Antibodies against the ectodomain of ErbB3 and uses thereof
An extracellular domain and structural domain technology, applied in the field of antibodies against the extracellular domain of ErbB3 and its application, can solve the problems that ErbB3 has not been taken seriously
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0300] Example 1: Preparation of Antibodies Using Phage Display
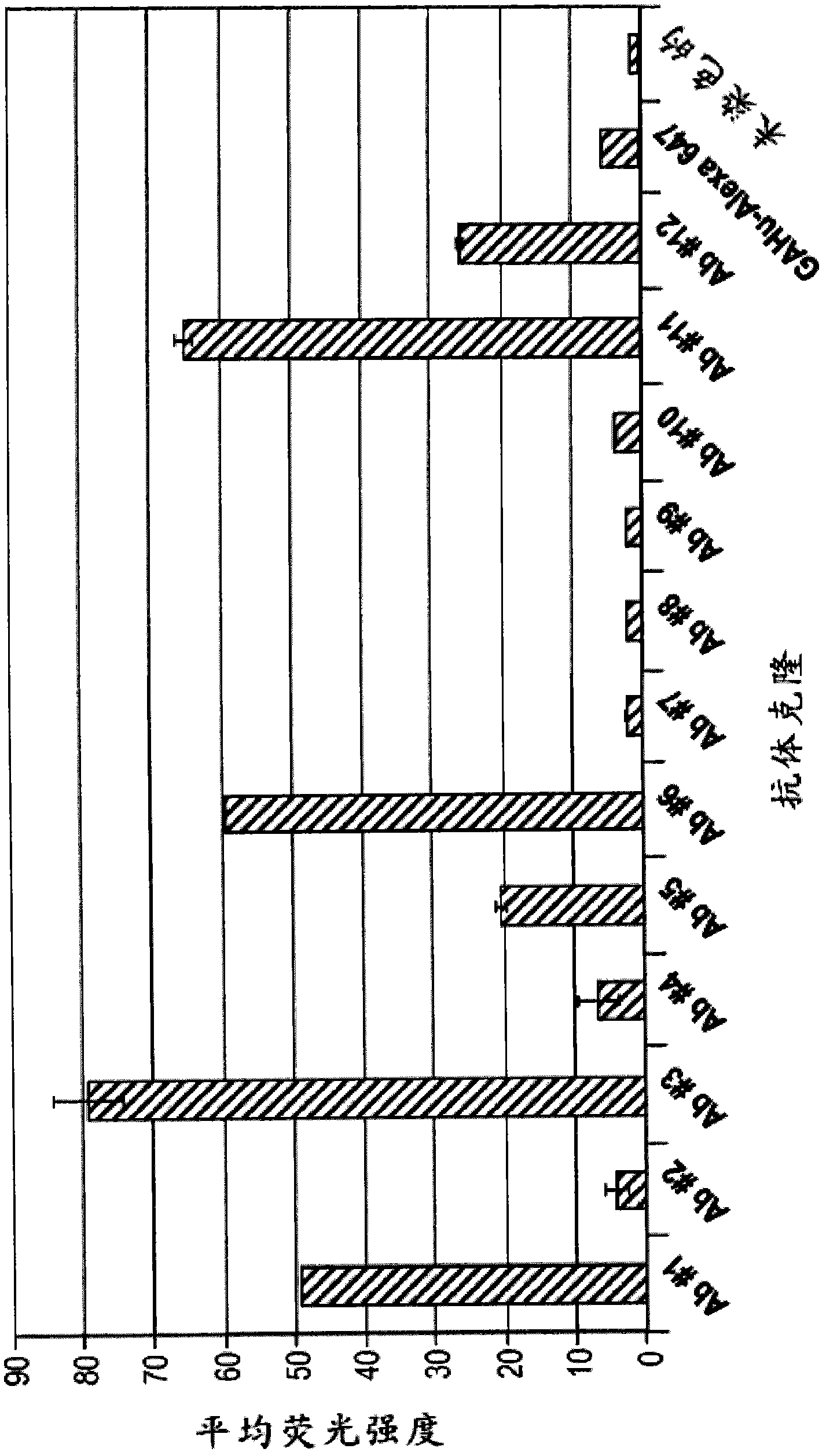
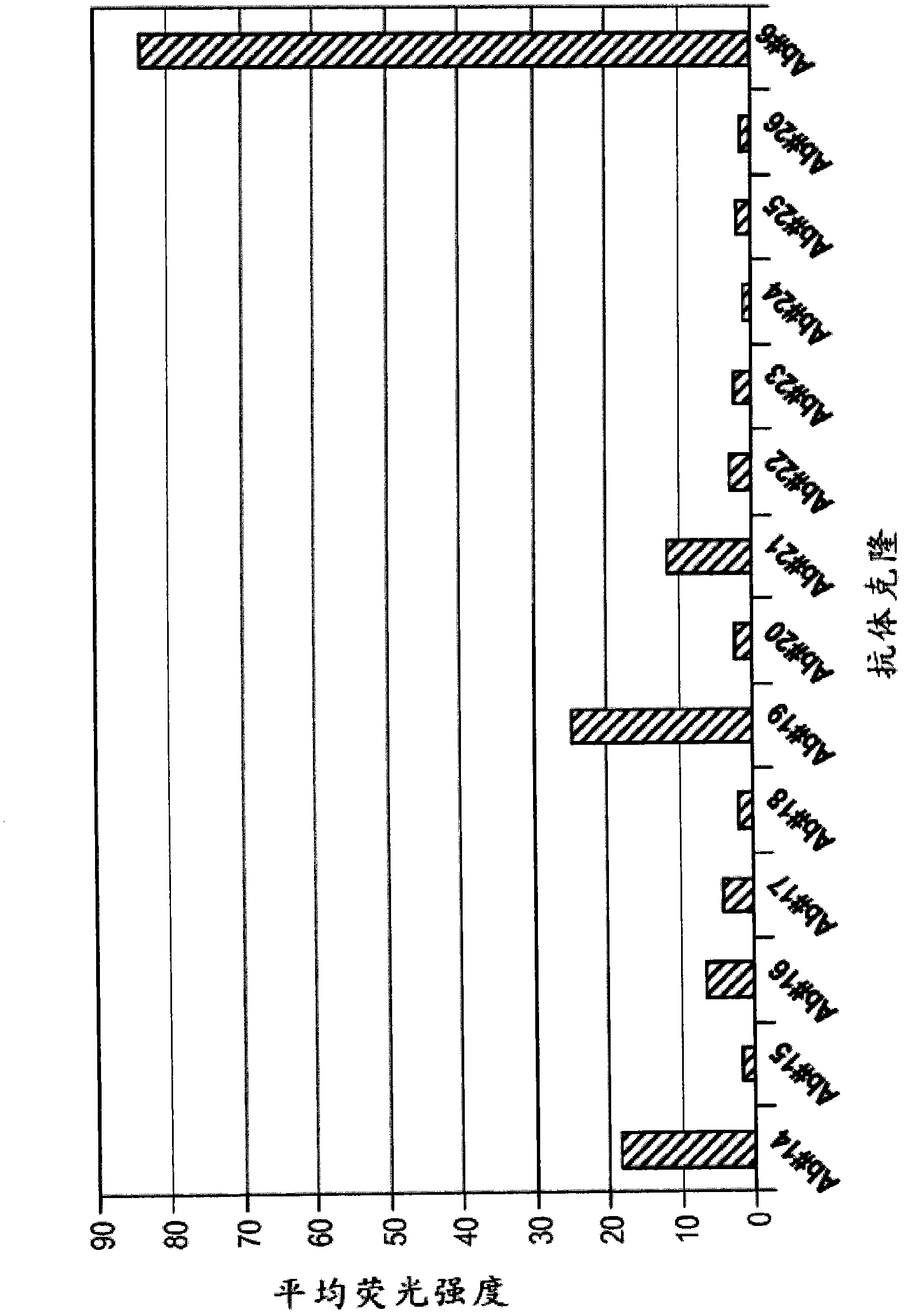
[0301] To obtain human anti-ErbB3 antibodies referred to herein as Ab #6, Ab #3, Ab #14, Ab #17, and Ab #19, human Fab phage containing a unique combination of immunoglobulin sequences from a human donor library (Hoet et al., supra) for initial screening of ErbB3 binders.
[0302] Using purified ErbB3 and a Chinese Hamster Ovary (CHO) cell line expressing cell surface ErbB3, 73 unique Fab sequences (obtained using the method described above or slight variations thereof) were identified from the library. These 73 clones were then reformatted into phage-free Fabs only. Using high-throughput methods, these Fabs were expressed on a small scale and tested for binding using ELISA and FLEXCHIP methods, which are a high-throughput surface plasmon resonance (SPR) technique. Phage-free 73 Fabs were spotted on the chip surface and binding kinetics and epitope blocking to ErbB3-his fusion target protein or ErbB3-Fc prot...
Embodiment 2
[0304] Example 2: Optimization of Anti-ErbB3 Fab
[0305] Following the identification of Fabs that block the binding of the ErbB3 ligand (neuretonin) to ErbB3, the following codon optimization was performed on the VH and VL sequences of the Fabs.
[0306] VH and VL regions were rearranged using expression constructs expressed as IgGl or IgG2 isotypes. This construct includes a SELEXIS backbone with expression cassettes for replacement of the appropriate heavy and light chain sequences. The SELEXIS vector contains the CMV promoter and matching poly-A signal.
[0307] The VH and VL nucleic acid sequences of codon-optimized Ab #6 (obtained using the method described above or slight variations thereof) are shown in SEQ ID NO: 25 and 26, respectively, and those sequences of Ab #3 are shown in SEQ ID NO: 27 and 28, as shown in Figure 22.
