Computational imaging method and imaging system based on nonplanar image sensor
An image sensor and imaging method technology, applied in the field of computational photography, can solve the problems of inability to effectively collect scene depth information, and achieve the effects of cost saving, accurate depth estimation results, and precise depth of field control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
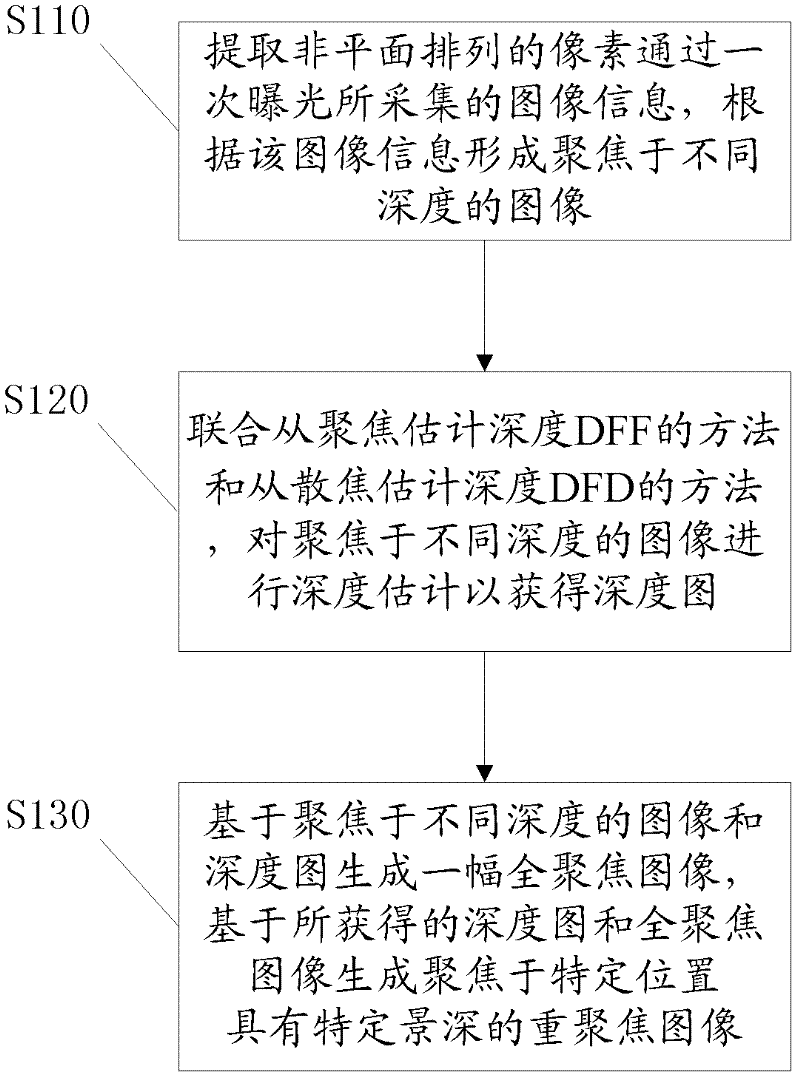
[0036] figure 1 It is a flowchart of a computational imaging method based on an image sensor according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, combined below figure 1 Describe the steps of the method in detail.
[0037] Step S110, extracting the image information collected by the non-planar arrangement of the lighting surfaces, and forming images focused at different depths according to the image information.
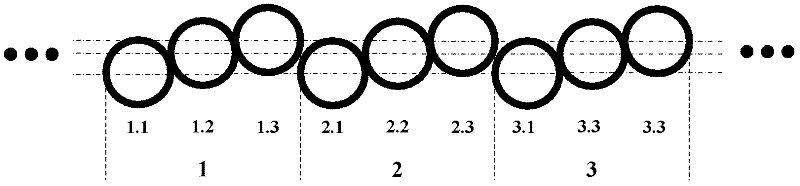
[0038] The image sensor involved in the computational imaging method of this embodiment adopts a non-planar lighting surface arrangement. In general, the lighting surface of the sensor is the sensor pixel. In order to obtain the imaging results of the scene under different focal planes in single-exposure acquisition, the pixel arrangement of the non-planar sensor surface is preferably divided into a specific number of height levels, and different The number of height levels corresponds to the number of different focal planes in the scene, and can also be determined ...
Embodiment 2
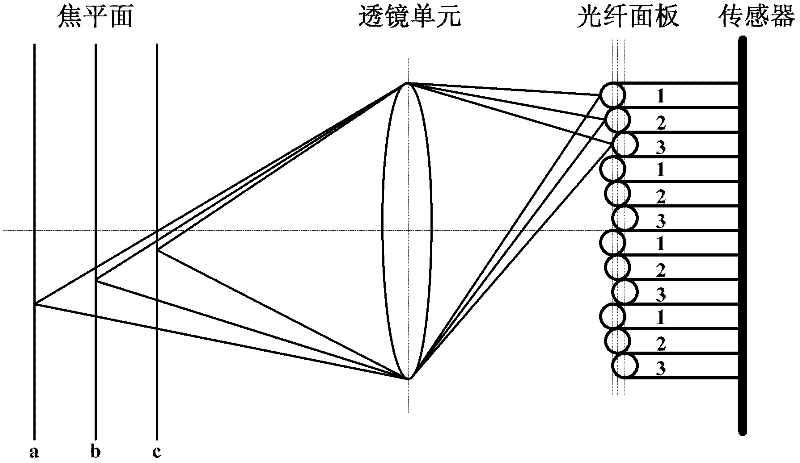
[0091] Figure 7 It is a schematic structural diagram of a computational imaging device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention, combined with Figure 7 Describe in detail the composition of the computational imaging device.
[0092] The computational imaging device includes the following units:
[0093] image sensor unit , the surface of which is arranged in a non-planar manner, extracting image information collected by a single exposure on the surface arranged in a non-planar manner, and forming images focused at different depths according to the collected image information.
[0094] The surface of the image sensor unit adopts a non-planar arrangement. In general, the surface of the sensor is the pixel of the sensor. In order to obtain the imaging results of the scene under different focal planes in single-exposure acquisition, the pixel arrangement of the non-planar sensor surface is preferably divided into a specific number of height levels. Select The numb...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com