Biological small-diameter artificial blood vessel and preparation method thereof
A small-bore, vascular technique with applications in biomedical engineering
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0059] In a specific embodiment, the preparation method of the present invention mainly includes the steps of decellularization treatment and cross-linking treatment.
[0060] In a specific embodiment, the preparation method of the present invention comprises:
[0061] (1) obtaining mammalian small-caliber blood vessel material;
[0062] (2) performing decellularization on the small-diameter blood vessel material to obtain a natural extracellular matrix that still preserves the shape of the blood vessel; and
[0063] (3) Using proanthocyanidins to cross-link the natural extracellular matrix.
[0064] Herein, small-diameter blood vessels refer to blood vessels with an inner diameter of 6 mm or less in mammals.
[0065] The present invention mainly uses small-diameter blood vessels of mammals (preferably larger mammals, such as pigs, cows, rabbits, sheep and dogs, etc.) to prepare the artificial small-diameter blood vessels of the present invention. Preferably, bovine or porc...
Embodiment 1
[0102] Example 1: Preparation of decellularized bovine carotid arteries with small caliber
[0103] 1. Decellularization of small-bore vascular raw materials
[0104] In this example, decellularized bovine carotid artery small-diameter blood vessels were used as raw materials, and the decellularized treatment included:
[0105] (1) Take fresh bovine carotid artery small-caliber blood vessels from the slaughterhouse, clean them three times with D-Hanks solution after removing fat and other sundries in a sterile environment;
[0106] (2) Soak in D-Hanks solution at 37°C for 30 minutes, perfuse 1-5 mL of preheated (about 37°C) D-Hanks solution with a concentration of 0.25% trypsin per centimeter of blood vessel length; then soak it for 37 minutes Digest at ℃ for 5 minutes;
[0107] (3) Perfuse 1-5 mL of D-Hanks solution below 4°C per centimeter of blood vessel length to stop digestion, and then wash with D-Hanks solution three times.
[0108] (4) Immerse the small-diameter blo...
Embodiment 2
[0117] Example 2: Performance testing of cross-linked decellularized small-bore blood vessels
[0118] The following nine methods were used to evaluate the properties of the cross-linked decellularized small-diameter blood vessels prepared by the method in Example 1.
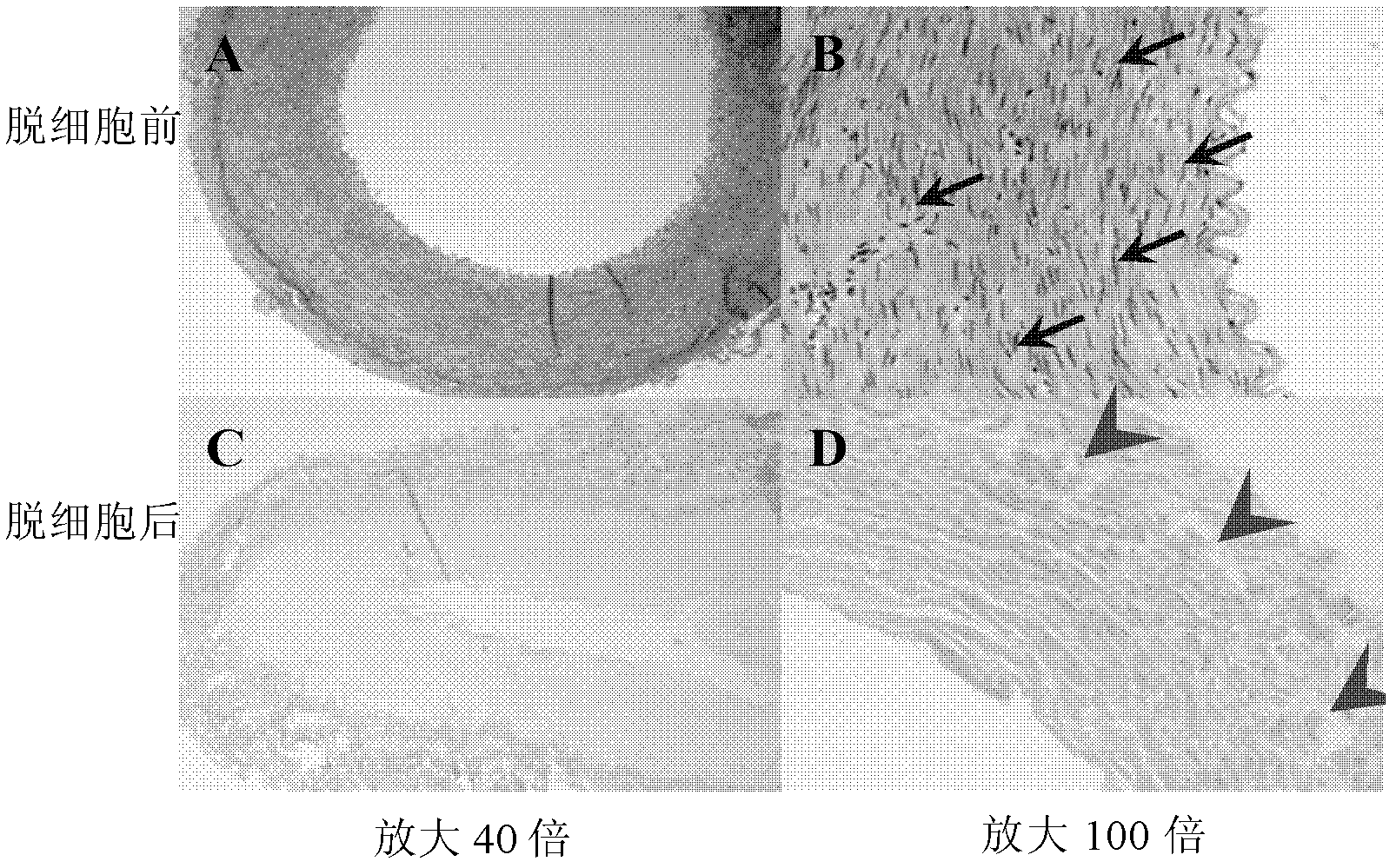
[0119] 1. Paraffin-embedded routine pathological section staining (HE staining) observation
[0120] The small-diameter blood vessels prepared according to the method of Example 1 were soaked and fixed in 4% formalin for 3 days; they were soaked in a series of ethanol solutions in sequence (volume fractions of ethanol were respectively 30%, 50%, 70% , 90%, 95%, 100%), each concentration was dehydrated for 10 minutes; the sample was immersed in conventional molten paraffin liquid for embedding, after sectioning, HE staining was performed by conventional methods, and observed under a microscope for cells or Cell debris remained and photographed. In addition, the PC-crosslinked decellularized small-diameter blood...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com