Method for calculating velocity ratio of longitudinal wave to transverse wave by using non-zero wellhead distance data
A technique of compressional-to-short-wave velocity ratio and well-to-source distance, which is applied in the fields of seismology and seismic signal processing for well logging records, can solve problems such as insufficient precision of calculation method design, rough estimation, and large equivalent velocity span
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
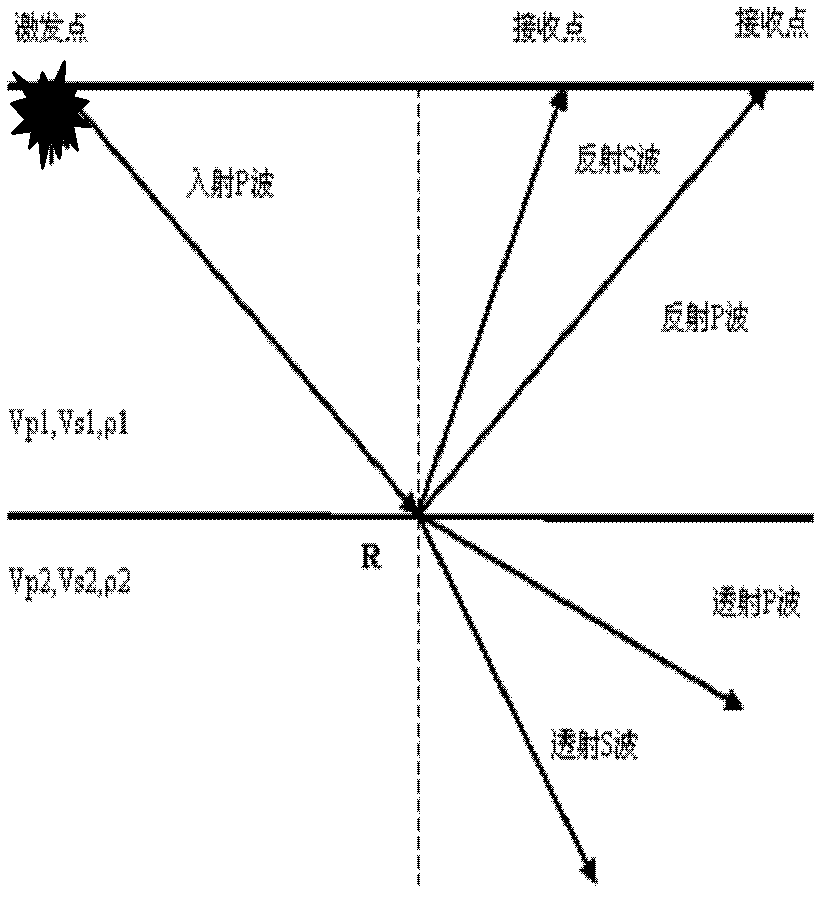
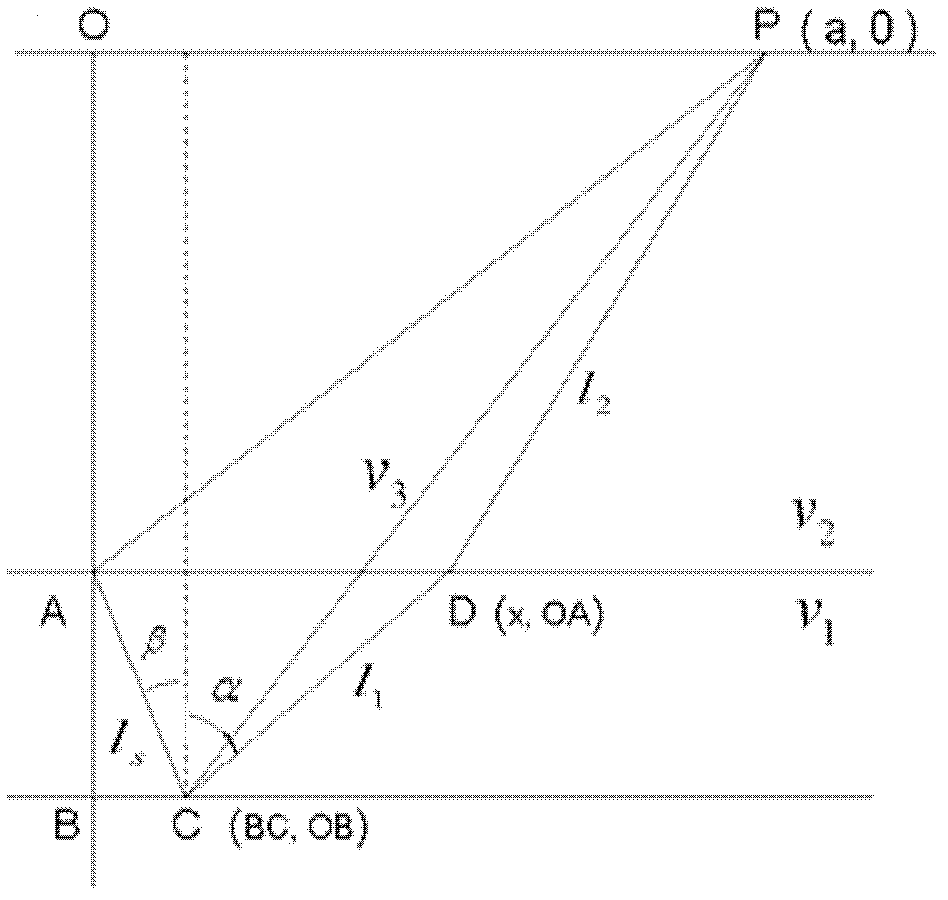
[0076] The invention mainly uses the VSP non-zero well source distance data collected in the field to obtain the reflection event time of the up-converted wave field to calculate the velocity ratio of compression and shear waves between adjacent detection points, and mainly reflects the characteristics of the velocity ratio of compression and shear waves near the well.
[0077] 1) Collect VSP non-zero well-source distance data in the field, and decode to obtain three-component seismic records. The three-component seismic records include a vertical component Z component and two horizontal components H 1 Quantity and H 2 The static correction processing is performed on the seismic records of the three components to obtain the seismic records of the three components after static correction. The static correction processing includes the static correction of the shot point and the static correction of the receiver point.
[0078] 2) Pick the first arrival of the vertical component ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com