Image processing method and image processing device
An image processing and image technology, applied in the direction of image data processing, image enhancement, image analysis, etc., can solve problems such as inapplicable images, and achieve the effect of reducing the impact
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
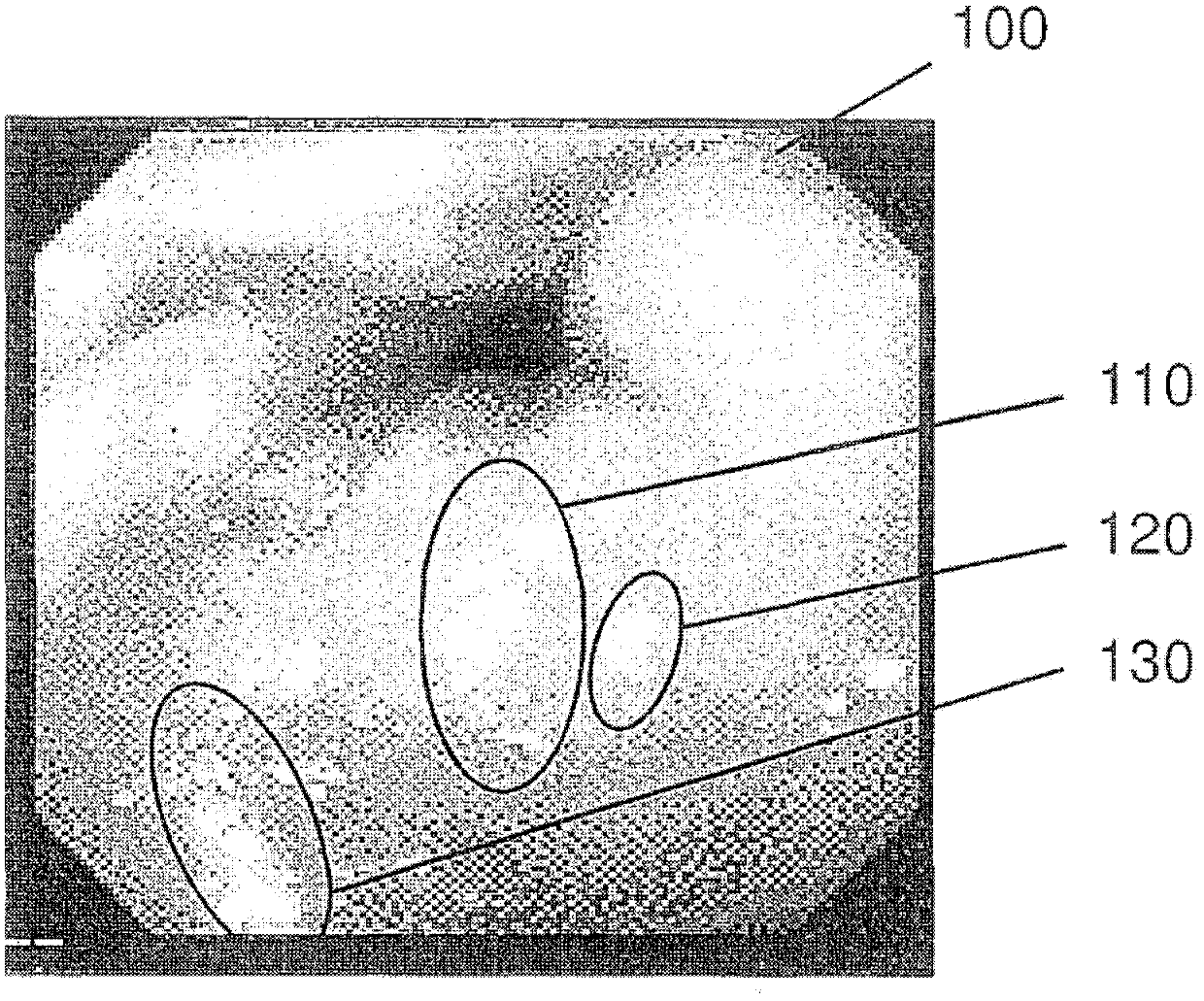
[0066] figure 1 is an example of an image 100 captured using an endoscope inspection apparatus (endoscope). As can be seen from image 100, the somewhat smaller saturated image areas of these portions of areas 110, 120 and 130 are formed by specular reflection. Therefore, no valid information exists at the location of the specular reflection.
