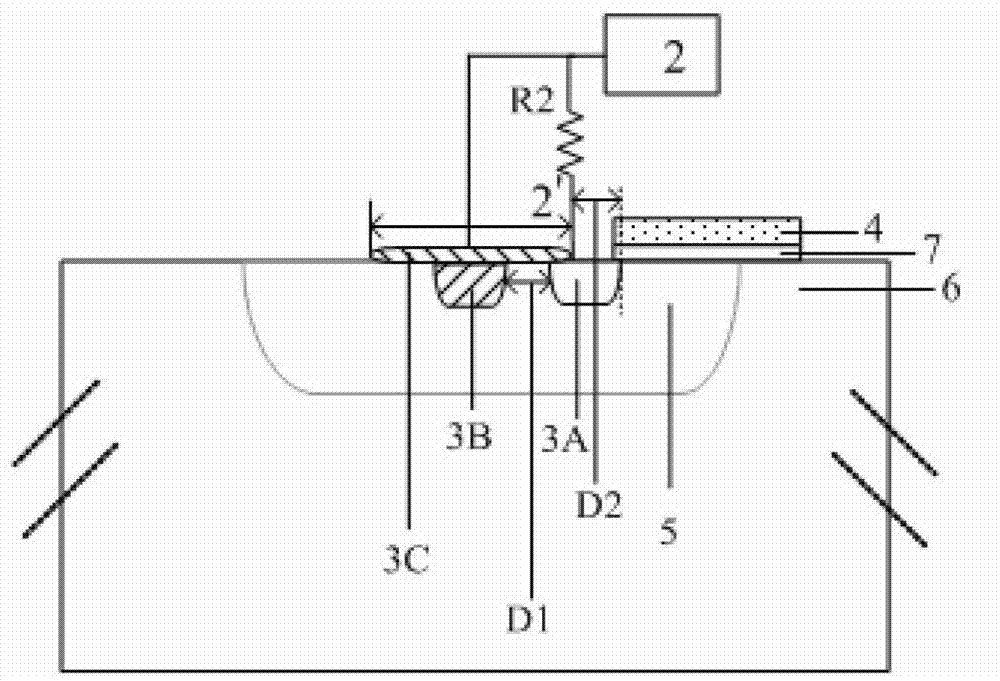
[0062] Such as Figure 8 and 9 As shown, the steps for forming each of the cells 8 are as follows: provide an epitaxial layer (not shown in the figure, please refer to Figure 2A to Figure 2C In the mark 6); form a second-type lightly doped region in the epitaxial layer (not shown in the figure, please refer to Figure 2A to Figure 2C Mark 5 in the above); on the epitaxial layer, a gate dielectric layer is sequentially formed from bottom to top (not shown in the figure, please refer to Figure 2A to Figure 2C Mark 7) and the first polysilicon strip 4; etch the first polysilicon strip 4 and the gate dielectric layer to expose the second-type lightly doped region; in the second-type lightly doped A first type hea...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Figure 12 The difference between the illustrated embodiment and the first and second embodiments is to provide a circular array layout structure in which the gate terminal and the source terminal of the power semiconductor device with anti-static discharge capability are simultaneously connected in series with resistors to form the gate and source.
[0073] In this embodiment, the changed embodiment 1 can be combined with the layout structure of embodiment 2 to form Figure 12 . The content of the changes in the first embodiment is as follows: a first port 1' is provided on the second polysilicon strip 4', and a second port 1' is provided on the second polysilicon strip 4' other than the first port 1' The gate 1 is formed, and the second polysilicon strip 4 ′ is a resistor R1 connected to the first port, and the first port 1 ′ has no direct electrical connection with the gate 1 . Then, the size of the resistor R1 connected in series with the gate terminal can be adju...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com