Process for producing butyric acid by using bagasse hydrolysate through clostridium tyrobutyricum fermentation
A Clostridium tyrobutyricum, bagasse fermented technology, applied in fermentation, microbial-based methods, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low butyric acid concentration and yield, difficult separation of butyric acid, and low butyric acid selectivity , to achieve the effect of easy industrial scale-up, eliminating repeated inoculation, and simplifying the operation process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
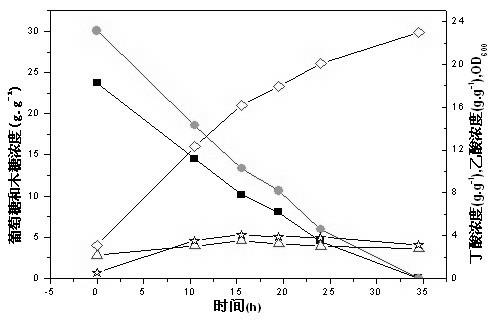
[0029] What present embodiment provides is the technology that carries out fiber bed immobilization Clostridium tyrobutyricum batch fermentation butyric acid with bagasse hydrolyzate as carbon source, and the steps are as follows:
[0030] 1) Dip the Clostridium tyrobutyricum bacteria liquid with an inoculation needle, streak on the enhanced medium plate containing 50 mg / mL sodium butyrate, and culture at 37 °C for 72 hours. The classification and naming of Clostridium tyrobutyricum (No. ATCC 25755): the Chinese name is Clostridium tyrobutyricum, and the Latin literary name is Clostridium tyrobutyricum , Clostridium tyrobutyricum was purchased from the American Type Culture Collection located in Washington, USA.
[0031] The enriched medium consisted of: glucose 30 g / l, yeast extract 5 g / l, peptone 5 g / l, (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 3 g / l, K 2 HPO 4 1.5 g / l, MgSO 4 7H 2 O, 0.6 g / l, FeSO 4 7H 2 O 0.03 g / l, 50 mg / mL sodium butyrate, culture conditions: 37°С, pH 6.0, anaerobic env...
Embodiment 2
[0039] What the present embodiment provides is the technology that is the carbon source fiber bed immobilization Clostridium tyrobutyricum fed-batch fermentation butyric acid with the bagasse hydrolyzate, and the steps are as follows:
[0040] 1) same as embodiment 1 step 1);
[0041] 2) same as embodiment 1 step 2);
[0042] 3) Same as step 3 of embodiment 1);
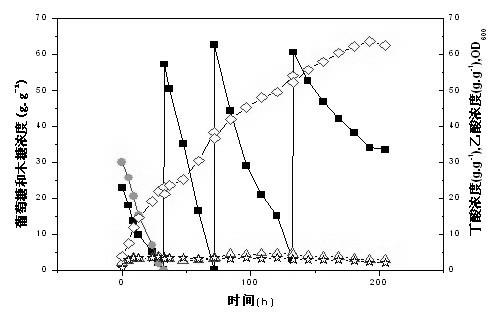
[0043] 4) The operation steps are the same as step 4) of Example 1, except that when the sugar concentration in the fermentation broth is close to 0, bagasse hydrolyzate is added, and a total of 3 batches are added until the final concentration of the fermentation product butyric acid no longer increases. The total sugar concentration did not decrease after 186 hours of fermentation, and the final concentration of butyric acid was 62.8 g / L as measured by gas chromatography. Kinetics of butyric acid in fed-fed fermentation as image 3 shown.
Embodiment 3
[0045] What the present embodiment provides is the technology that is that carbon source fiber bed immobilized Clostridium tyrobutyricum ferments repeatedly batches of butyric acid with the bagasse hydrolyzate, and the steps are as follows:
[0046] 1) same as embodiment 1 step 1);
[0047] 2) same as embodiment 1 step 2);
[0048] 3) Same as step 3 of embodiment 1);
[0049] 4) The operation steps are the same as step 4) of Example 1, the difference is that during the fermentation process, when the sugar concentration is close to 0, the fermentation medium of bagasse hydrolyzed liquid is replaced, and a total of 5 batches are replaced. The average final concentration of butyric acid measured by gas chromatography is 22.9 g / L, the kinetics of repeated batch fermentation of butyric acid is as follows Figure 4 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com