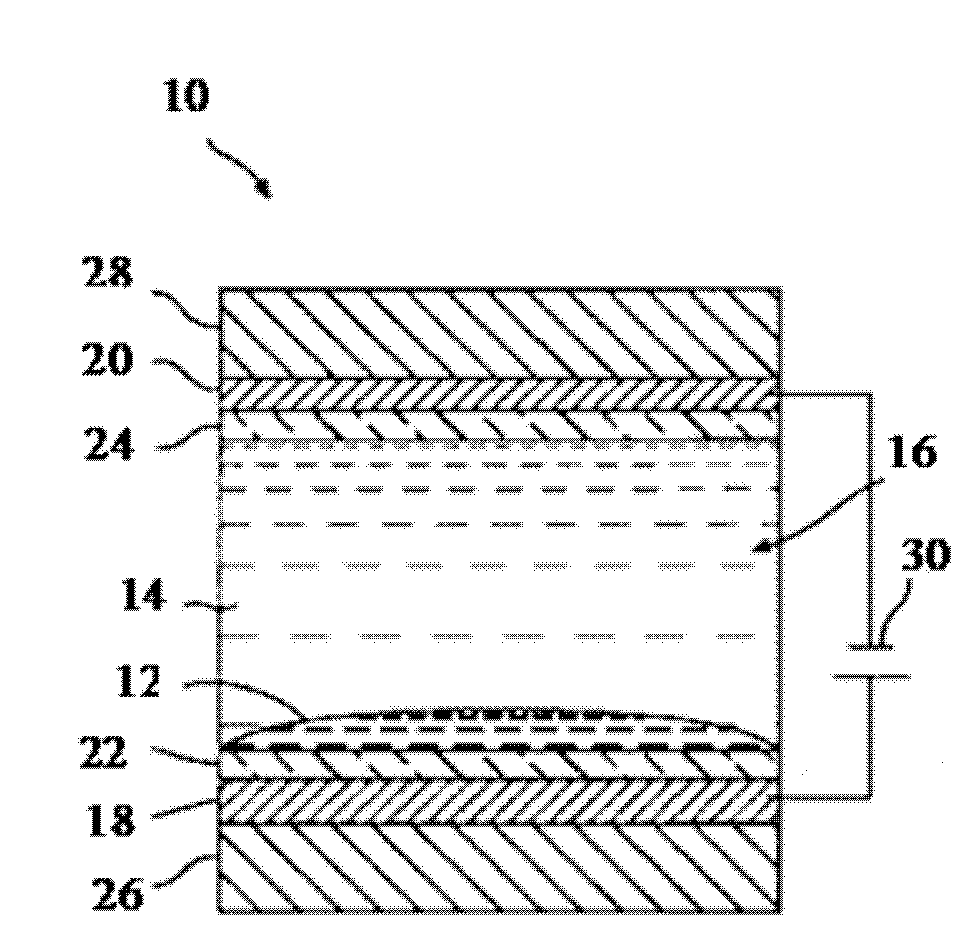
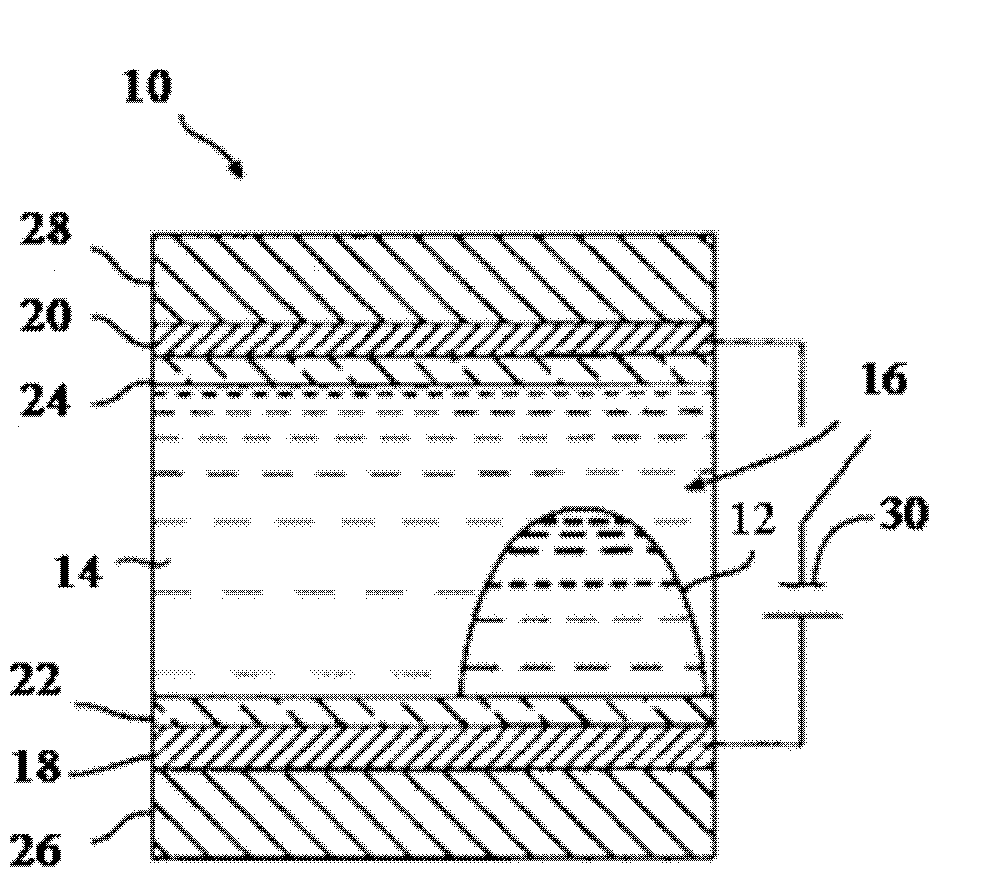
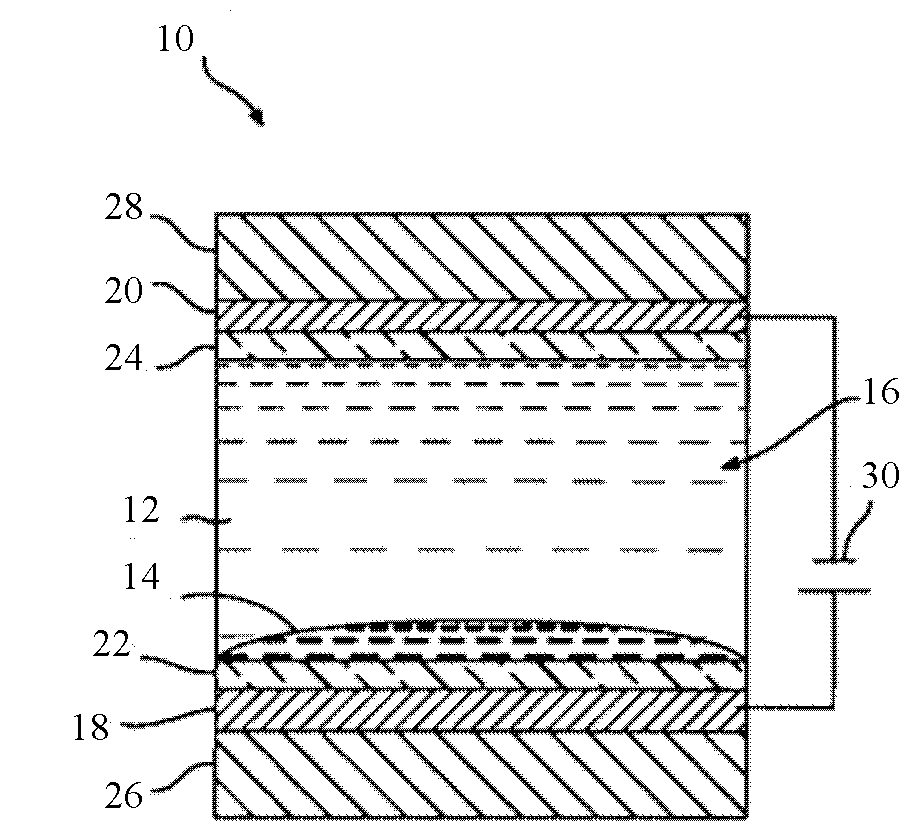
Colored fluids for electrowetting, electrofluidic, and electrophoretic technologies
An electro-wetting, electro-fluid technology, applied in the field of electro-wetting, can solve problems such as limited application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0093] 100 parts of a 10% aqueous dispersion of self-dispersing C.I. Pigment Blue 15:4 (available from Cabot) 250C and 100 parts of deionized water were placed in a glass beaker and acidified with 50 parts of 30% HCl. The slurry was heated to 85-90°C and stirred at this temperature for one hour. The hot suspension was filtered, the filter cake was washed to neutral pH with deionized water, two washes with 100 parts methanol, and the pigment was dried overnight in a 50°C oven.
[0094] The dark blue powder is then ground. 10 parts of pigments were premixed with 90 parts of non-aqueous polar solvent propylene glycol (PG), followed by grinding the slurry for one hour to obtain a cyan fluid.
Embodiment 2
[0096] The fluid was prepared as described in Example 1, but using the non-aqueous polar solvent propylene carbonate instead of PG to obtain a cyan fluid.
Embodiment 3
[0098] The fluid was prepared as described in Example 1, but using a 10% aqueous dispersion of self-dispersing C.I. Pigment Red 122 (available from Cabot) 260M instead 250C. The crimson powder is then ground. 10 parts of pigment were premixed with 90 parts of propylene carbonate (PC), followed by grinding the slurry for one hour to obtain a red fluid.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dynamic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Weight average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dynamic viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com