Multilayer growth by gas phase deposition
A gas phase and coating technology, applied in coatings, electrical components, gaseous chemical plating, etc., can solve problems such as hazards and hindering coatings
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
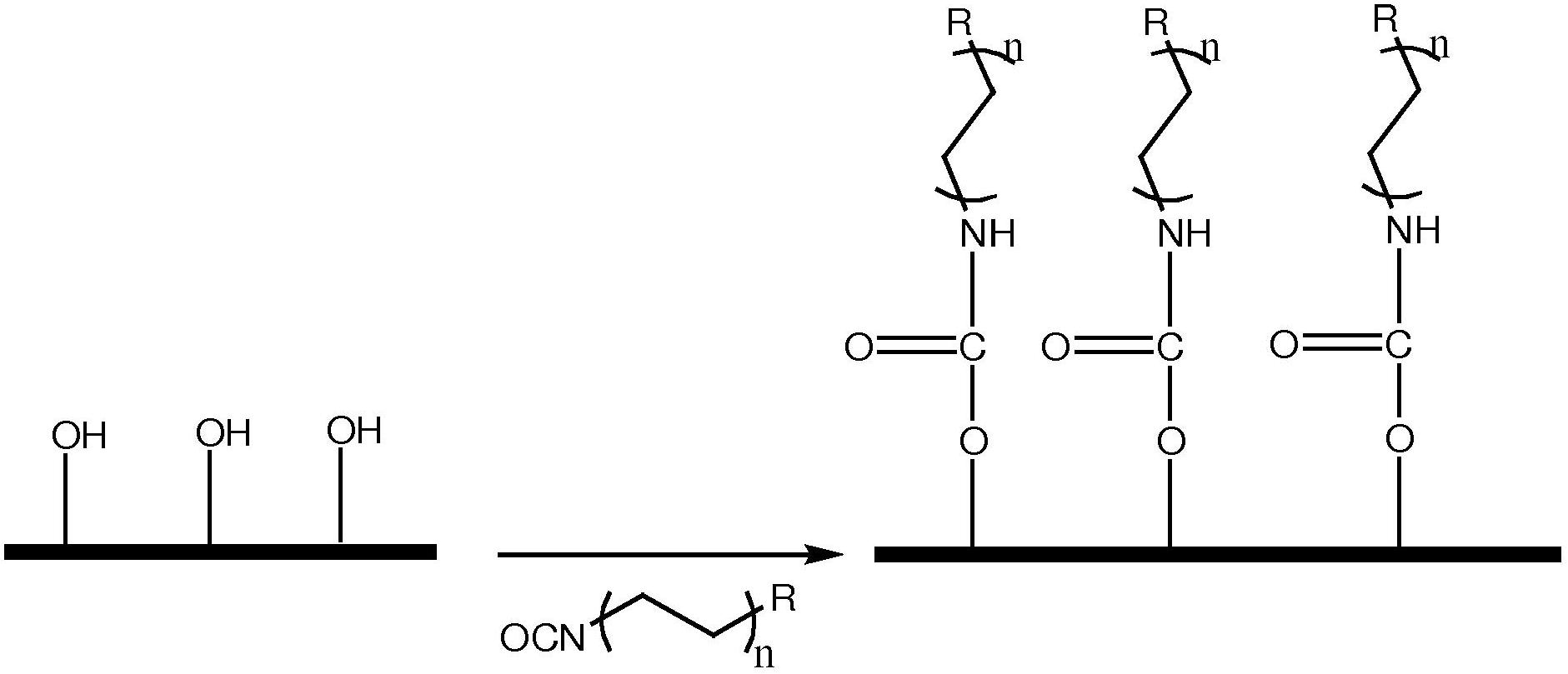
[0041] exist figure 1 An example of application of Chemical A to start application of a multi-layer system is shown in . Substrates with -OH reactive sites react with isocyanates.
[0042] R can be a carbon chain where n is 1 to 30, R is a charged species for cation / anion chromatography, or isocyanate or thioisocyanate.
