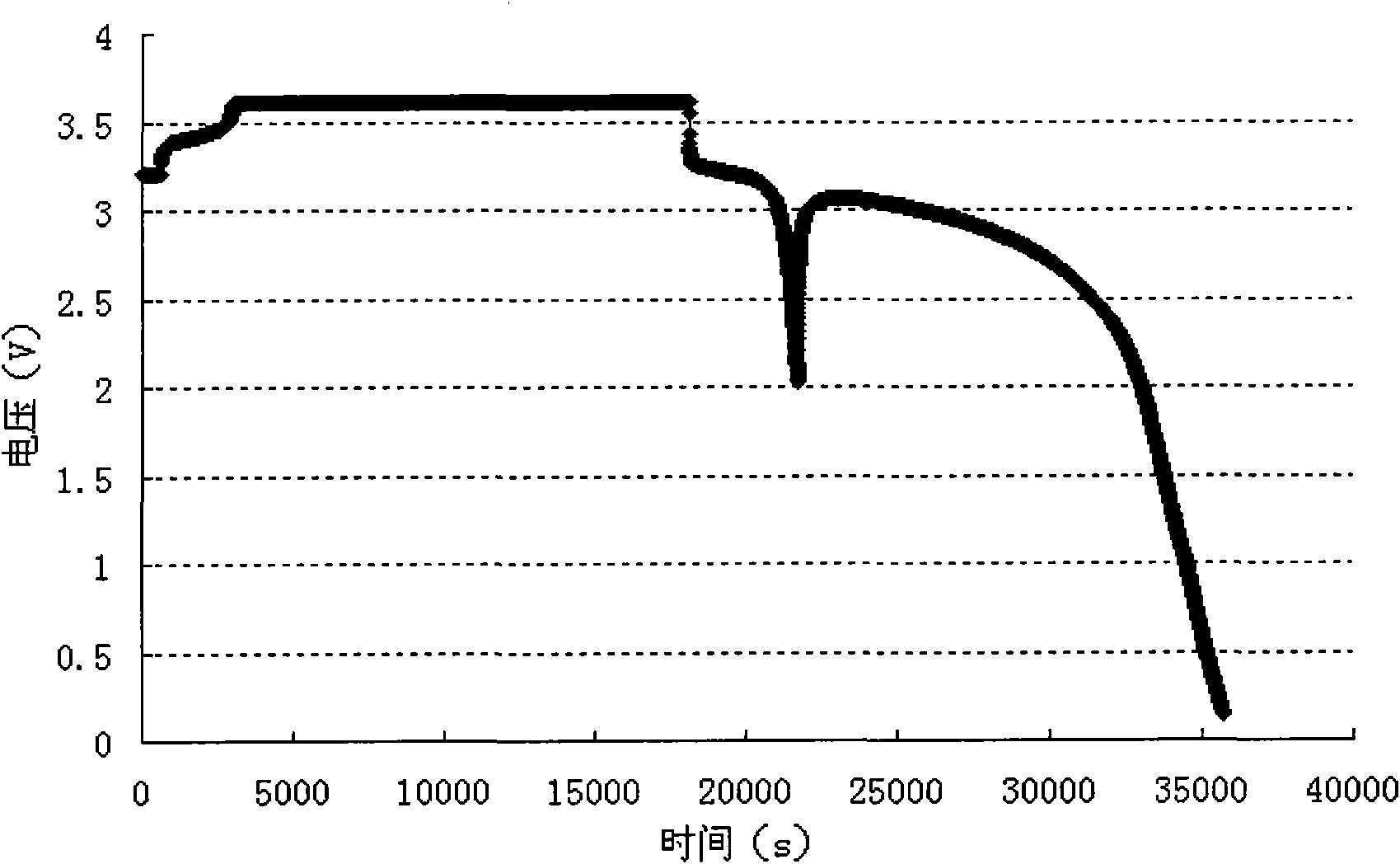
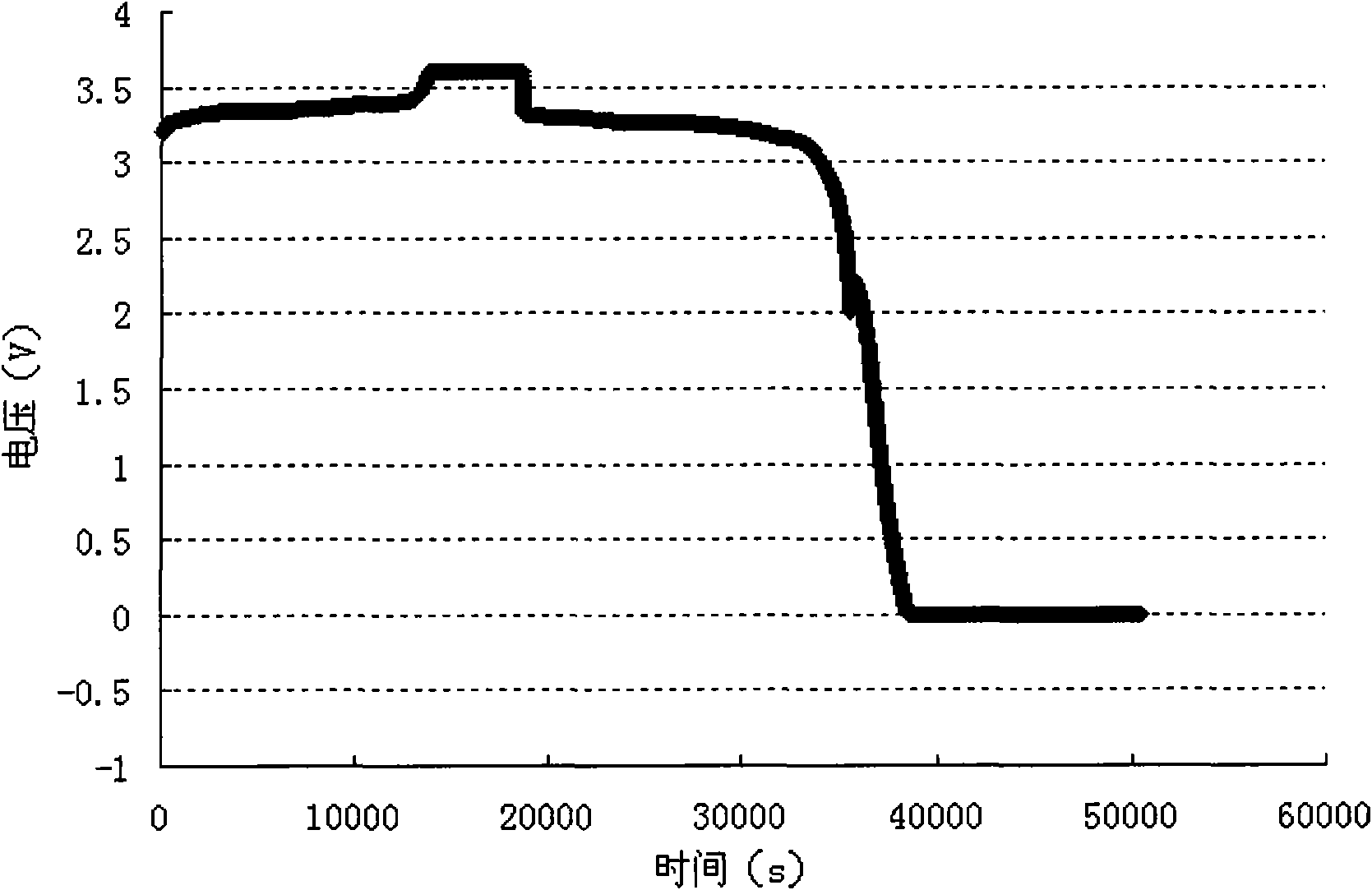
A lithium ion secondary battery
A secondary battery and lithium ion technology, applied in secondary batteries, battery electrodes, battery components, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, low cost, poor discharge safety performance, etc., and achieve improved safety performance and stable discharge voltage , The effect of improving the discharge safety performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The preparation of the lithium-ion secondary battery includes preparing the positive electrode, the negative electrode and the electrolyte of the battery, and winding the positive electrode and the negative electrode through a separator to form an electrode group, placing the electrode group into the battery case, adding the electrolyte, and then sealing A battery case, wherein the negative pole is the negative pole provided by the present invention.
[0031] The positive electrode and electrolyte can be prepared by existing methods. For example, a conventional positive electrode preparation method includes coating or filling a slurry containing positive electrode active materials and a binder on a wide-width electrode sheet, drying, rolling and slitting to obtain a positive electrode. Wherein, the solvent used to form the slurry containing the positive electrode active material and binder can be selected from various conventional solvents, such as N-methylpyrrolidone (...
Embodiment 1
[0037] This example is used to illustrate the preparation of the lithium ion secondary battery of the present invention.
[0038] (1) Preparation of positive electrode:
