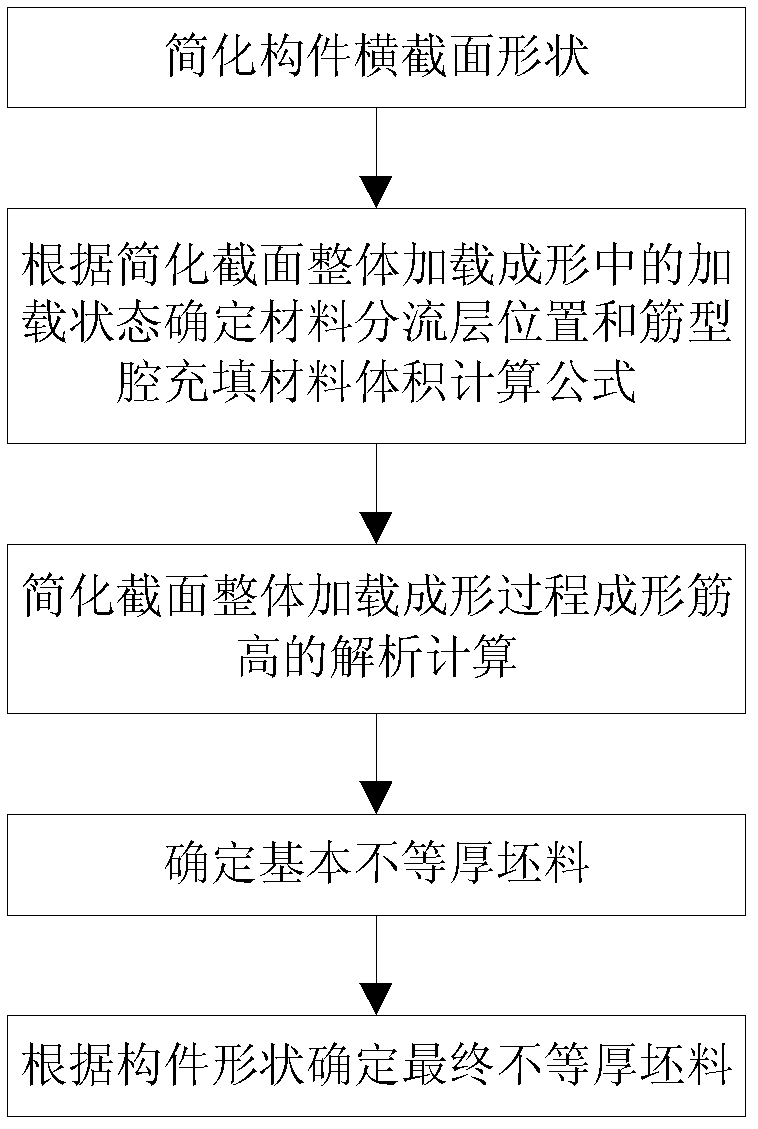
Method for determining blank with different thicknesses for two-dimensional integrated loading and forming
A billet and unequal technology, applied in the field of hot forging of difficult-to-deform alloys, can solve problems such as high cost, failure to consider local loading characteristics, and areas that cannot be filled
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0107] This embodiment is a method for determining the unequal-thickness blanks for integral loading and forming of rib-like members.
