Method for measuring heat consuming user heating load of vertical single tube cocurrent type system and heating metering distributing system of vertical single tube cocurrent type system
A heat supply and heat user technology, applied in the field of heating metering and distribution systems, can solve the problems of difficult heat metering renovation of vertical single-pipe downstream systems in buildings, and achieve the effects of simple and easy renovation, less disturbance to residents, and low renovation cost.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
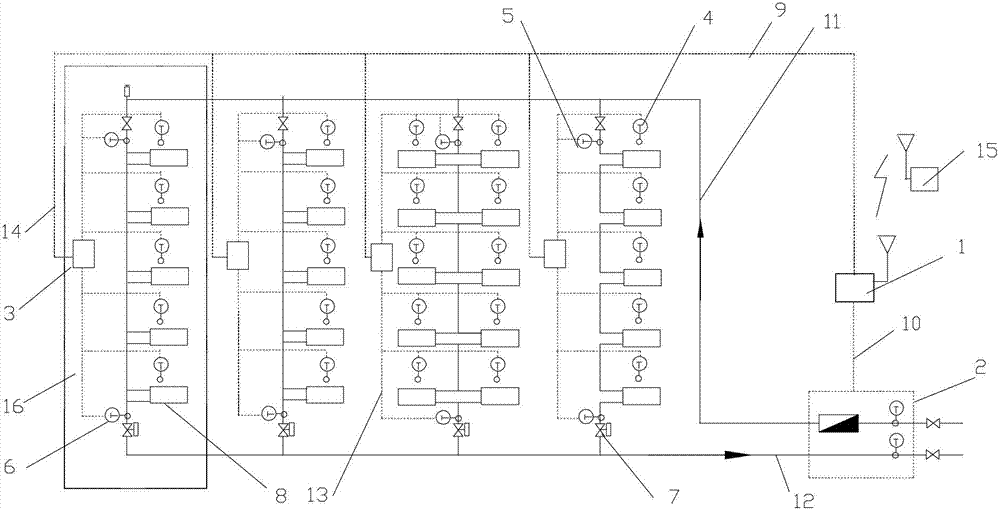
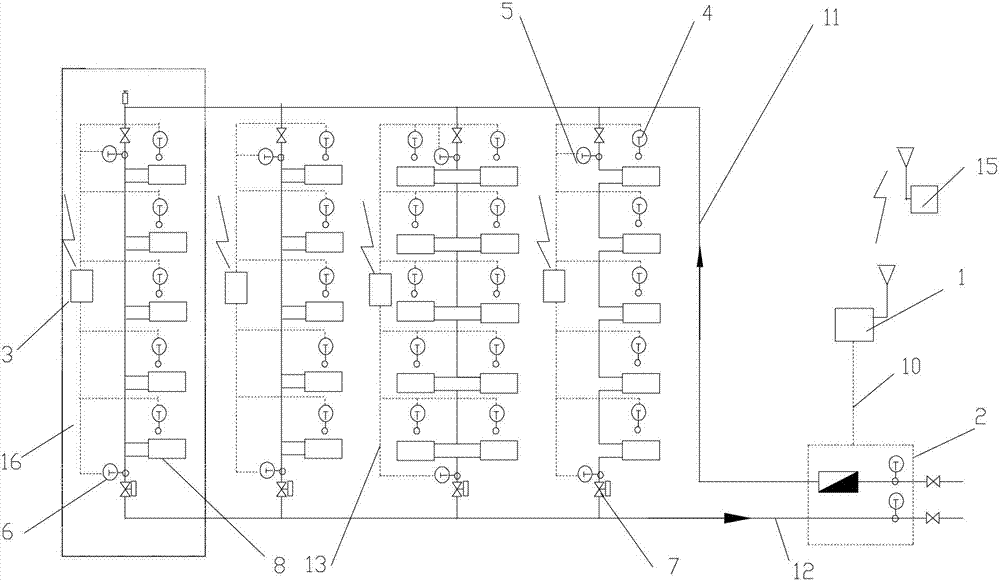
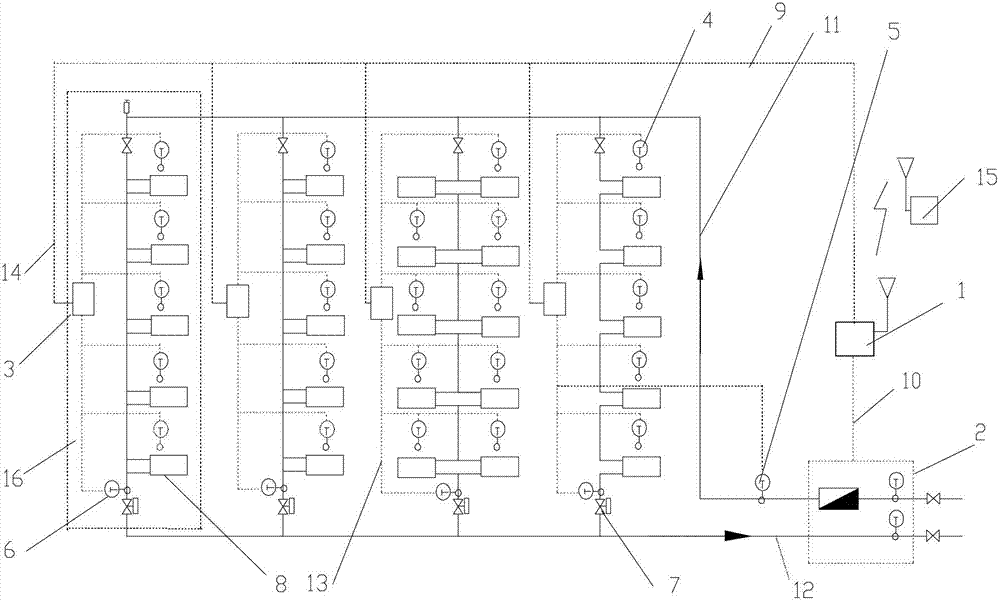
[0064] Specific implementation mode one: see Figure 5 To illustrate this embodiment, the specific calculation process of the method for measuring the heat supplied to users in a vertical single-pipe downstream system described in this embodiment is:
[0065] Step 1, collect the total heat supply of the building through the heat meter;
[0066] Step 2, collect the actual room temperature of each user in the building through the room temperature sensor installed in each household;
[0067] Step 3, collect the water supply temperature of the standpipe through the water supply temperature sensor arranged at the uppermost end of each standpipe of the heating system;
[0068] Step 4: Collect the return water temperature of the standpipe through the return water temperature sensor at the bottom of each standpipe in the heating system;