Embodiment 2
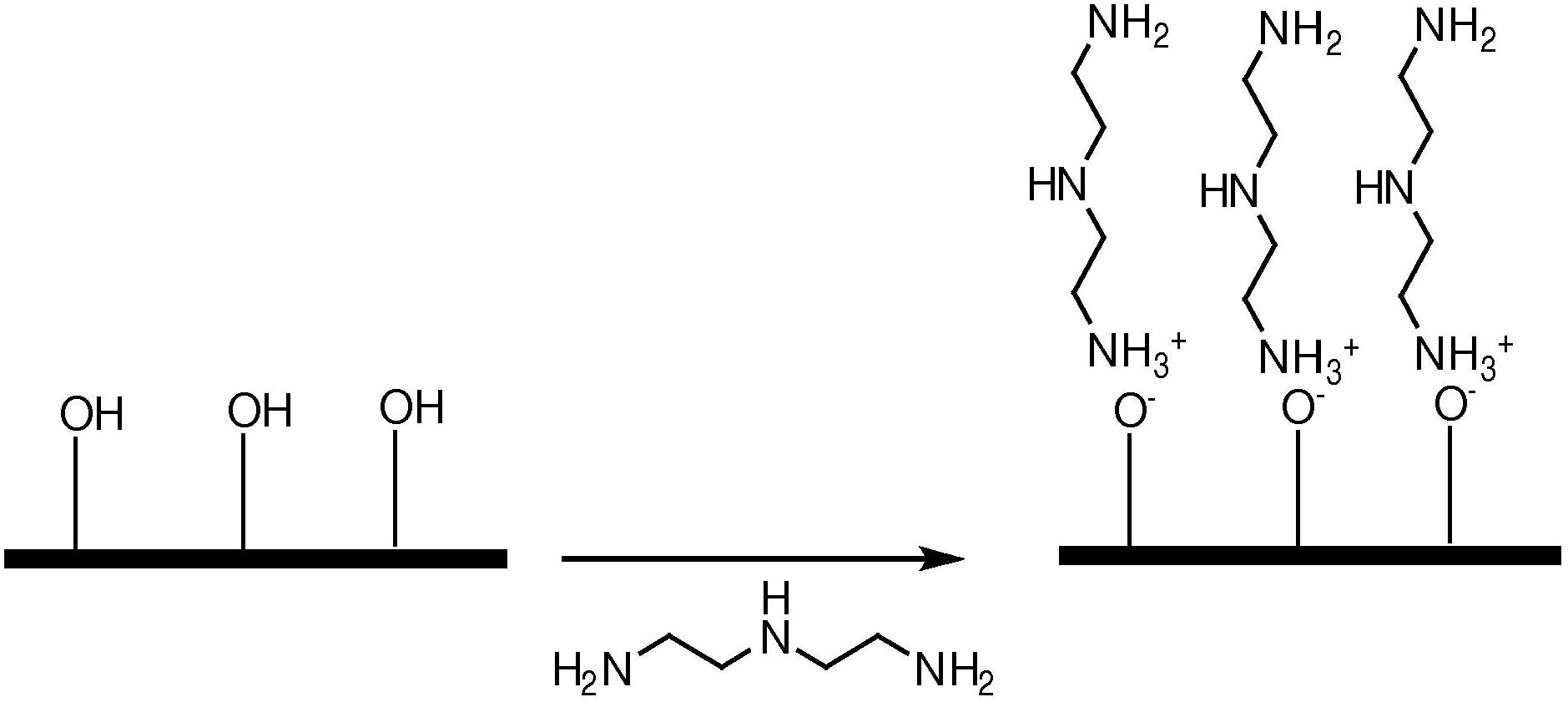
[0044] exist figure 2Another example of applying chemical A to form a multilayer system is shown in , where chemical A is a triamine. Since surface alcohols are acidic, they can form ionic bonds with triamines. In addition, the free amine——NH 2 Functional groups - can react with chemicals such as those with isocyanato groups to create bonded and cross-linked layers.