Embodiment 3
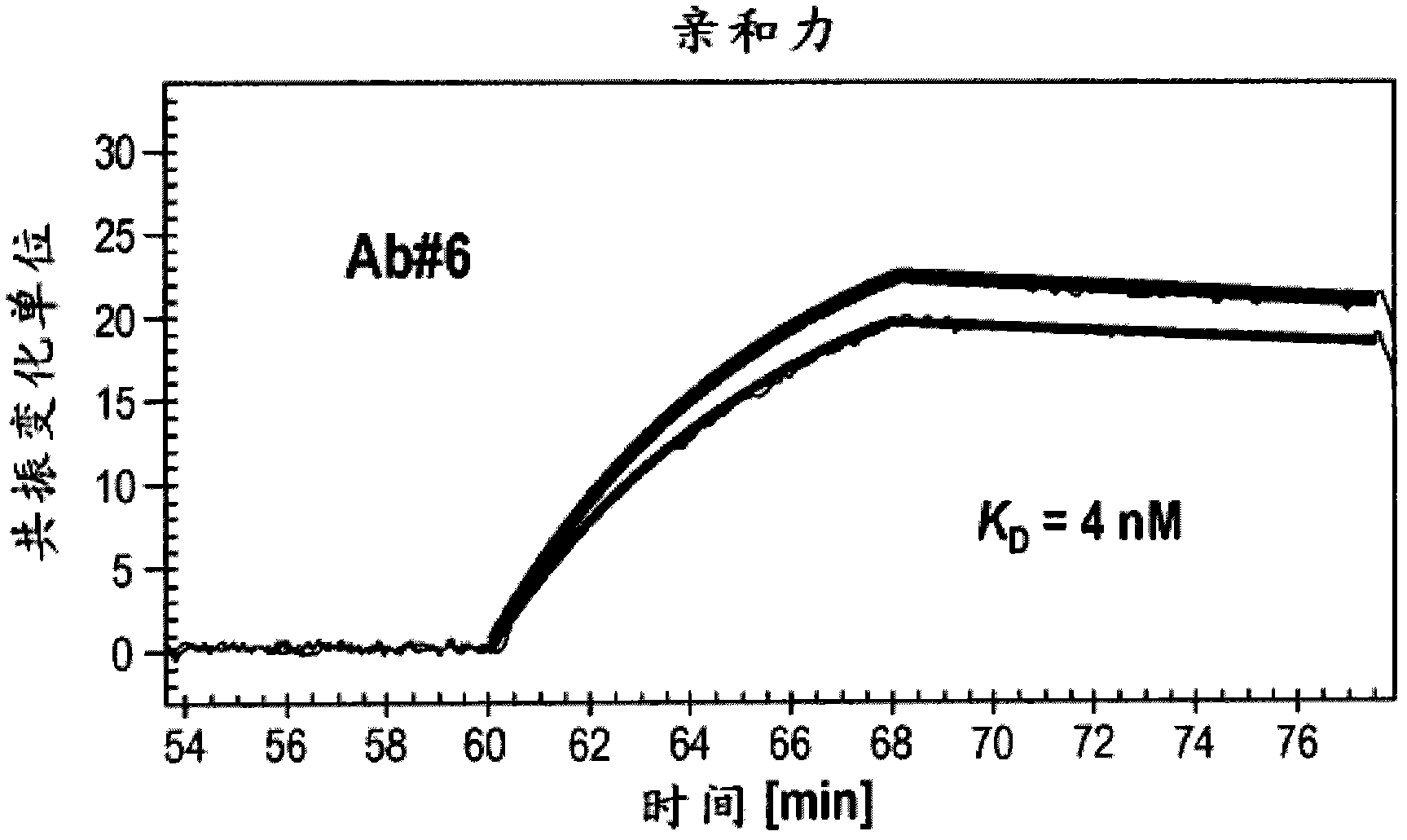
[0308] Example 3: Binding affinity of ErbB3
[0309] The dissociation constants of anti-ErbB3 antibodies were measured using two independent techniques, surface plasmon resonance analysis and cell binding assay using MALME-3M cells.
[0310] Surface Plasmon Resonance Analysis
[0311] Surface plasmon resonance analysis (e.g. FLEXCHIP analysis) was generally performed on a BIACORE 3000 instrument, etc., as described in Wassaf et al. ). Based on formula K D =K d / K a to calculate K D value.
[0312] K of Ab #6 and Ab #3 measured using the method described above or a slight variation thereof using surface plasmon resonance analysis D The values are shown in Figure 2A and 2B middle. K of Ab #6 D Values are shown as approximately 4nM, K for Ab #3 DValues are shown to be approximately 8nM. Furthermore, surface plasmon resonance indicated that Ab #6 competes with HRG for binding to ErbB3.
[0314] Perform cell binding assay to d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| affinity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com