Process for producing tea extract
A manufacturing method and technology of tea extract, which is applied in tea extraction, tea, food science, etc., can solve the problems of reducing commodity value, and achieve the effect of high refreshment, high transparency, and rich aroma
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Example 1: Oolong Tea Extract (1)
[0062] (1) Manufacture of oolong tea extract
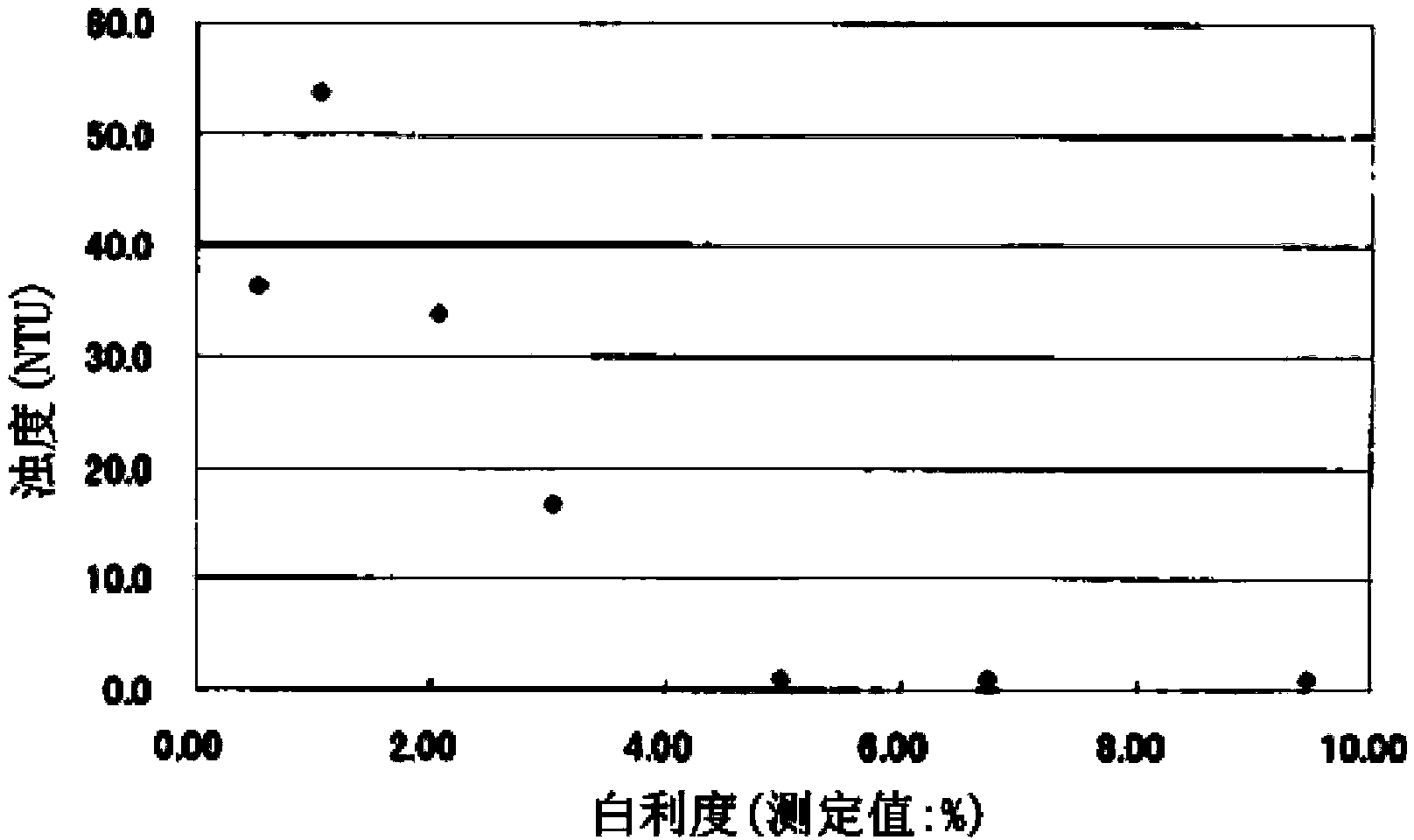
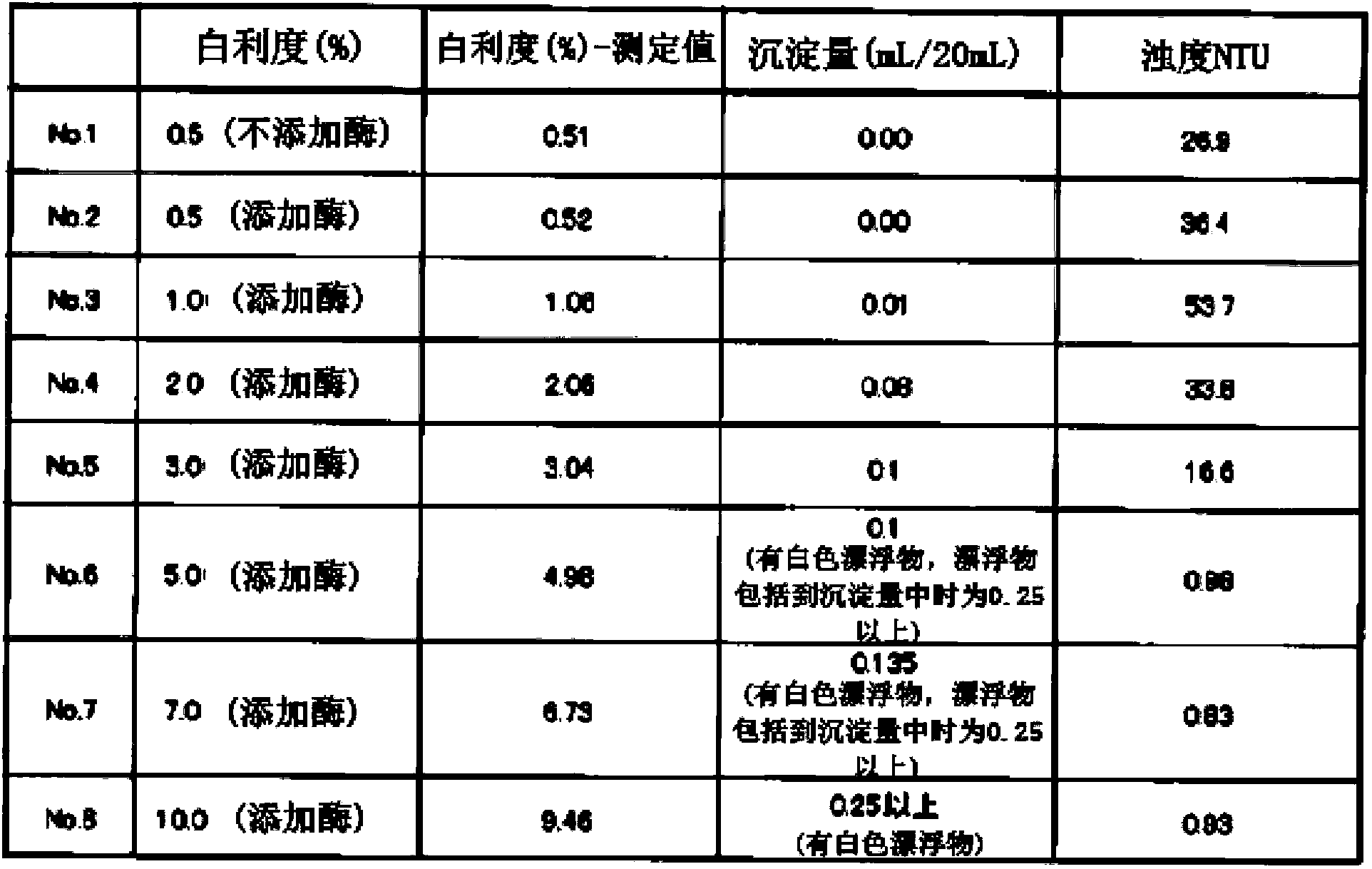
[0063] 100 g of oolong tea (Fujian Province, Sezhong) was extracted with 6000 mL of 90° C. ion-exchanged water for 15 minutes. After the obtained extract was roughly filtered with a 150-mesh metal filter, it was cooled to below 30°C to obtain an oolong tea extract (Brix 0.5, measured with a digital display refractometer RX-5000α manufactured by ATAGO, Japan. The following , used for the determination of Brix). Concentrate the extract to a Brix of 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 5.0, 7.0, 10.0 using a vacuum evaporation and concentration device to obtain a concentrate. A glycoside decomposing enzyme (β-glucosidase) preparation "Amano" (manufactured by Amano Enzyme