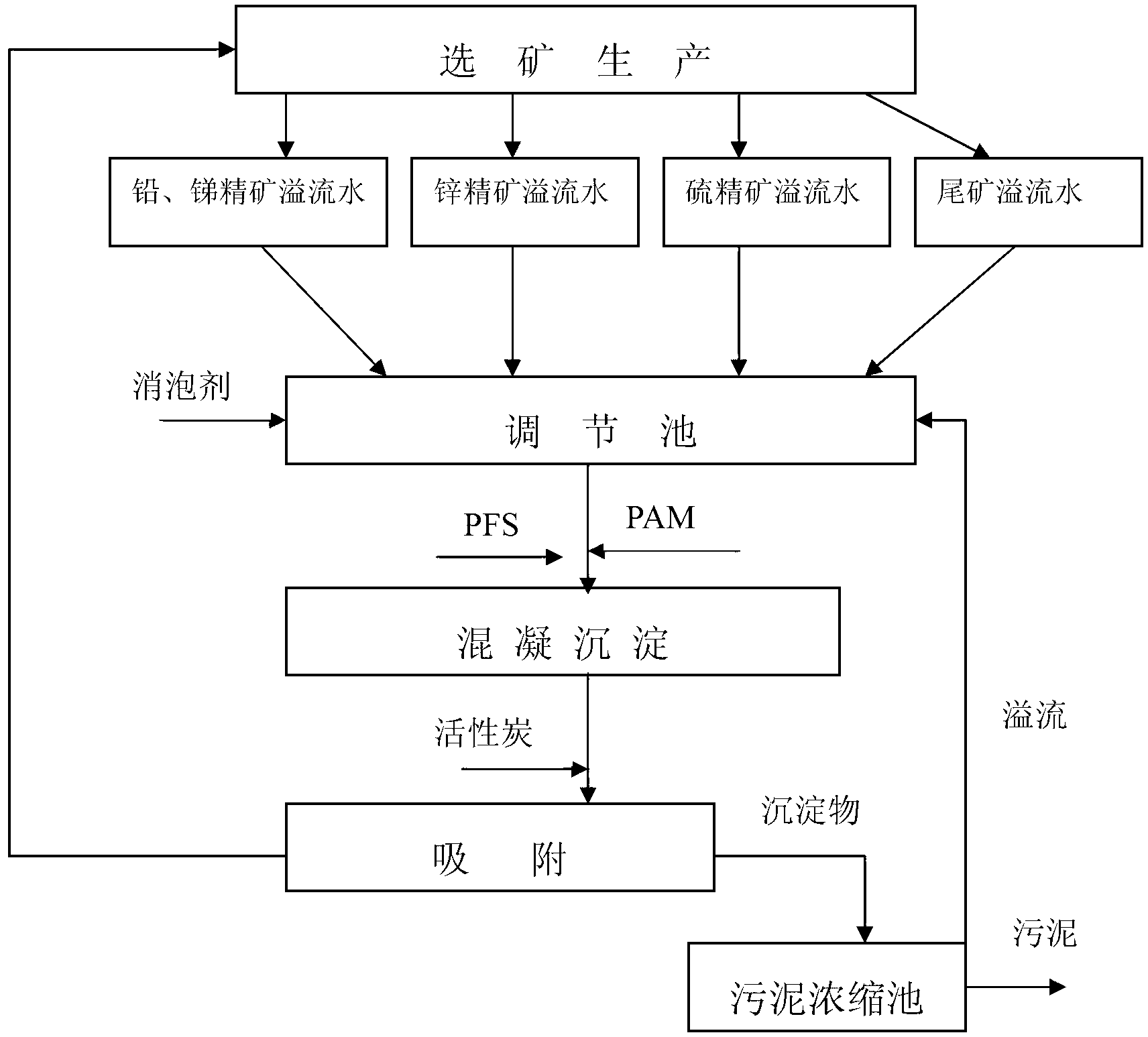
In-process circular and comprehensive recovery technology for mineral processing wastewater of tin-lead-zinc polymetallic sulphide ores
A mineral processing wastewater and polymetallic technology, which is applied in mining wastewater treatment, energy wastewater treatment, chemical instruments and methods, etc., can solve the problems of large consumption of reagents, incomplete decontamination, secondary pollution, etc., and achieve good results and high production efficiency The effect of producing less mud and slag and occupying less land
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
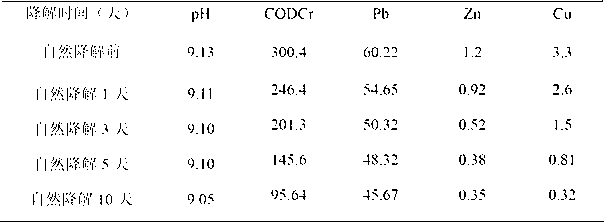
[0037] The tailings water is directly flowed from the concentrator to the tailings pond. After natural purification and degradation of various chemicals in the tailings pond, the water quality tends to be stable, and then it is pumped into the high-level pool and enters the mineral processing system. The natural settlement water quality analysis of tailings overflow water in the tailings pond is shown in Table 7-1.
[0038] Table 1: Water quality analysis results before and after natural degradation (mg / L)
[0039]
[0040] The tailings water was naturally placed for several days, and the water quality was analyzed before and after the placement. The results are shown in Table 7-1. It can be seen from Table 7-1 that after natural purification and degradation, heavy metal ions in tailings water can remove Pb 2+ In addition, there has been a decline.
Embodiment 2
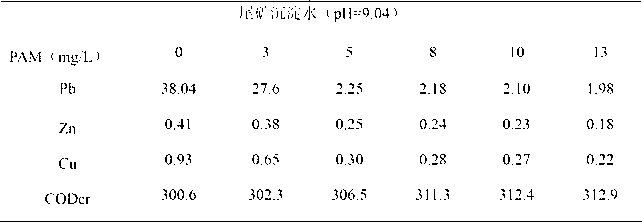
[0042] The organic polymer coagulant PAM was used for the sedimentation test, and PAM was added as the coagulation and sedimentation agent. Under the condition of the current pH of the tailings sedimentation water = 9.10, the dosage experiment of PAM was carried out respectively. The experimental results are shown in Table 7-2.
[0043] Table 2: Effect of PAM dosage on coagulation and sedimentation effect
[0044]
[0045] It can be seen that with the increase of the amount of PAM, the indicators of the water samples have been significantly improved, the concentration of Pb in the sedimentation water decreased from 38.04mg / L to 2.21mg / L; the concentration of Zn decreased from 0.41mg / L to 0.24mg / L ; Cu concentration decreased from 0.93mg / L to 0.28mg / L; CODcr increased slightly, which was due to the addition of organic coagulant PAM.
Embodiment 3
[0047] Add a certain amount of PAM to the tailings sedimentation water after natural precipitation, and then add a certain amount of granular activated carbon after coagulation and precipitation, and examine the influence of adsorption time and adsorbent dosage on the adsorption effect. The results are as follows: The amount of granular activated carbon has an effect on adsorption The test results of effect influence are shown in Table 3
[0048] Table 3: Influence of the amount of granular activated carbon on the adsorption effect
[0049]
[0050] It can be seen from Table 3 that after adding 100mg / L granular activated carbon and stirring with wastewater for 30 minutes, the Pb concentration and COD in the effluent Cr Respectively from 0.85mg / L and 168.5mg / L to 0.75mg / L and 80.2mg / L, all lower than the national discharge standards, while the foaming of wastewater has weakened. This shows that granular activated carbon is quite effective for secondary purification of waste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com