Semantic marking method for image scene based on geodesic transmission
A technology of semantic marking and geodesic, applied in the direction of instruments, character and pattern recognition, computer parts, etc., can solve the problems of slow processing speed, not completing semantic marking, and not considering the accuracy of image marking, etc., to achieve fast and accurate marking , the effect of reducing complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0038] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
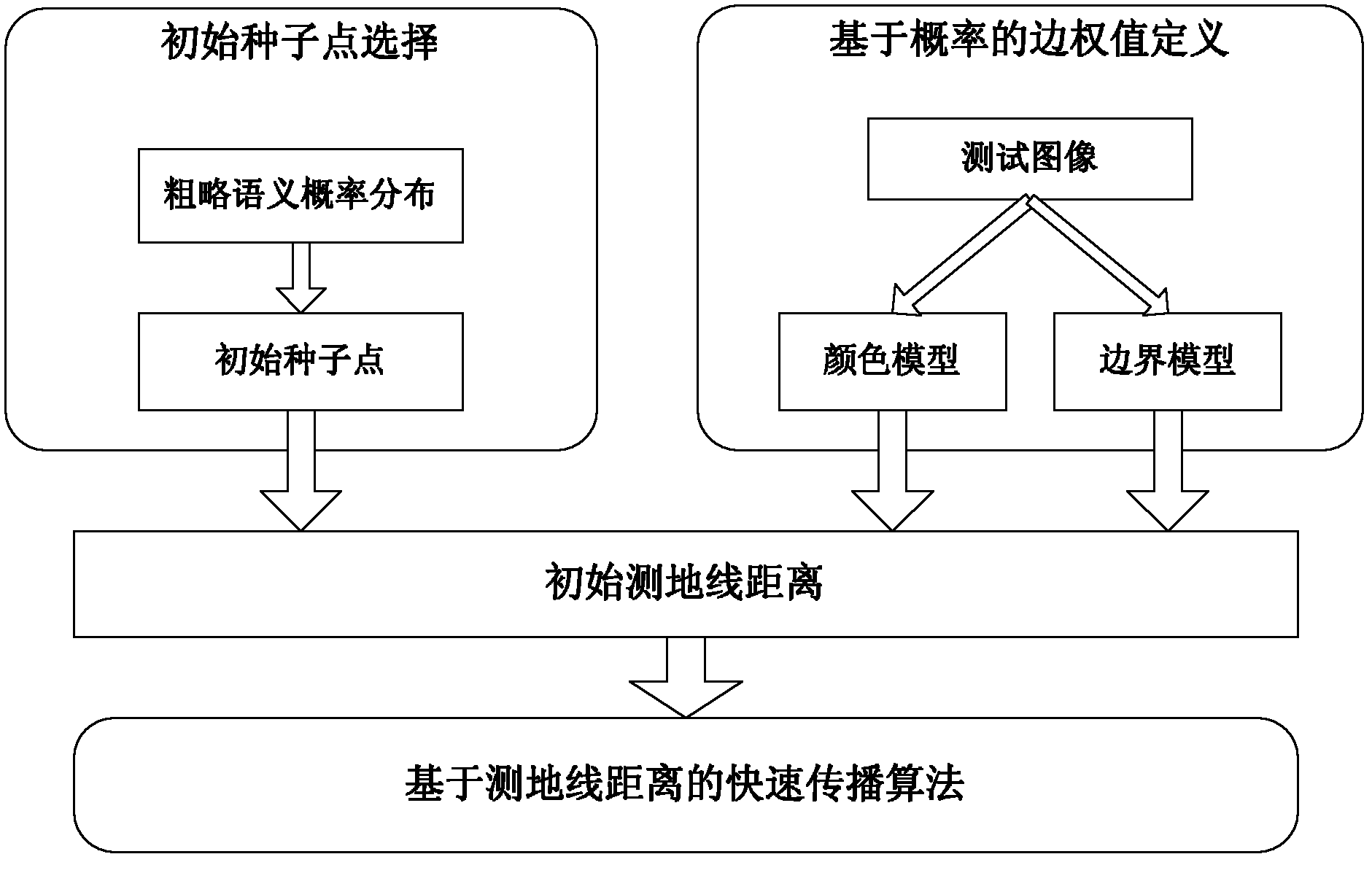
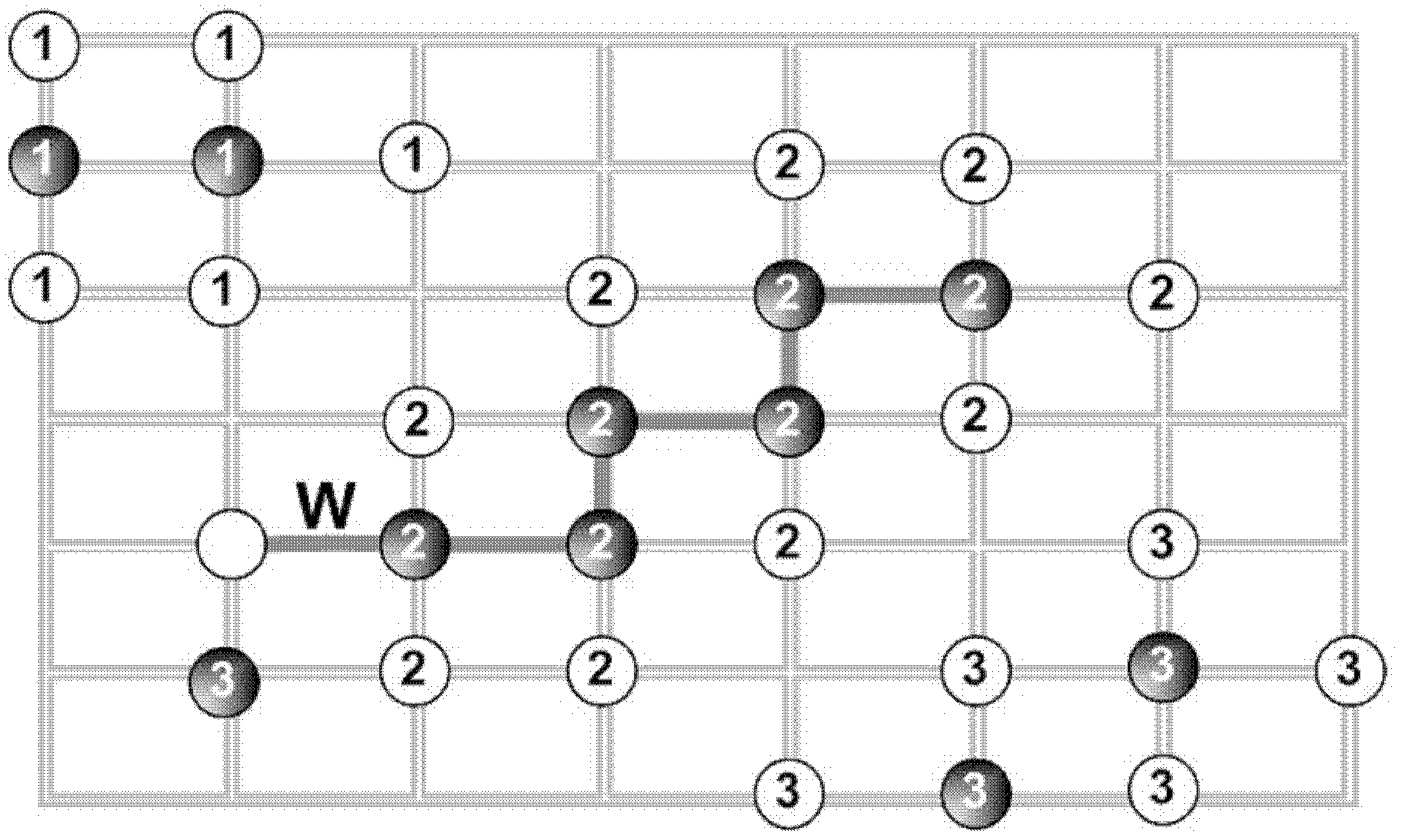
[0039] An image scene semantic labeling method based on geodesic propagation, the overall process is as follows figure 1 shown. The main process of the method is as follows: firstly, use the object discrimination algorithm to obtain the rough probability map of the scene object semantics and the rough semantic labeling result map; then, combine the color information of the image scene and the rough semantic labeling result map to estimate the Color feature distribution, while estimating the boundary features in the image scene; and combining the color features and boundary features to define the geodesic distance of multiple objects on its mixed flow pattern; then, using the mean shift algorithm in the rough probability map of the scene object semantics Find the local extremum point, and use this local extremum point as the initial seed point for geodesic propagatio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com