[0039] Lithium iron phosphate, binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), conductive agent (Supper-p), dispersant polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), N-methylpyrrolidone in mass ratio 100:4:5:0.5:90 Stir in a vacuum mixer to form a uniform positive electrode slurry. The positive electrode slurry was evenly coated on both sides of an aluminum foil with a thickness of 20 μm, and then dried at 150° C. After rolling and cutting, a positive electrode sheet with a size of 453×40 mm was obtained.
[0040] (2) Preparation of negative electrode:
[0041] Natural graphite, binder styrene-butadiene rubber emulsion (SBR), binder carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), deionized water are stirred in a vacuum mixer in a mass ratio of 100:2:2:130 to form a uniform Negative slurry. The negative electrode slurry was evenly coated on both sid...
Embodiment 2
[0047] (1) Preparation of positive electrode:
[0048] Lithium iron phosphate, binder polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF), conductive agent (Supper-p), dispersant polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP), N-methylpyrrolidone in mass ratio 100:4:5:0.5:90 Stir in a vacuum mixer to form a uniform positive electrode slurry. The positive electrode slurry was evenly coated on both sides of an aluminum foil with a thickness of 20 μm, and then dried at 150° C. After rolling and cutting, a positive electrode sheet with a size of 453×40 mm was obtained.
[0049] (2) Preparation of negative electrode:
[0050] Natural graphite, binder styrene-butadiene rubber emulsion (SBR), binder carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC), deionized water are stirred in a vacuum mixer in a mass ratio of 100:2:2:130 to form a uniform Negative slurry. The negative electrode slurry was evenly coated on both sides of a copper foil with a thickness of 12 microns, and then dried at 90°C. After rolling, cutting. Add 0.025 g of lithium...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com