Co., Ltd.) (β-glucoside Combination of 13% enzyme and 87% excipient. Source: Penicillium Multicolor, potency: β-glucosidase potency 800U / g or more), in a constant temperature room at 45°C for 3 hours enzyme treatment. After the enzyme treatm...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Example 2: Oolong Tea Extract (2)
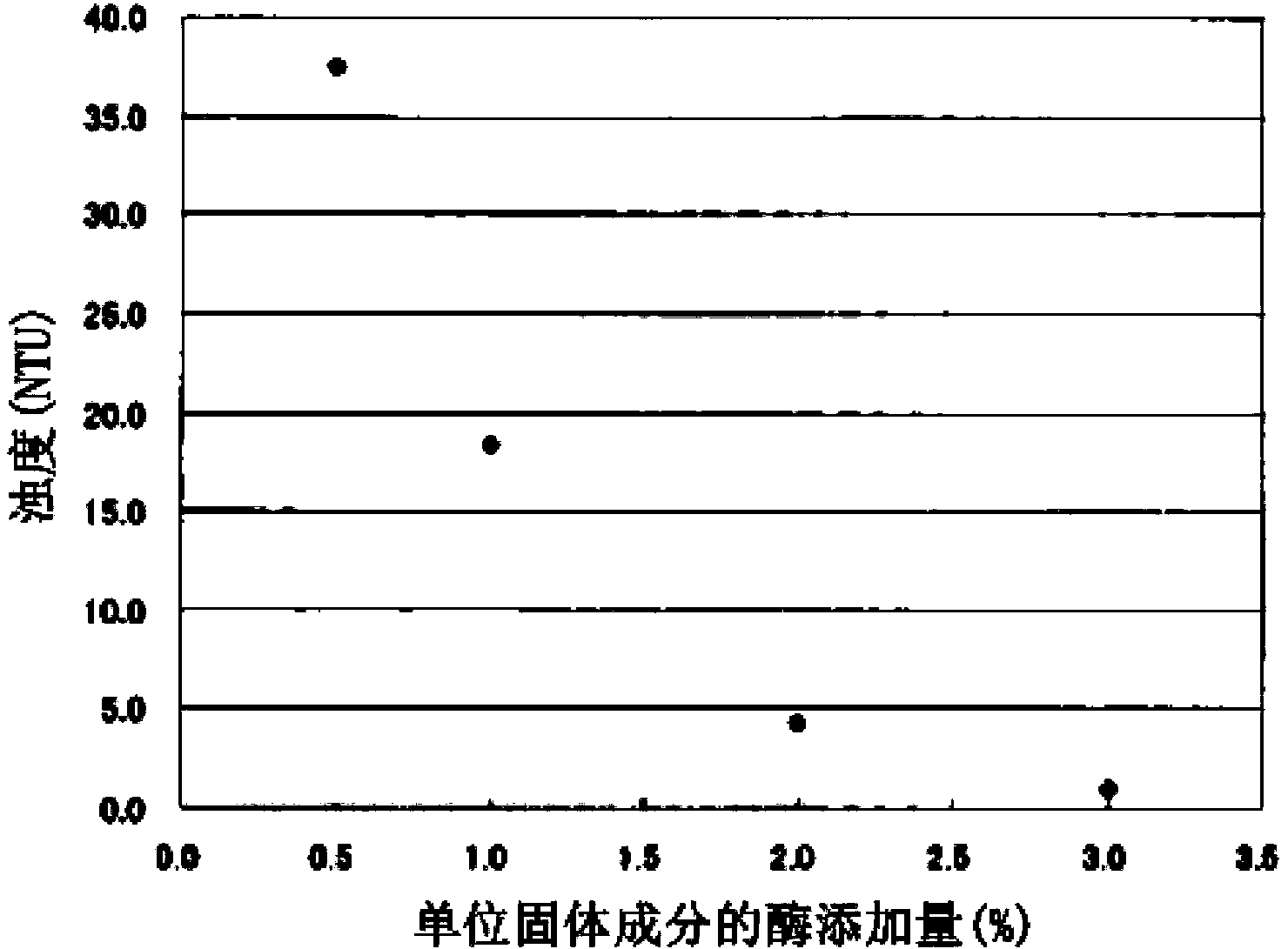
[0085] When the Brix of the tea extract (concentrate) during enzyme treatment is 5.0, the amount of enzyme added becomes 0.5, 1.0, 2.0, and 3.0 per unit solid content. Except for 2 hours, the oolong tea extract was produced in the same manner as in No. 6 of Example 1. In the same manner as in Example 1, the turbidity of a liquid obtained by diluting the supernatant after centrifugation to a Brix of 0.5 was measured while measuring the sedimentation amount of the enzyme treatment liquid.
[0086] The results are shown in Table 3. It can be seen more clearly from Table 3 that there is no correlation between the amount of enzyme added and the amount of precipitation, but as the amount of enzyme added increases, the transparency of the obtained tea extract increases. In particular, it can be seen that when an enzyme preparation of 2% or more, preferably 3% or more is added to the unit solid content, it becomes a tea extract with very hi...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Example 3: Green Tea Extract
[0090] Extract green tea (sanbancha, usually heated) with 10 times the amount of boiling water for 10 minutes. The obtained extract was concentrated to a Brix of 4.5 using a vacuum evaporation concentration device to obtain a green tea concentrate. Glycoside decomposing enzyme was added at a concentration of 3% by weight relative to the solid content to this concentrate, and enzyme treatment was performed at 50° C. for 2 hours. After the enzyme treatment, heat at 90°C for 30 minutes to inactivate the enzyme, cool to below 30°C to obtain the enzyme treatment solution, and pass it through a centrifugal separation device (type H-26F manufactured by Kokusan Co., Ltd. of Japan) at 3000rpm for solidification. Liquid separation treatment was performed for 10 minutes, and after filtration with a 500-mesh filter, 20 mL of the aqueous solution (supernatant) was extracted for turbidity analysis. In addition, as a comparison, a sample subjected to c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com