Method for identifying nucleotide point mutation of phytophthora sojae beta-microtubulin gene and use thereof for diagnosing zoxamide resistance
A technology of Phytophthora sojae and tubulin, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of long detection period, many human resources and materials, and large workload, and achieve the effect of delaying further development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0028] Embodiment 1, the sensitivity determination of Phytophthora sojae to benzilamide
[0029] 8 sensitive strains Ps4, Ps6, Ps9, Ps13, Ps52, Ps53, AH1302 and PsJMS2; 8 resistant strains RZ2-2, RZ5-1, RZ6-2, RZ9-2, RZ10-1, RZ12-1, RZ14 -1 and RZ15-1.
[0030] Carrot culture medium: 200g carrots, squeeze the juice, filter through 4 layers of gauze, distill water to 1L, and sterilize with damp heat at 121°C for 20 minutes.
[0031] 1. The experimental steps are as follows:
[0032] 1) Mix benzamid with dimethyl sulfoxide (dimethyl sulfoxide DMSO) to make 10 5 μg / mL stock solution. Dilute benzamid into concentration gradients of 200 μg / mL, 300 μg / mL, 400 μg / mL, 500 μg / mL, 600 μg / mL and 700 μg / mL, and use 1‰ DMSO as a blank control to determine 8 strains of Phytophthora sojae Sensitivity of susceptible strains. For the sensitivity determination of 8 Phytophthora soybean resistant strains, 1‰DMSO was used as a blank control, and it was measured at 10 5 Inhibition rate at μg / m...
Embodiment 2
[0041] Example 2, Discovery of β-tubulin gene and its corresponding protein mutation site in Phytophthora soybean
[0042] 1. Strains: resistant strains RZ2-2, RZ5-1, RZ6-2, RZ9-2, RZ10-1, RZ12-1, RZ14-1 and RZ15-1, sensitive strains Ps9, Ps13, Ps52, Ps53, AH1302 and PsJMS2.
[0043] 2. Method:
[0044] 1) Strain cultivation: use carrot culture medium (200 g of carrots, juice squeezed, filtered with 4 layers of gauze, distilled water to make up to 1 L, 121° C. moist heat sterilization for 20 minutes, after moist heat sterilization for later use) to cultivate Phytophthora soybean at 25° C. The pre-cultured Phytophthora sojae sensitive strains were inoculated on PDA medium covered with cellophane, cultured in the dark at 25°C for 5 days, the mycelia were collected, frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at -80°C for genomic DNA extraction.
[0045] 2) Genomic DNA of resistant strains and sensitive strains were extracted respectively.
[0046] 3) PCR amplification of the full se...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Embodiment 3, the method for detecting mutation site in Phytophthora soybean
[0055] 1. Primer design
[0056] The strains are the strains PsJMS2 and RZ2-2 used in Example 1.
[0057] The primers are shown in Table 2. Allele specific-PCR primers were designed according to the sequence of the mutant β-tubulin gene. The last base at the 3'-end of the forward primer RZ-FT was consistent with the mutated base. In order to increase the For specificity, a mismatched base was introduced at the second base at the 3'-end of the forward primer (primers RZ-FA, RZ-FC and RZ-FG). The reverse primer is SRZ-A.
[0058] Table 2PCR detects the primers used for Phytophthora sojae strains showing resistance to benzamid
[0059]
[0060]
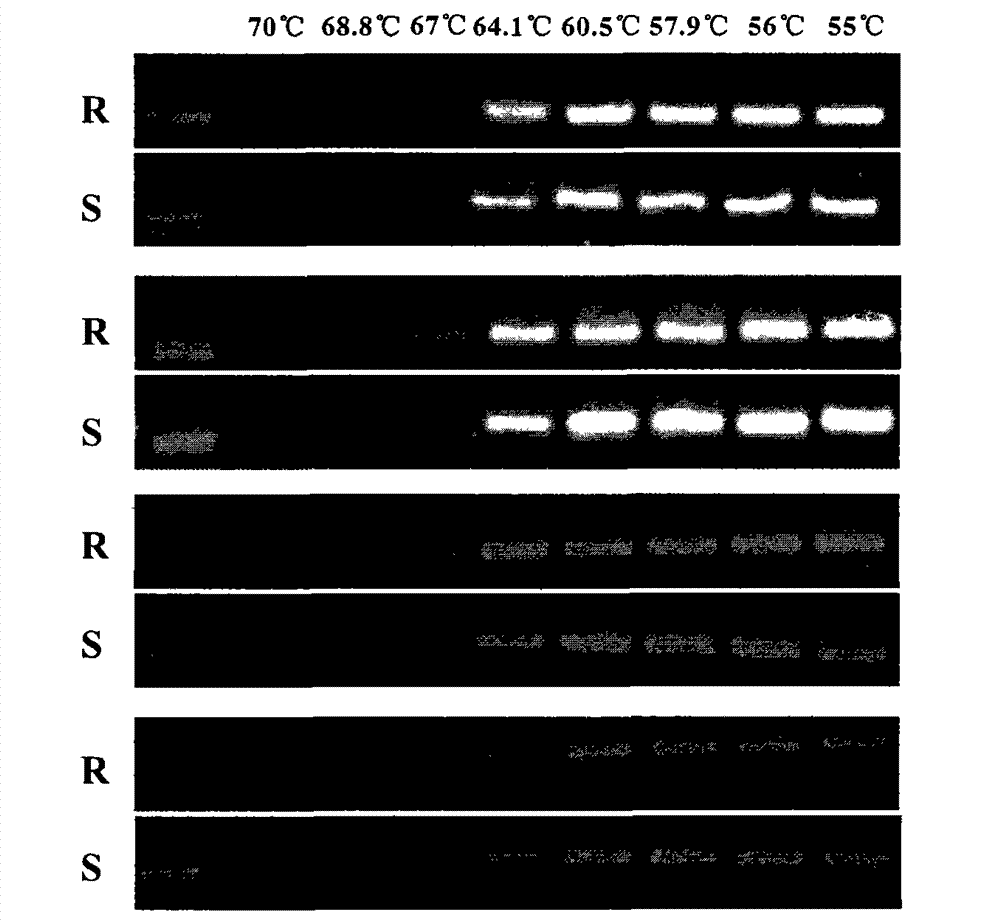
[0061] The specific reaction system is the same as in Example 2. The primers were subjected to temperature gradient PCR with different annealing temperatures to determine the annealing temperature with high specificity. The reaction program w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com