Controllable variable-stiffness flexible elbow joint rehabilitation robot
An elbow joint with variable stiffness technology, which is applied in the field of controllable variable stiffness flexible elbow joint rehabilitation robot, can solve the problems of difficulty in accurately controlling its displacement, complicated control, and small stroke
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0017] A preferred embodiment of the present invention is described below in conjunction with accompanying drawing:
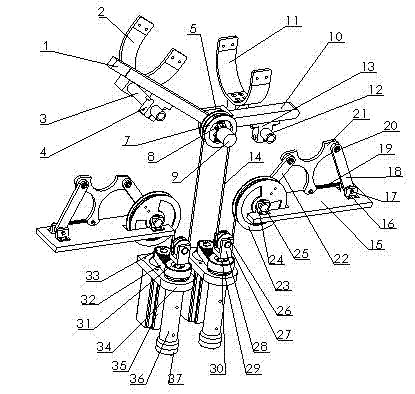
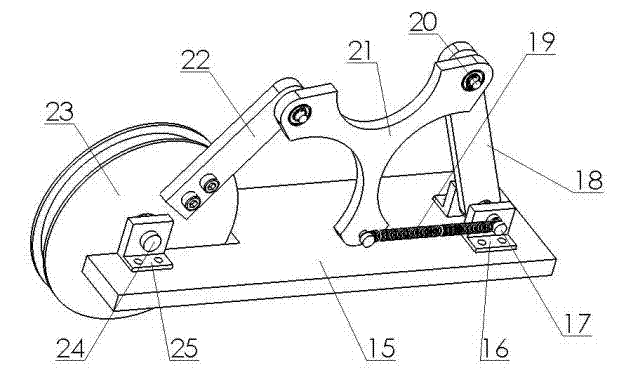
[0018] see Figure 1 ~ Figure 4 The controllable variable stiffness flexible elbow joint rehabilitation robot includes a wearable exoskeleton mechanism, two connecting rod-spring nonlinear mechanisms and two motor screw linear motion mechanisms; it is characterized in that:
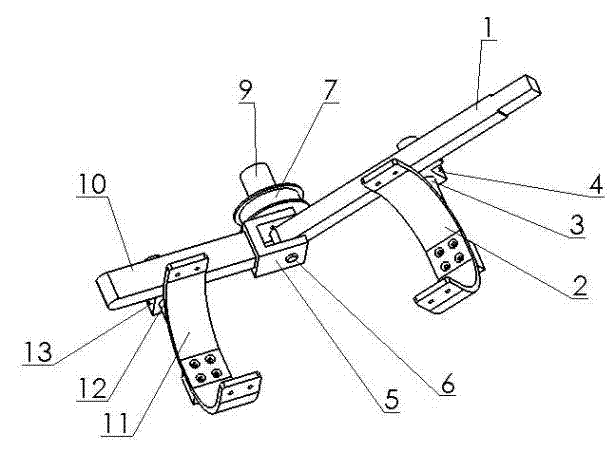
[0019] 1). The wearable exoskeleton mechanism includes a large arm (1), a large arm support frame (2), a large arm adjustment shaft (3), a large arm support frame base (4), an elbow joint connection block (5), Joint connection pin (6), elbow joint drive wheel (7), encoder mounting spring (8), encoder (9), forearm (10), forearm support frame (11), forearm adjustment shaft ( 12) and the forearm support base (13), the boom support frame (2) is a U-shaped bracket, the bottom of the U-shaped bracket is fixedly connected with the boom adjustment shaft (3), and the boom adjustment shaft (3) is p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com