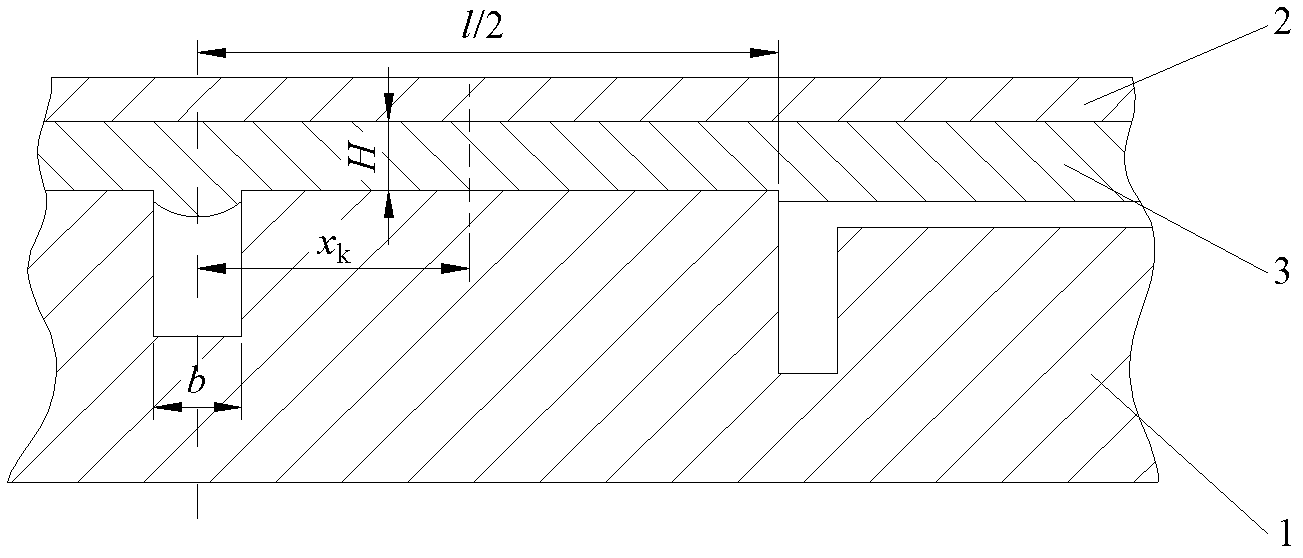
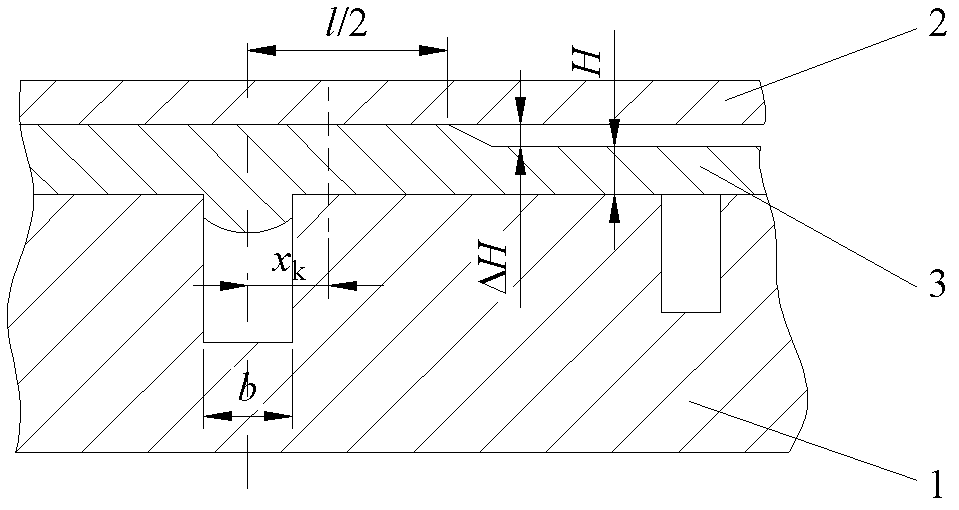
[0108] Such as Figure 4 As shown, the lower surface of the forming member in this embodiment has six ribs, and two of the ribs are located at both ends of the member. The widths of the ribs at the two ends of the component are different. Starting from one end of the rib with the wide end face, each rib is sequentially recorded as the first rib to the sixth rib. The material of the component is Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy. The forming process in this embodiment shares one loading step.
[0109] In this embodiment, the integral loading forming of the rib-like member adopts an isothermal forming process, the forming temperature is 950°C, the upper die loading speed is 1 mm / s, and the friction factor m is taken as 0.3.
[0110] The specific process of determining the shape of unequal thickness blanks is as follows:
[0111] Step 1, simplify the cross-sec...
Embodiment 2
[0184] This embodiment is a method for determining the unequal-thickness blanks for integral loading and forming of rib-like components, such as Figure 8 As shown, the upper surface and the lower surface of the component of this embodiment each have 3 ribs; the ribs on the upper surface and the lower surface of the component are symmetrically distributed. And a pair of ribs are located at the ends of a pair of components. The material of the components is 7075 aluminum alloy. The forming process in this embodiment shares one loading step.
[0185] In this embodiment, the integral loading forming of the rib-like member adopts a hot die forging process, the blank temperature is 450°C, the mold temperature is 400°C, the upper mold loading speed is 10mm / s, and the friction factor m is 0.3.
[0186] The specific process of determining the shape of unequal thickness blanks is as follows:
[0187] Step 1, simplify the cross-sectional shape of the component;
[0188] The upper surface and ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com