[0069] Step 5, by adjusting the opening of the flow controller arranged on each standpipe, the heating system is adjusted to balance, and the flow...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0077] Embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and the method for measuring the heat supply of heat users in the vertical single-pipe downstream system described in Embodiment 1 is that the calculation of the heat supply of each standpipe in the step 8 The method is:
[0078] For a building with m risers, where m is a natural number greater than 1, the characteristic coefficient a of riser i calculated according to step 7 i The value is calculated according to the formula (5), i is the serial number of the riser, and i is any natural number less than or equal to m,
[0079] Q ij =a i x ij (5)
[0080] In the formula:
[0081] Q ij Indicates the heat supply of standpipe i under working condition j, the unit is KJ;
[0082] a i Indicates the characteristic coefficient a value of riser i;
[0083] x ij Indicates the unit heat dissipation of the radiator on the riser i under the j working condition, which is determined according to the temperature di...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0085] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and the method for measuring the heat supply of heat users in the vertical single-pipe downstream system described in Embodiment 1 is that the method for calculating the flow rate of each standpipe in the above step 9 is as follows: :
[0086] According to the water supply temperature, return water temperature and heat supply of standpipe i obtained in step 3, step 4 and step 8 in working condition j, the flow rate of standpipe is calculated according to formula (6),
[0087] G ij = Q ij c ( t ijg - t ijh ) - - - ( 6 )
[0088] In ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com