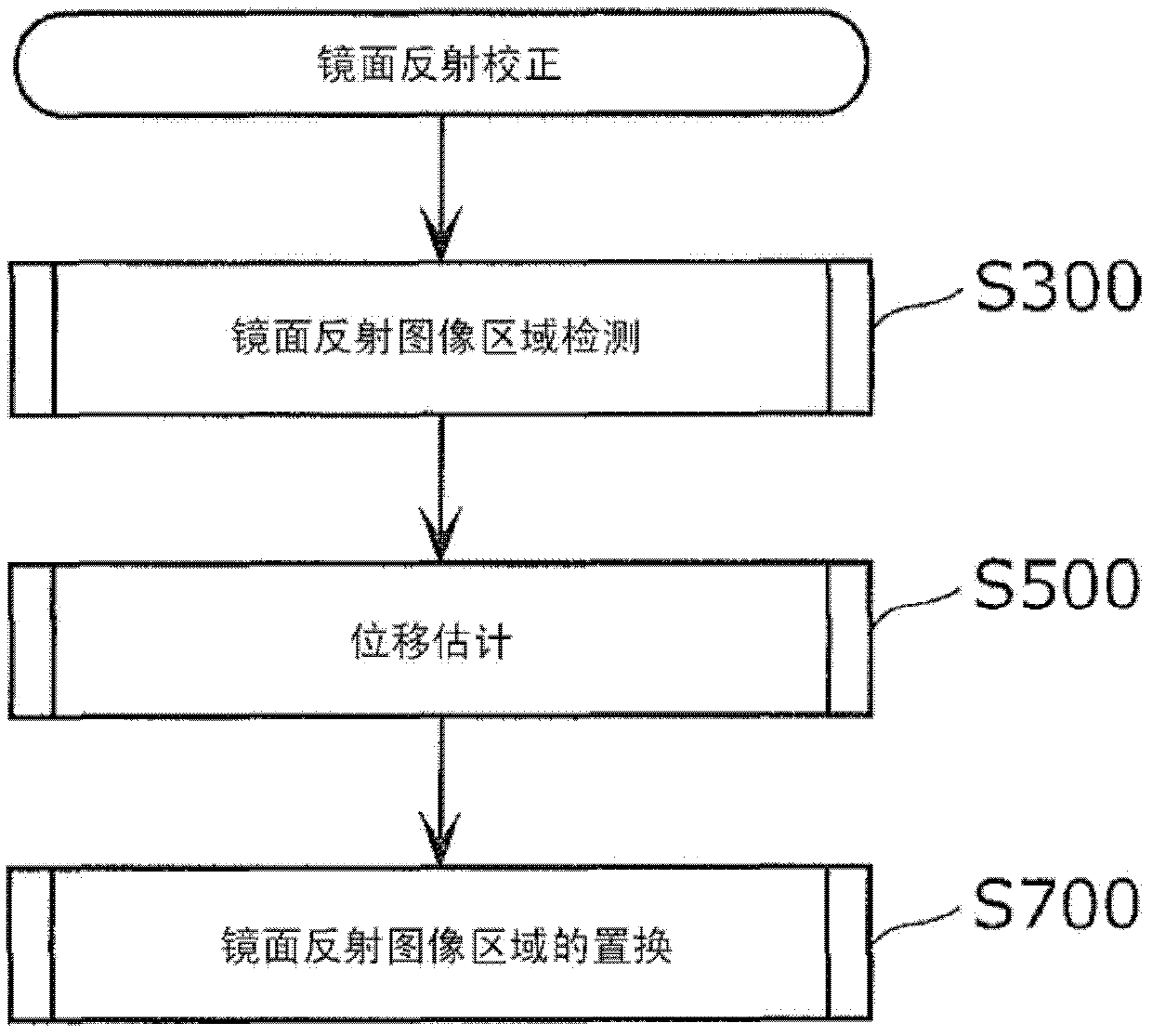
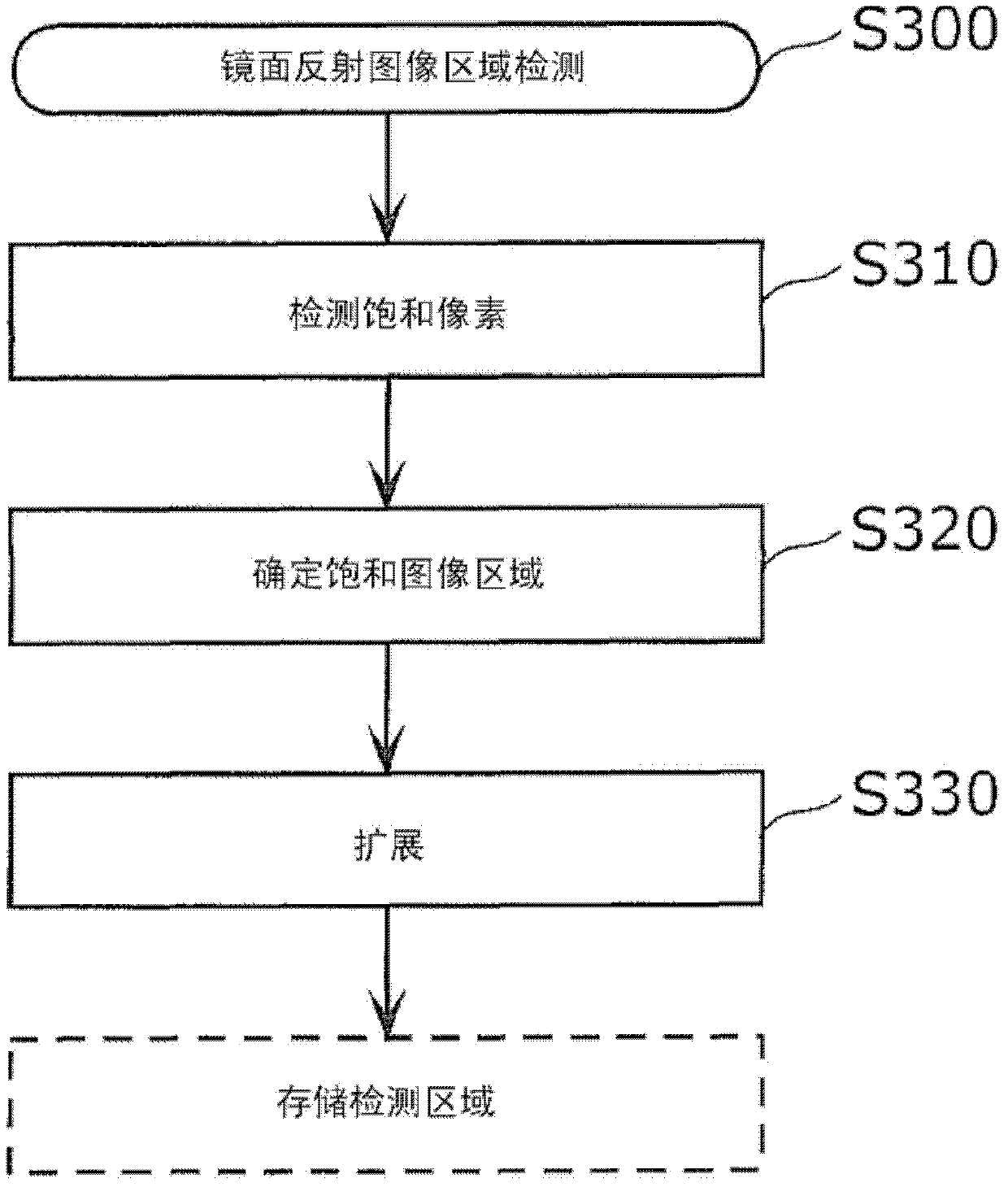
[0067] figure 2 It is a flowchart of a method for detecting and reducing specular reflection in a captured video sequence of the present invention. In the specular reflection reduction method of the present invention, first, a specular reflection area in a captured image is detected (S300). In subsequent S500, another image or a plurality of images is searched for an area corresponding to an image area covered by specular reflection in the captured image. Finally, the specular reflection in the captured image is replaced with information from a single or multiple images (S700). Here, the image to be searched is an image of another ...
Embodiment approach 2
[0157] In Embodiment 1, a specular reflection area is targeted for replacement, while in Embodiment 2, a saturated area, which is an image area where pixel values are saturated, and a false color area located around the saturated area are targeted for replacement. The false color area refers to an area in which a blue false color is generated around the saturated pixel value.
[0158] In addition, in the following description, the content different from Embodiment 1 will be mainly described, and the description of the same process will be omitted suitably.
[0159] The image to be processed in Embodiment 2 is a color image composed of RGB components, YUV components, or YCbCr components.
[0160] Figure 13 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of an image processing device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention.
[0161] The image processing device according to Embodiment 2 includes a saturated area detection unit 2501 , a false color area detection u...
Embodiment approach 3
[0190] In Embodiment 2, the interpolation of the false color area is performed using pixel values in the same image. In contrast, in the third embodiment, the interpolation of the false color area is performed using pixel values in other images.
[0191] In addition, in the following description, the content different from Embodiment 1 and 2 will be mainly described, and the description of the same process will be omitted suitably.
[0192] The image to be processed in Embodiment 3 is a color image composed of RGB components, YUV components, or YCbCr components.
[0193] Figure 22 It is a block diagram showing the configuration of an image processing device according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention.
[0194] The image processing device according to Embodiment 3 includes a saturated area detection unit 2601 , a false color area detection unit 2602 , a displacement estimator 2603 , and a replacement unit 2604 .
[0195]The saturated area detection unit 2601 dete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com