A method and system for detecting a downlink control channel of a relay node
A relay node, line control technology, applied in transmission systems, digital transmission systems, baseband system components and other directions, can solve problems such as no R-PDCCH, no implementation method, no solution, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
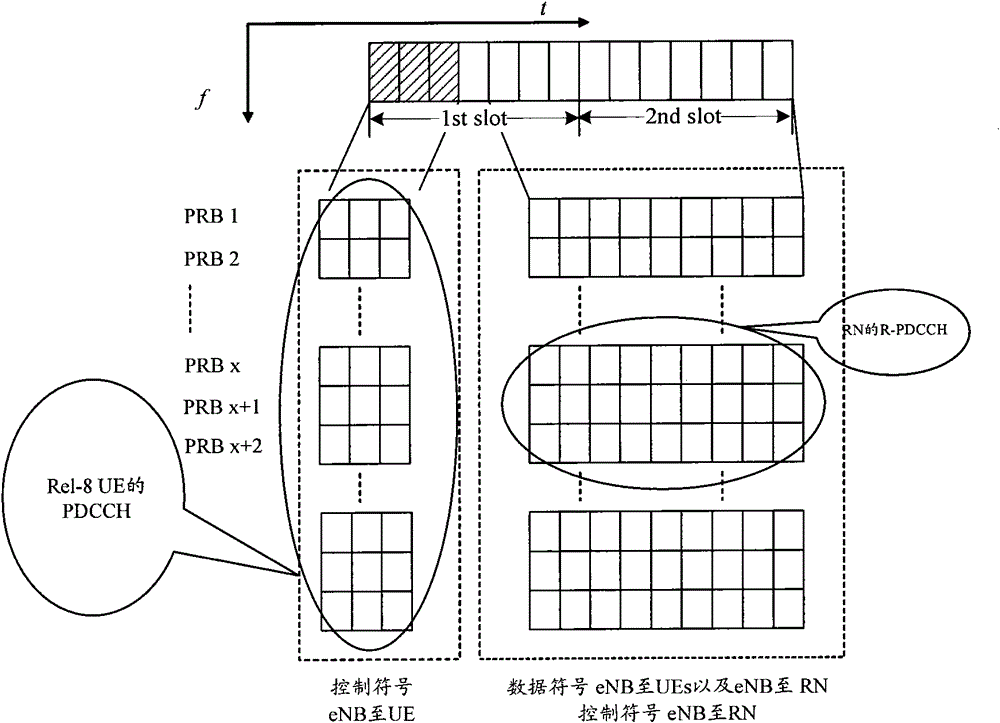
[0076] In this example, the reserved N PRBs used to bear the R-PDCCH uniquely correspond to the division method of the subsets; wherein, the number of subsets that can be divided is set to m. Describe it in detail below.
[0077] The base station divides the N PRBs reserved semi-statically for carrying the R-PDCCH into m subsets, and the value of m and the size of the m subsets are uniquely determined by the value of N. The specific determination method is shown in Table 1, wherein the PRBs contained in each subset can be continuous or discrete, but the division method is unique, and the specific division method is shown in Table 1. The maximum number of subsets in Table 1 is 5. You can also set more than 5 subsets as needed. In Table 1, when there are multiple subsets, the PRBs allocated in each subset are as equal as possible.
[0078] Among them, no matter what the value of N is, there is a possibility that there is only one subset, as shown in Table 1, under various val...
Embodiment 2
[0085] In this example, the reserved N PRBs used to bear the R-PDCCH uniquely correspond to the division method of the subsets; wherein, the number of subsets that can be divided is set to m. The method for determining the value of m is exactly the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0086] In this example, in addition to notifying the RN of all subset division methods, the base station also implicitly notifies each RN of the subset index number (subsetindex) to which each RN belongs.
[0087] First, the RN learns all subsets according to the N value and Table 1 notified by the network side; secondly, according to the implicit relationship between parameters such as the total number of subsets and the relay node identifier (RN-ID), the RN that bears itself is known. - the subset index where the PDCCH is located. As an implementation, the subsetindex where the R-PDCCH bearing the RN is located can be determined in the following manner:
[0088] subsetindex=RN-IDmodN subset , whe...
Embodiment 3
[0091] In this example, the reserved N PRBs used to bear the R-PDCCH uniquely correspond to the division method of the subsets; wherein, the number of subsets that can be divided is set to m. For the case where the m value is determined by the N value but not unique, the specific processing method is as follows:
[0092] The base station limits the value of m to {1, 2, 3, 4}, that is, the same value of N corresponds to 4 different values of m. In order for the RN to determine the value of m, the network side needs to use 2 bits in the R-PBCH to notify the RN. For example, when N=15, the m value can be indicated in the following manner:
[0093] When the indication bit carried in the R-PBCH is 00, it means m=1, that is, there is only 1 subset;
[0094] When the indication bit carried in the R-PBCH is 01, it means that m=2, that is, it is divided into 2 subsets, and each subset has 7 and 8 PRBpairs respectively;
[0095] When the indication bit carried in the R-PBCH is 10, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com