Embodiment 3
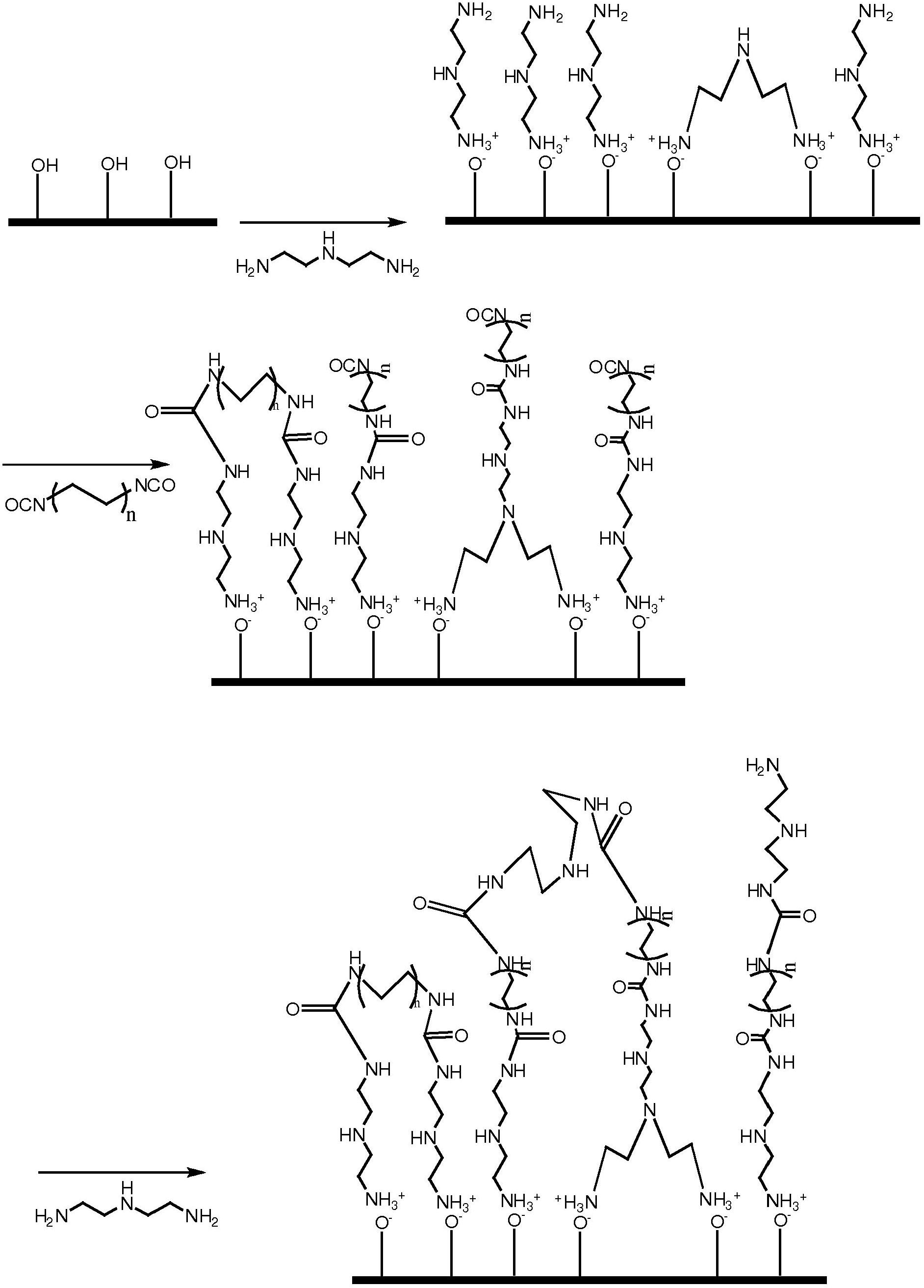
[0046] An amino terminated monolayer as in Example 2 can be reacted with Chemical B, an isocyanate, to produce a crosslinked material that will be stable under acidic conditions. Apply a monolayer and react like Figure 3A shown. The AB multilayer is then reacted with a triamine (same as chemical A), which is then reacted with chemical C with terminal reactive groups, as in Figure 3B shown.
[0047] The multilayer system can be characterized as ABCD, where C=A, where A=triamine, B=diisocyanate, D=monoisocyanate or monoepoxide with an alkyl chain length of 2-30 carbon units. This method produces highly crosslinked stationary phases, which can be attributed to diisocyanates or triamines. In addition, A and B layers can be similarly applied to form AB) n CD or (AB) n C multi-layer system, wherein n is 2 or more.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com